Intest Res.
2018 Jul;16(3):393-399. 10.5217/ir.2018.16.3.393.
Immunohistochemical differentiation between chronic enteropathy associated with SLCO2A1 gene and other inflammatory bowel diseases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Iwate Medical University School of Medicine, Morioka, Japan. shonaka@iwate-med.ac.jp
- 2Division of Molecular Diagnostic Pathology, Department of Pathology, Iwate Medical University School of Medicine, Morioka, Japan.
- 3Department of Medicine and Clinical Science, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan.
- KMID: 2417651
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2018.16.3.393
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
We recently identified recessive mutations in the solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 2A1 gene (SLCO2A1) as causative variants of chronic enteropathy associated with SLCO2A1 (CEAS). The aim of this study was to evaluate SLCO2A1 protein expression in the intestinal tissues of patients with CEAS, intestinal Behçet's disease (BD), simple ulcer (SU), and Crohn's disease (CD).
METHODS
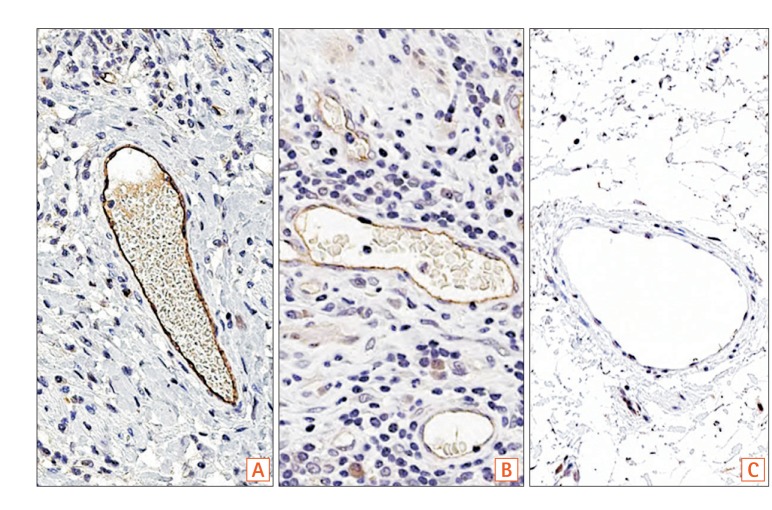
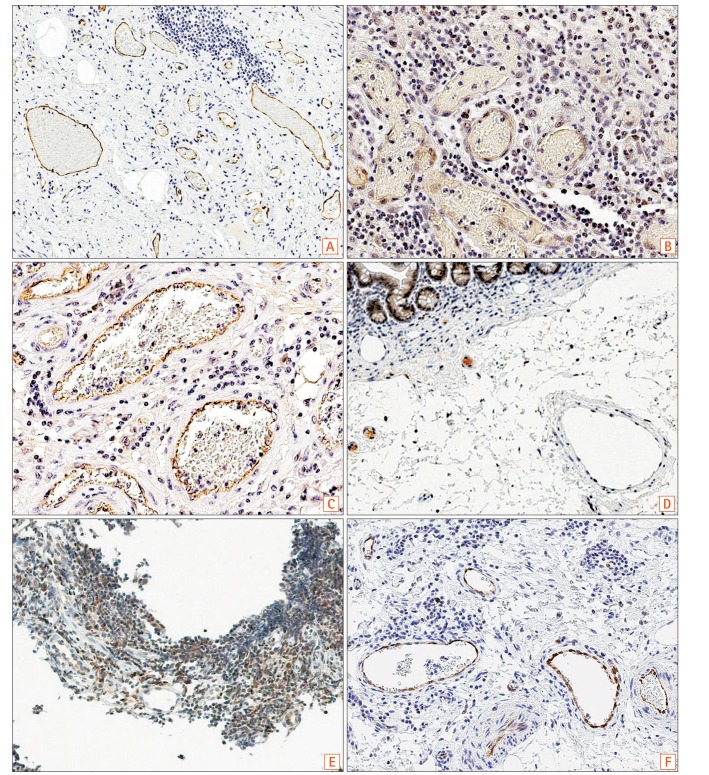
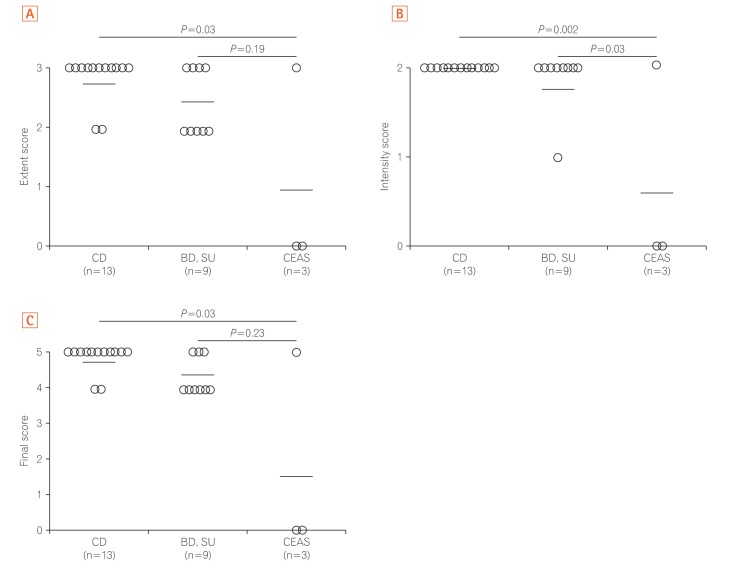
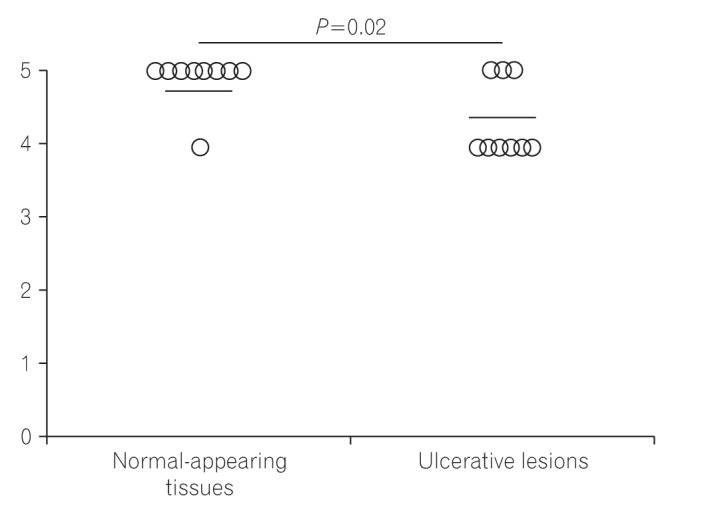
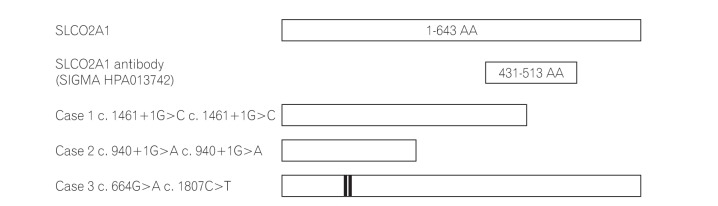
Immunohistochemical staining using a polyclonal anti-SLCO2A1 antibody was performed on the resected intestinal specimens from 13 cases of CD, 9 cases of intestinal BD/SU, and 3 cases of CEAS. The extent of SLCO2A1 expression was determined by counting positively-staining vascular endothelial cells and scored as 0 (no cells), 1 (1%-30% cells), 2 (31%-60%), or 3 (>60%). The intensity of SLCO2A1 expression was scored either as 0 (negative), 1 (intermediate), or 2 (strong). The extent score and intensity score were summed for the final score of 0, 2, 3, 4, or 5.
RESULTS
SLCO2A1 protein expression was observed in 1 of 3 cases of CEAS (33%), all 13 cases of CD (100%), and all 9 cases of BD/SU (100%). The mean final expression scores of CEAS, CD, and BD/SU were 1.6 (range, 0-5), 4.8 (range, 4-5), and 4.3 (range, 4-5), respectively. The final expression score in CEAS was significantly lower than in CD (P=0.03).
CONCLUSIONS
Immunohistochemical staining of the SLCO2A1 protein is considered useful to distinguish CEAS from other inflammatory bowel diseases.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Matsumoto T, Iida M, Matsui T, et al. Non-specific multiple ulcers of the small intestine unrelated to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Clin Pathol. 2004; 57:1145–1150. PMID: 15509673.
Article2. Matsumoto T, Iida M, Matsui T, Yao T. Chronic nonspecific multiple ulcers of the small intestine: a proposal of the entity from Japanese gastroenterologists to Western enteroscopists. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66(3 Suppl):S99–S107. PMID: 17709045.
Article3. Matsumoto T, Kubokura N, Matsui T, Iida M, Yao T. Chronic nonspecific multiple ulcer of the small intestine segregates in offspring from consanguinity. J Crohns Colitis. 2011; 5:559–565. PMID: 22115375.
Article4. Esaki M, Umeno J, Kitazono T, Matsumoto T. Clinicopathologic features of chronic nonspecific multiple ulcers of the small intestine. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2015; 8:57–62. PMID: 25788296.
Article5. Umeno J, Hisamatsu T, Esaki M, et al. A hereditary enteropathy caused by mutations in the SLCO2A1 gene, encoding a prostaglandin transporter. PLoS Genet. 2015; 11:e1005581. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005581. PMID: 26539716.
Article6. Zhang Z, Xia W, He J, et al. Exome sequencing identifies SLCO2A1 mutations as a cause of primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy. Am J Hum Genet. 2012; 90:125–132. PMID: 22197487.
Article7. Busch J, Frank V, Bachmann N, et al. Mutations in the prostaglandin transporter SLCO2A1 cause primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy with digital clubbing. J Invest Dermatol. 2012; 132:2473–2476. PMID: 22696055.
Article8. Diggle CP, Parry DA, Logan CV, et al. Prostaglandin transporter mutations cause pachydermoperiostosis with myelofibrosis. Hum Mutat. 2012; 33:1175–1181. PMID: 22553128.
Article9. Compton RF, Sandborn WJ, Yang H, et al. A new syndrome of Crohn's disease and pachydermoperiostosis in a family. Gastroenterology. 1997; 112:241–249. PMID: 8978365.
Article10. Hisabe T, Hirai F, Matsui T, Watanabe M. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for Crohn's disease in Japan. J Gastroenterol. 2014; 49:93–99. PMID: 23546557.
Article11. Hisamatsu T, Ueno F, Matsumoto T, et al. The 2nd edition of consensus statements for the diagnosis and management of intestinal Behçet's disease: indication of anti-TNFalpha monoclonal antibodies. J Gastroenterol. 2014; 49:156–162. PMID: 23955155.
Article12. Muto T. Historical review of so-called “simple ulcer” of the intestine. Stomach Intestine. 1979; 14:739–749.13. Matsukawa M, Yamasaki T, Kouda T, Kurihara M. Endoscopic therapy with absolute ethanol for postoperative recurrent ulcers in intestinal Behçe's disease, and simple ulcers. J Gastroenterol. 2001; 36:255–258. PMID: 11324729.
Article14. Allred DC, Clark GM, Elledge R, et al. Association of p53 protein expression with tumor cell proliferation rate and clinical outcome in node-negative breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993; 85:200–206. PMID: 8423624.
Article15. Harvey JM, Clark GM, Osborne CK, Allred DC. Estrogen receptor status by immunohistochemistry is superior to the ligand-binding assay for predicting response to adjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999; 17:1474–1481. PMID: 10334533.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Distinction between Chronic Enteropathy Associated with the SLCO2A1 Gene and Crohn's Disease
- A Novel Chronic Enteropathy Associated with SLCO2A1 Gene Mutation: Enterography Findings in a Multicenter Korean Registry
- Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of Korean Patients Diagnosed with Chronic Enteropathy Associated with SLCO2A1 Gene: A KASID Multicenter Study
- Imaging Techniques and Differential Diagnosis for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced enteropathy