J Korean Fract Soc.
2018 Jul;31(3):94-101. 10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.3.94.
Comparative Analysis of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis and Intramedullary Nailing in the Treatment of the Distal Tibia Fractures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea. kys73740@naver.com
- KMID: 2417151
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.3.94
Abstract
- PURPOSE
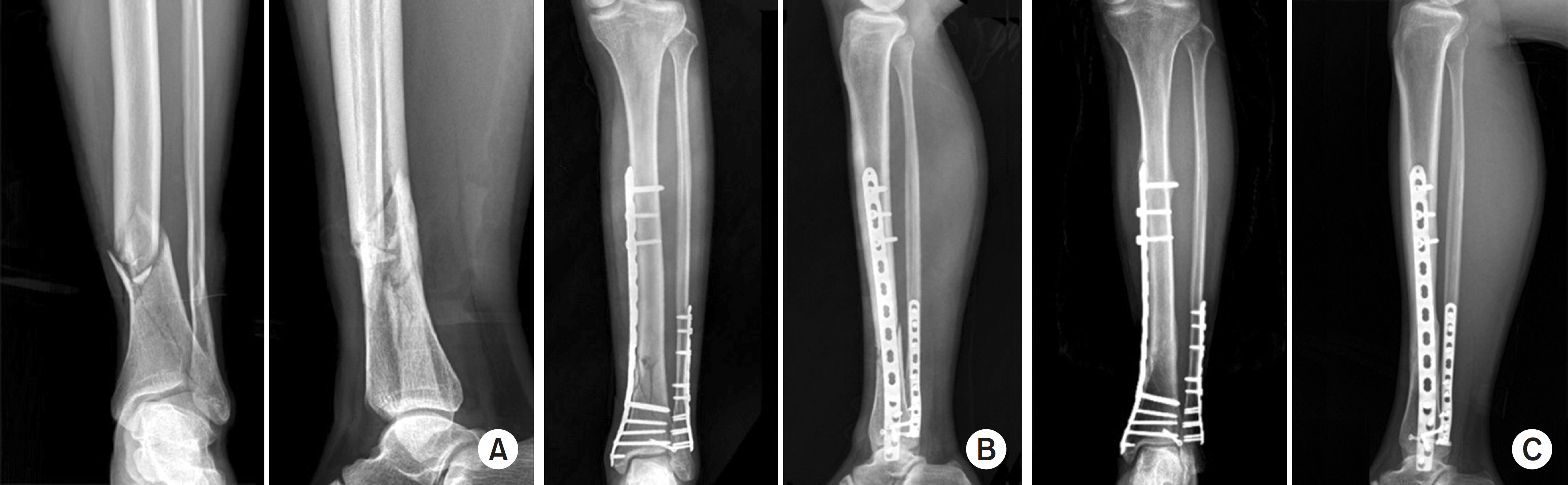
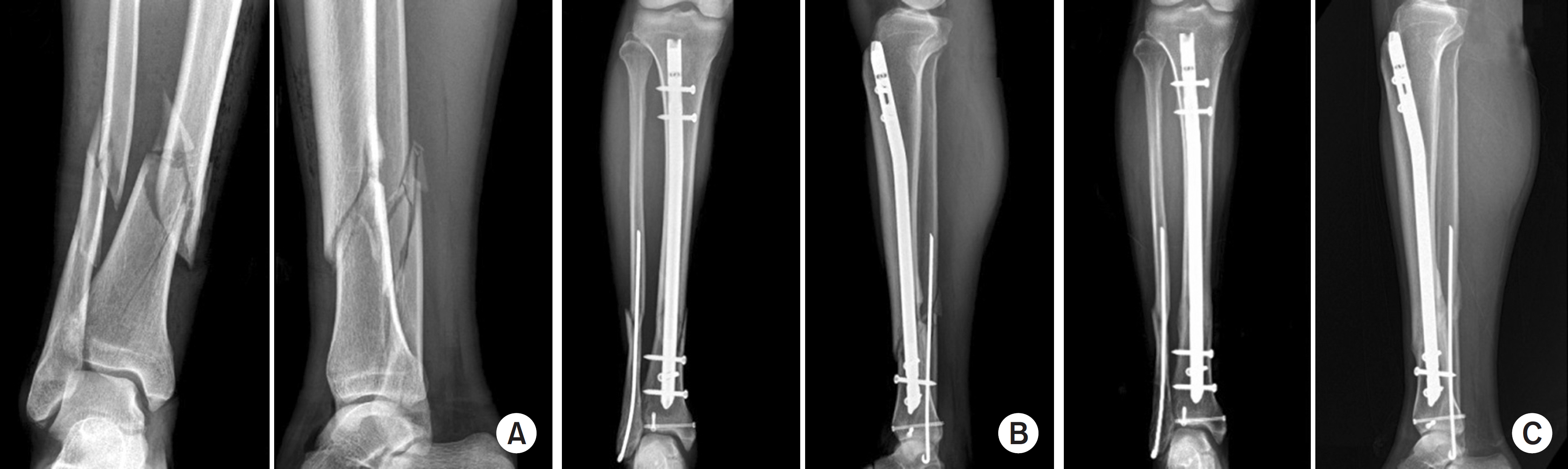
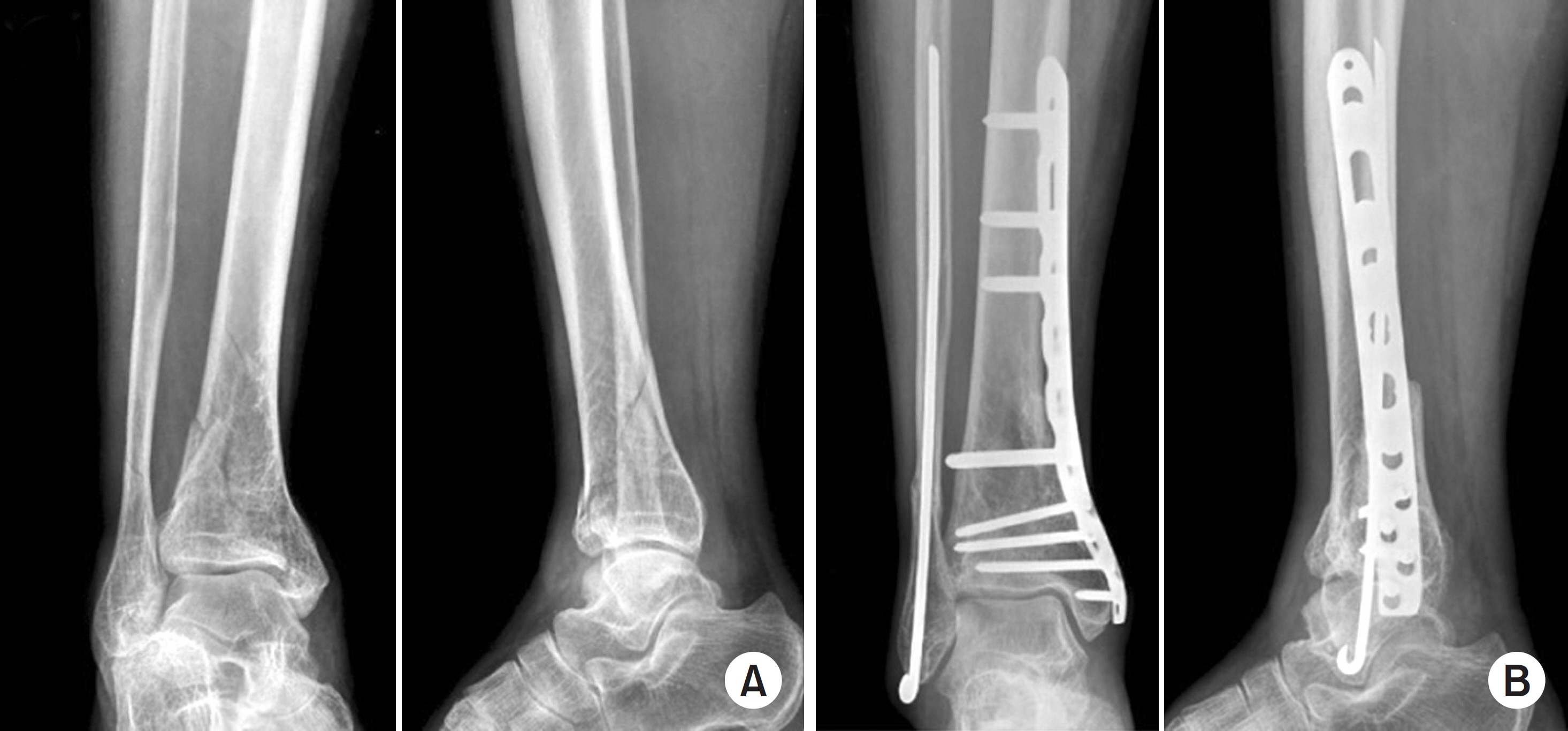
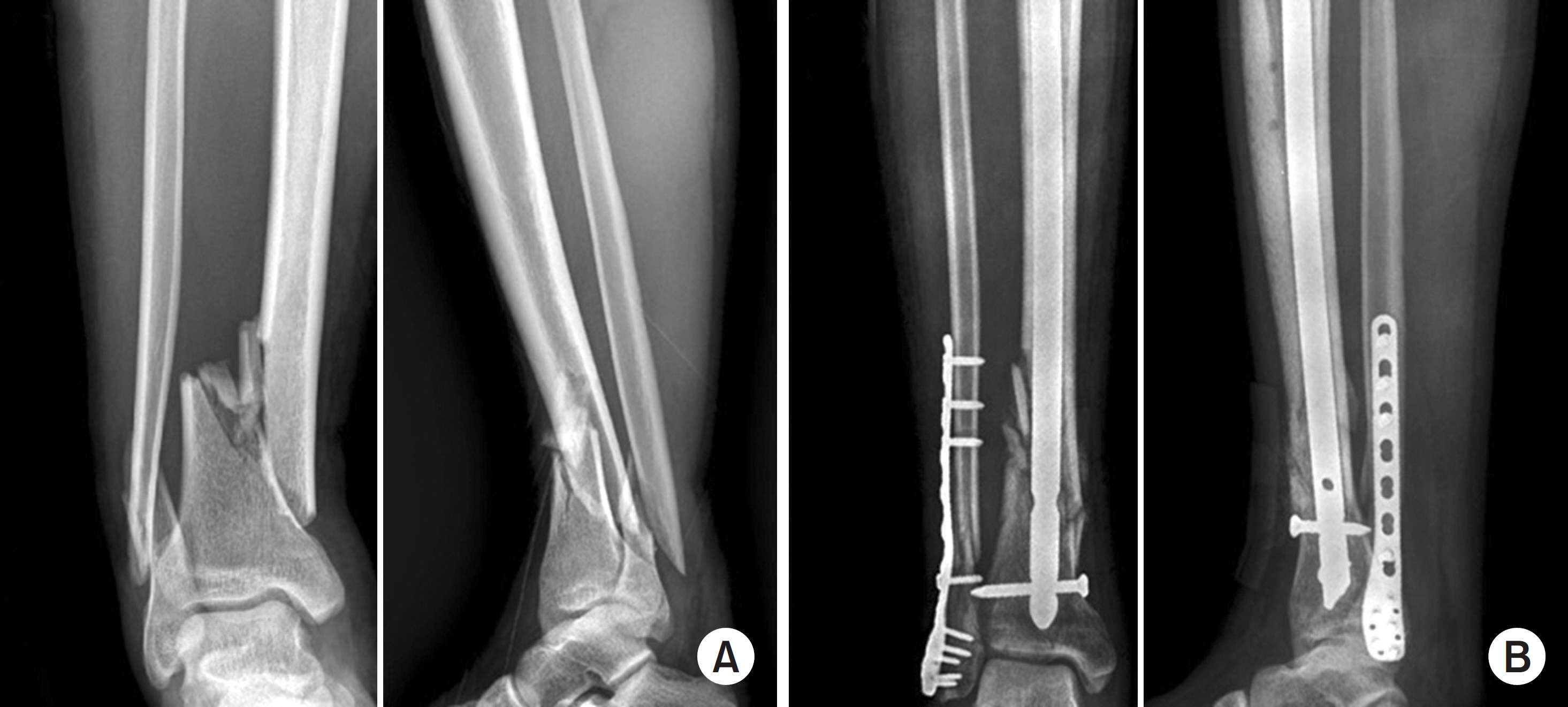
This study compared the radiological and clinical results of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) and intramedullary nailing (IMN) of distal tibial fractures, which were classified as the simple intra-articular group and extra-articular group.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifty patients with distal tibial fractures, who could be followed-up more than 12 months, were evaluated. Group A consisted of 19 patients treated with MIPO and group B consisted of 31 patients treated with IMN. The results of each group were analyzed by radiological and clinical assessments.
RESULTS
The mean operation times in groups A and B were 72.4 minutes and 65.7 minutes, respectively. The mean bone union times in groups A and B were 16.4 weeks and 15.7 weeks, respectively. The bone union rate in groups A and B were 100% and 93%, respectively. The ranges of ankle motion were similar in the two groups at the last follow-up. The mean American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society score was similar: 90.1 in group A and 90.5 in group B. The radiological and clinical results were similar in the intra and extra-articular groups. In groups A and B, two cases of posterior angulation and five cases of valgus deformity of more than 5° were encountered.
CONCLUSION
Both MIPO and IMN achieved satisfactory results in extra-articular AO type A and simple articular extension type C1 and C2 distal tibia fractures.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Intramedullary Nailing versus Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Distal Tibia Shaft Fractures: Retrospective Comparison of Functional and Cosmetic Outcomes
Kahyun Kim, In Hee Kim, Geon Jung Kim, SungJoon Lim, Ji Young Yoon, Jong Won Kim, Yong Min Kim
J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2023;27(3):93-98. doi: 10.14193/jkfas.2023.27.3.93.
Reference
-
References
1. Wyrsch B, McFerran MA, McAndrew M, et al. Operative treatment of fractures of the tibial plafond. A randomized, prospective syudy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 78:1646–1657. 1996.2. Kim SK, Lee KB, Lim KY, Moon ES. Minimally invasive osteosynthesis with locking compression plate for distal tibia fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 24:33–40. 2011.
Article3. Cheng W, Li Y, Manyi W. Comparison study of two surgical options for distal tibia fracture-minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis vs. open reduction and internal fixation. Int Orthop. 35:737–742. 2011.
Article4. Collinge C, Protzman R. Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 24:24–29. 2010.
Article5. Lee GC, Lee JY, Ha SH, Sohn HM, Park YK. Comparative analysis of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis using periarticular plate and intramedullary nailing in distal tibial metaphyseal fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 25:20–25. 2012.
Article6. Park KC, Park YS. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for distal tibial metaphyseal fracture. J Korean Fract Soc. 18:264–268. 2005.
Article7. Kruppa CG, Hoffmann MF, Sietsema DL, Mulder MB, Jones CB. Outcomes after intramedullary nailing of distal tibial fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 29:e309–e315. 2015.
Article8. Vidović D, Matejčić A, Ivica M, Jurišić D, Elabjer E, Bakota B. Minimally-invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibial fractures: results and complications. Injury. 46(Suppl 6):S96–S99. 2015.
Article9. Viberg B, Kleven S, Hamborg-Petersen E, Skov O. Complications and functional outcome after fixation of distal tibia fractures with locking plate: a multicentre study. Injury. 47:1514–1518. 2016.10. Martin JS, Marsh JL, Bonar SK, DeCoster TA, Found EM, Brandser EA. Assessment of the AO/ASIF fracture classification for the distal tibia. J Orthop Trauma. 11:477–483. 1997.
Article11. Afsari A, Liporace F, Lindvall E, Infante A Jr, Sagi HC, Haidukewych GJ. Clamp-assisted reduction of high subtrochanteric fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 91:1913–1918. 2009.
Article12. Beytemür O, Barış A, Albay C, Yüksel S, Çağlar S, Alagöz E. Comparison of intramedullary nailing and minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis in the treatment of simple intraarticular fractures of the distal tibia (AO-OTA type 43 C1-C2). Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 51:12–16. 2017.
Article13. Kitaoka HB, Alexander IJ, Adelaar RS, Nunley JA, Myerson MS, Sanders M. Clinical rating systems for the ankle-hindfoot, midfoot, hallux, and lesser toes. Foot Ankle Int. 15:349–353. 1994.
Article14. Lee KB, Song SY, Kwon DJ, Lee YB, Rhee NK, Choi JH. A comparison between minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis & interlocking intramedullary nailing in distal tibia fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 21:286–291. 2008.15. Im GI, Kim DY, Shin JH, Youn KS, Cho WH. Comparative analysis of interlocking nail and anatomical plate in the treatment of distal tibial fracture. J Korean Soc Fract. 12:632–637. 1999.
Article16. Guo JJ, Tang N, Yang HL, Tang TS. A prospective, randomised trial comparing closed intramedullary nailing with percutaneous plating in the treatment of distal metaphyseal fractures of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 92:984–988. 2010.
Article17. Shon OJ, Park CH. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of distal tibial fractures: a comparison of medial and lateral plating. J Orthop Sci. 17:562–566. 2012.
Article18. Yang SW, Tzeng HM, Chou YJ, Teng HP, Liu HH, Wong CY. Treatment of distal tibial metaphyseal fractures: plating versus shortened intramedullary nailing. Injury. 37:531–535. 2006.
Article19. Janssen KW, Biert J, van Kampen A. Treatment of distal tibial fractures: plate versus nail: a retrospective outcome analysis of matched pairs of patients. Int Orthop. 31:709–714. 2007.20. Vallier HA, Le TT, Bedi A. Radiographic and clinical comparisons of distal tibia shaft fractures (4 to 11 cm proximal to the plafond): plating versus intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 22:307–311. 2008.
Article21. Kuhn S, Greenfield J, Arand C, et al. Treatment of distal intraarticular tibial fractures: a biomechanical evaluation of intramedullary nailing vs. angle-stable plate osteosynthesis. Injury. 46(Suppl 4):S99–S103. 2015.
Article22. Marcus MS, Yoon RS, Langford J, et al. Is there a role for intramedullary nails in the treatment of simple pilon fractures? Rationale and preliminary results. Injury. 44:1107–1111. 2013.
Article23. Konrath G, Moed BR, Watson JT, Kaneshiro S, Karges DE, Cramer KE. Intramedullary nailing of unstable diaphyseal fractures of the tibia with distal intraarticular involvement. J Orthop Trauma. 11:200–205. 1997.
Article24. Robinson CM, McLauchlan GJ, McLean IP, Court-Brown CM. Distal metaphyseal fractures of the tibia with minimal involvement of the ankle. Classification and treatment by locked intramedullary nailing. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 77:781–787. 1995.
Article25. Kim YS, Chung PH, Hwang CS, Kang S, Kim JP, Lee HM. Interlocking intramedullary nailing in distal tibial metaphyseal fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 18:269–274. 2005.
Article26. Vallier HA, Cureton BA, Patterson BM. Randomized, prospective comparison of plate versus intramedullary nail fixation for distal tibia shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 25:736–741. 2011.
Article27. Krettek C, Stephan C, Schandelmaier P, Richter M, Pape HC, Miclau T. The use of Poller screws as blocking screws in stabilizing tibial fractures treated with small diameter intramedullary nails. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 81:963–968. 1999.28. Scolaro JA, Broghammer FH, Donegan DJ. Intramedullary tibial nail fixation of simple intraarticular distal tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 30(Suppl 4):S12–S16. 2016.
Article29. Gueorguiev B, Ockert B, Schwieger K, et al. Angular stability potentially permits fewer locking screws compared with conventional locking in intramedullary nailed distal tibia fractures: a biomechanical study. J Orthop Trauma. 25:340–346. 2011.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparative Analysis of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis Using Periarticular Plate and Intramedullary Nailing in Distal Tibial Metaphyseal Fractures
- A Comparison of the Results between Intramedullary Nailing and Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis in Distal Tibia Fractures
- Comparative Study Using of Treatment with Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis Using Periarticular Plate and Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing in Distal Tibia Fractures
- Comparative Study of Intramedullary Nailing and Plate for Metaphyseal Fractures of the Distal Tibia
- Intramedullary Nailing versus Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Distal Tibia Shaft Fractures: Retrospective Comparison of Functional and Cosmetic Outcomes