Ann Rehabil Med.
2018 Aug;42(4):601-608. 10.5535/arm.2018.42.4.601.
Investigation of the Diagnostic Value of Ultrasonography for Radial Neuropathy Located at the Spiral Groove
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. gstinfog@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2420053
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2018.42.4.601
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
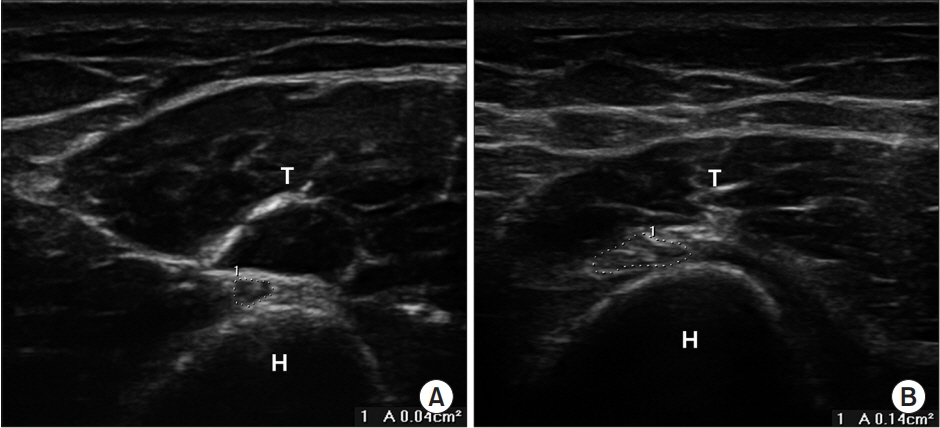
To determine a diagnostic cut-off value for the cross-sectional area (CSA) of the radial nerve using ultrasonography for radial neuropathy located at the spiral groove (SG).
METHODS
Seventeen patients with electrodiagnostic evidence of radial neuropathy at the SG and 30 healthy controls underwent ultrasonography of the radial nerve at the SG . The CSAs at the SG were compared in the patient and control groups. The CSA at the SG between the symptomatic and asymptomatic sides (ΔSx-Asx and Sx/Asx, respectively) were analyzed to obtain the optimal cut-off value. The relationship between the electrophysiological severity of radial neuropathy and CSA was also evaluated.
RESULTS
Among the variables examined, there were statistically significant differences in the CSA between the patient and control groups, ΔSx-Asx, and Sx/Asx at the SG. In a receiver operating characteristics analysis, the cut-off CSA was 5.75 mm² at the SG (sensitivity 52.9%, specificity 90%), 1.75 mm² for ΔSx-Asx (sensitivity 58.8%, specificity 100%), and 1.22 mm² for Sx/Asx (sensitivity 70.6%, specificity 93.3%) in diagnosing radial neuropathy at the SG. There was no significant correlation between CSA and electrophysiological severity score for either patient group.
CONCLUSION
The reference value obtained for CSA of the radial nerve at the SG may facilitate investigation of radial nerve pathologies at the SG.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wang LH, Weiss MD. Anatomical, clinical, and electrodiagnostic features of radial neuropathies. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2013; 24:33–47.
Article2. Kara M, Ozcakar L, De Muynck M, Tok F, Vanderstraeten G. Musculoskeletal ultrasound for peripheral nerve lesions. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2012; 48:665–74.3. Lo YL, Fook-Chong S, Leoh TH, Dan YF, Tan YE, Lee MP, et al. Rapid ultrasonographic diagnosis of radial entrapment neuropathy at the spiral groove. J Neurol Sci. 2008; 271:75–9.
Article4. Preston DC, Shapiro BE. Electromyography and neuromuscular disorders: clinical-electrophysiological correlation. 3rd ed. London: Elsevier/Saunders;2013. p. 336–40.5. Dumitru D, Amato AA, Zwarts MJ. Electrodiagnostic medicine. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Hanley & Belfus;2002. p. 1089–90.6. Girtler MT, Krasinski A, Dejaco C, Kitzler HH, Cui LG, Sherebrin S, et al. Feasibility of 3D ultrasound to evaluate upper extremity nerves. Ultraschall Med. 2013; 34:382–7.
Article7. Ong C, Nallamshetty HS, Nazarian LN, Rekant MS, Mandel S. Sonographic diagnosis of posterior interosseous nerve entrapment syndrome. Radiol Case Rep. 2016; 2:1–4.
Article8. Yalcin E, Akyuz M, Onder B. Early radial digital neuropathy of the thumb due to flexor pollicis longus tendinitis: value of ultrasound in an uncommon mild neuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 2013; 47:772–5.
Article9. Kutlar N, Bayrak AO, Bayrak İK, Canbaz S, Turker H. Diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome with Doppler ultrasonography: a comparison of ultrasonographic measurements and electrophysiological severity. Neurol Res. 2017; 39:126–32.
Article10. Cartwright MS, Passmore LV, Yoon JS, Brown ME, Caress JB, Walker FO. Cross-sectional area reference values for nerve ultrasonography. Muscle Nerve. 2008; 37:566–71.
Article11. Chiou HJ, Chou YH, Cheng SP, Hsu CC, Chan RC, Tiu CM, et al. Cubital tunnel syndrome: diagnosis by high-resolution ultrasonography. J Ultrasound Med. 1998; 17:643–8.
Article12. Beekman R, Visser LH. High-resolution sonography of the peripheral nervous system: a review of the literature. Eur J Neurol. 2004; 11:305–14.13. Visser LH, Hens V, Soethout M, De Deugd-Maria V, Pijnenburg J, Brekelmans GJ. Diagnostic value of highresolution sonography in common fibular neuropathy at the fibular head. Muscle Nerve. 2013; 48:171–8.
Article14. Kerasnoudis A, Tsivgoulis G. Nerve ultrasound in peripheral neuropathies: a review. J Neuroimaging. 2015; 25:528–38.
Article15. Mondelli M, Morana P, Ballerini M, Rossi S, Giannini F. Mononeuropathies of the radial nerve: clinical and neurographic findings in 91 consecutive cases. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2005; 15:377–83.
Article16. van Veen KE, Wesstein M, van Kasteel V. Ultrasonography and electrodiagnostic studies in ulnar neuropathy: an examination of the sensitivity and specificity and the correlations between both diagnostic tools. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2015; 32:240–3.17. Nakamichi K, Tachibana S. Ultrasonographic measurement of median nerve cross-sectional area in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome: diagnostic accuracy. Muscle Nerve. 2002; 26:798–803.
Article18. Cartwright MS, Yoon JS, Lee KH, Deal N, Walker FO. Diagnostic ultrasound for traumatic radial neuropathy. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2011; 90:342–3.
Article19. Qi HT, Wang XM, Li SY, Wang GB, Wang DH, Wang ZT, et al. The role of ultrasonography and MRI in patients with non-traumatic nerve fascicle torsion of the upper extremity. Clin Radiol. 2013; 68:e479. –83.
Article20. Choi SY, Park JW, Kim DH. Ultrasonographic and surgical findings of acute radial neuropathy following blunt trauma. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2016; 95:e177. –e182.
Article21. Won SJ, Kim BJ, Park KS, Yoon JS, Choi H. Reference values for nerve ultrasonography in the upper extremity. Muscle Nerve. 2013; 47:864–71.
Article22. Chen J, Wu S, Ren J. Ultrasonographic reference values for assessing normal radial nerve ultrasonography in the normal population. Neural Regen Res. 2014; 9:1844–9.
Article23. Qrimli M, Ebadi H, Breiner A, Siddiqui H, Alabdali M, Abraham A, et al. Reference values for ultrasonograpy of peripheral nerves. Muscle Nerve. 2016; 53:538–44.
Article24. Boehm J, Scheidl E, Bereczki D, Schelle T, Aranyi Z. High-resolution ultrasonography of peripheral nerves: measurements on 14 nerve segments in 56 healthy subjects and reliability assessments. Ultraschall Med. 2014; 35:459–67.
Article25. Kerasnoudis A, Pitarokoili K, Behrendt V, Gold R, Yoon MS. Cross sectional area reference values for sonography of peripheral nerves and brachial plexus. Clin Neurophysiol. 2013; 124:1881–8.
Article26. Tagliafico A, Cadoni A, Fisci E, Bignotti B, Padua L, Martinoli C. Reliability of side-to-side ultrasound cross-sectional area measurements of lower extremity nerves in healthy subjects. Muscle Nerve. 2012; 46:717–22.
Article27. Tagliafico A, Martinoli C. Reliability of side-to-side sonographic cross-sectional area measurements of upper extremity nerves in healthy volunteers. J Ultrasound Med. 2013; 32:457–62.
Article28. Yalcin E, Unlu E, Akyuz M, Karaahmet OZ. Ultrasound diagnosis of ulnar neuropathy: comparison of symptomatic and asymptomatic nerve thickness. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2014; 39:167–71.
Article29. Bayrak AO, Bayrak IK, Turker H, Elmali M, Nural MS. Ultrasonography in patients with ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: comparison of cross-sectional area and swelling ratio with electrophysiological severity. Muscle Nerve. 2010; 41:661–6.
Article30. Ellegaard HR, Fuglsang-Frederiksen A, Hess A, Johnsen B, Qerama E. High-resolution ultrasound in ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: a prospective study. Muscle Nerve. 2015; 52:759–66.
Article31. Mondelli M, Filippou G, Frediani B, Aretini A. Ultrasonography in ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: relationships to clinical and electrophysiological findings. Neurophysiol Clin. 2008; 38:217–26.
Article32. Kim MK, Jeon HJ, Park SH, Park DS, Nam HS. Value of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome: correlation with electrophysiological abnormalities and clinical severity. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2014; 55:78–82.
Article33. Zyluk A, Walaszek I, Szlosser Z. No correlation between sonographic and electrophysiological parameters in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2014; 39:161–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Radial Neuropathy after Cryolipolysis
- Optimal Radial Motor Nerve Conduction Study Using Ultrasound in Healthy Adults
- Superficial Radial Neuropathy due to Anatomic Variation: A Case Report
- Ultrasonographic Findings of the Normal Nerves in Common Entrapment Site; Cross-Sectional Area Reference Value and Normal Variant
- Surgical Treatment of a True Radial Artery Aneurysm in the Thenar Groove of the Palm, and This Was Caused by Handclapping and Repetitive Occupational Scissoring : A case report