Clin Orthop Surg.
2018 Sep;10(3):352-357. 10.4055/cios.2018.10.3.352.
Accuracy of Preoperative Ultrasonography for Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: A Comparison with Intraoperative Findings
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. oscho5362@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2418756
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.3.352
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The aim of this study was to assess the consistency between preoperative ultrasonographic and intraoperative measurements of the ulnar nerve in patients with cubital tunnel syndrome.
METHODS
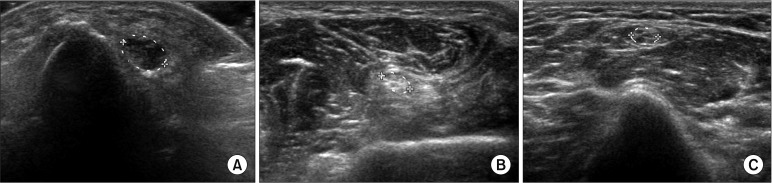
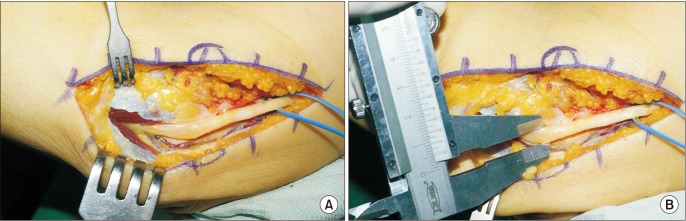
Twenty-six cases who underwent anterior transposition of the ulnar nerve for cubital tunnel syndrome were enrolled prospectively. On preoperative ultrasonography, largest cross-sectional diameters of the ulnar nerve were measured at the level of medial epicondyle (ME) and 3 cm proximal (PME) and distal (DME) to the ME on the transverse scan by a single experienced radiologist. Intraoperative direct measurements of the largest diameter at the same locations were performed by a single surgeon without knowledge of the preoperative values. The consistency between ultrasonographic and intraoperative values including the largest diameter and swelling ratio were assessed.
RESULTS
Significant differences between ultrasonographic and intraoperative values of the largest diameter were found at all levels. The mean difference was 1.29 mm for PME, 1.38 mm for ME, and 1.12 mm for DME. The mean ME-PME swelling ratio for ultrasonographic and intraoperative measurements was 1.50 and 1.39, respectively, showing significant difference. The mean ME-DME swelling ratio for ultrasonographic and intraoperative measurements was 1.53 and 1.43, respectively, showing no significant difference.
CONCLUSIONS
Ultrasonographically measured largest diameters of the ulnar nerve at any levels were smaller than the real values determined intraoperatively. The ME-DME swelling ratio of the ulnar nerve measured by ultrasonography was consistent with the intraoperative measurement.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chiou HJ, Chou YH, Cheng SP, et al. Cubital tunnel syndrome: diagnosis by high-resolution ultrasonography. J Ultrasound Med. 1998; 17(10):643–648. PMID: 9771609.
Article2. Wiesler ER, Chloros GD, Cartwright MS, Shin HW, Walker FO. Ultrasound in the diagnosis of ulnar neuropathy at the cubital tunnel. J Hand Surg Am. 2006; 31(7):1088–1093. PMID: 16945708.
Article3. Jeon IH, Lee SM, Choi JW, Kim PT. Dynamic morphologic study of the ulnar nerve around the elbow using ultrasonography. J Korean Shoulder Elbow Soc. 2007; 10(1):99–105.
Article4. Gruber H, Glodny B, Peer S. The validity of ultrasonographic assessment in cubital tunnel syndrome: the value of a cubital-to-humeral nerve area ratio (CHR) combined with morphologic features. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2010; 36(3):376–382. PMID: 20133042.
Article5. Kim BK, Shin HD, Kim KC, Park JY. Tardy ulnar nerve palsy secondary to the anconeus epitrochlearis muscle: 2 case report. Clin Should Elbow. 2010; 13(2):270–274.6. Park GY, Kim JM, Lee SM. The ultrasonographic and electrodiagnostic findings of ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004; 85(6):1000–1005. PMID: 15179657.7. Thoirs K, Williams MA, Phillips M. Ultrasonographic measurements of the ulnar nerve at the elbow: role of confounders. J Ultrasound Med. 2008; 27(5):737–743. PMID: 18424649.8. Volpe A, Rossato G, Bottanelli M, et al. Ultrasound evaluation of ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: correlation with electrophysiological studies. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009; 48(9):1098–1101. PMID: 19567661.
Article9. Bayrak AO, Bayrak IK, Turker H, Elmali M, Nural MS. Ultrasonography in patients with ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: comparison of cross-sectional area and swelling ratio with electrophysiological severity. Muscle Nerve. 2010; 41(5):661–666. PMID: 19941341.
Article10. Beekman R, Visser LH, Verhagen WI. Ultrasonography in ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: a critical review. Muscle Nerve. 2011; 43(5):627–635. PMID: 21484821.
Article11. Mondelli M, Filippou G, Frediani B, Aretini A. Ultrasonography in ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: relationships to clinical and electrophysiological findings. Neurophysiol Clin. 2008; 38(4):217–226. PMID: 18662618.
Article12. Bartels RH, Meulstee J, Verhagen WI, Luttikhuis TT. Ultrasound imaging of the ulnar nerve: correlation of preoperative and intraoperative dimensions. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2008; 110(7):687–690. PMID: 18486322.
Article13. Practice parameter for electrodiagnostic studies in ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: summary statement. American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine, American Academy of Neurology, American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Muscle Nerve. 1999; 22(3):408–411. PMID: 10086904.14. Scheidl E, Bohm J, Farbaky Z, Simo M, Bereczki D, Aranyi Z. Ultrasonography of ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: axonal involvement leads to greater nerve swelling than demyelinating nerve lesion. Clin Neurophysiol. 2013; 124(3):619–625. PMID: 23068559.
Article15. Yoon JS, Walker FO, Cartwright MS. Ultrasonographic swelling ratio in the diagnosis of ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. Muscle Nerve. 2008; 38(4):1231–1235. PMID: 18785184.
Article16. Okamoto M, Abe M, Shirai H, Ueda N. Diagnostic ultrasonography of the ulnar nerve in cubital tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg Br. 2000; 25(5):499–502. PMID: 10991822.
Article17. Okamoto M, Abe M, Shirai H, Ueda N. Morphology and dynamics of the ulnar nerve in the cubital tunnel. Observation by ultrasonography. J Hand Surg Br. 2000; 25(1):85–89. PMID: 10763732.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Diagnosed by Ultrasonography in Patient with Normal Electrodiagnostic Studies
- Ulnar neuropathy
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Caused by Osteochondroma: A Case Report
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Caused by Ulnar Nerve Schwannoma: A Case Report
- Ultrasonographic Findings of Ulnar Nerve in the Cubital Tunnel Syndrome