Ann Dermatol.
2018 Oct;30(5):639-641. 10.5021/ad.2018.30.5.639.
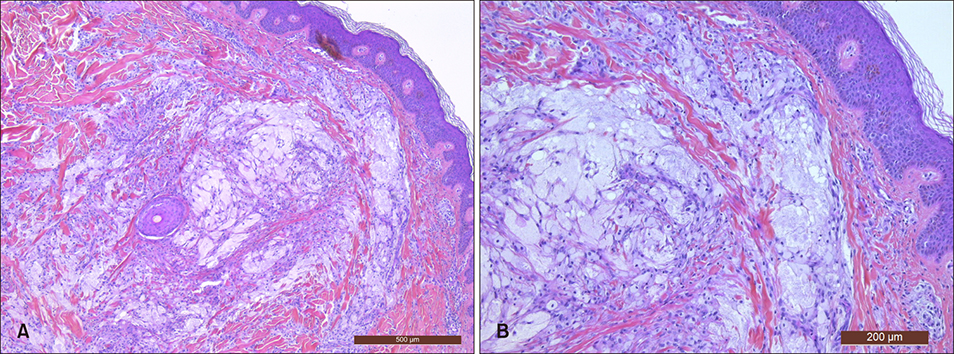
Normolipemic Papuloeruptive Xanthomas after Tattooing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Dermatology, Allergology and Venereology, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Central Hospital, Helsinki, Finland. nicolas.kluger@hus.fi
- 2Cabinet de Pathologie SO PATH, Toulouse, France.
- 3Dermatology, Villefranche de Lauragais, France.
- KMID: 2419767
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2018.30.5.639
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Weiss G, Shemer A, Trau H. The Koebner phenomenon: review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2002; 16:241–248.
Article2. Gao H, Chen J. Eruptive xanthomas presenting in tattoos. CMAJ. 2015; 187:356.
Article3. Brazzelli V, Rivetti N, Carugno A, Barruscotti S, Croci GA, Perani G, et al. Eruptive xanthomas after extensive tattooing: a case report and literature review. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2015; 150:770–771.4. Miwa N, Kanzaki T. The Koebner phenomenon in eruptive xanthoma. J Dermatol. 1992; 19:48–50.
Article5. Miller DM, Brodell RT. Eruptive xanthomatosis with linear koebnerization. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995; 33:834–835.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Diffuse Normolipemic Plane Xanthoma Associated with Multiple Myeloma
- A Case of Diffuse Normolipemic Plane Xanthoma Associated with Multiple Myeloma
- A Case of Tattooing Following the Acupuncture in Oriental Medical Clinic and Other Place
- Preoperative Colonoscopic Tattooing with Autologous Blood in Laparoscopic Colorectal Cancer Surgery: Red-Flagging for an Invisible Enemy
- Facial Verruca Plana That Developed after Semipermanent Tattooing