J Gastric Cancer.
2018 Mar;18(1):99-107. 10.5230/jgc.2018.18.e8.
IgG4-related Disease in the Stomach which Was Confused with Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST): Two Case Reports and Review of the Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Department of Surgery, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Uijeongbu, Korea. skygs@catholic.ac.kr esjung@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Hospital Pathology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. skygs@catholic.ac.kr esjung@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2414551
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2018.18.e8
Abstract
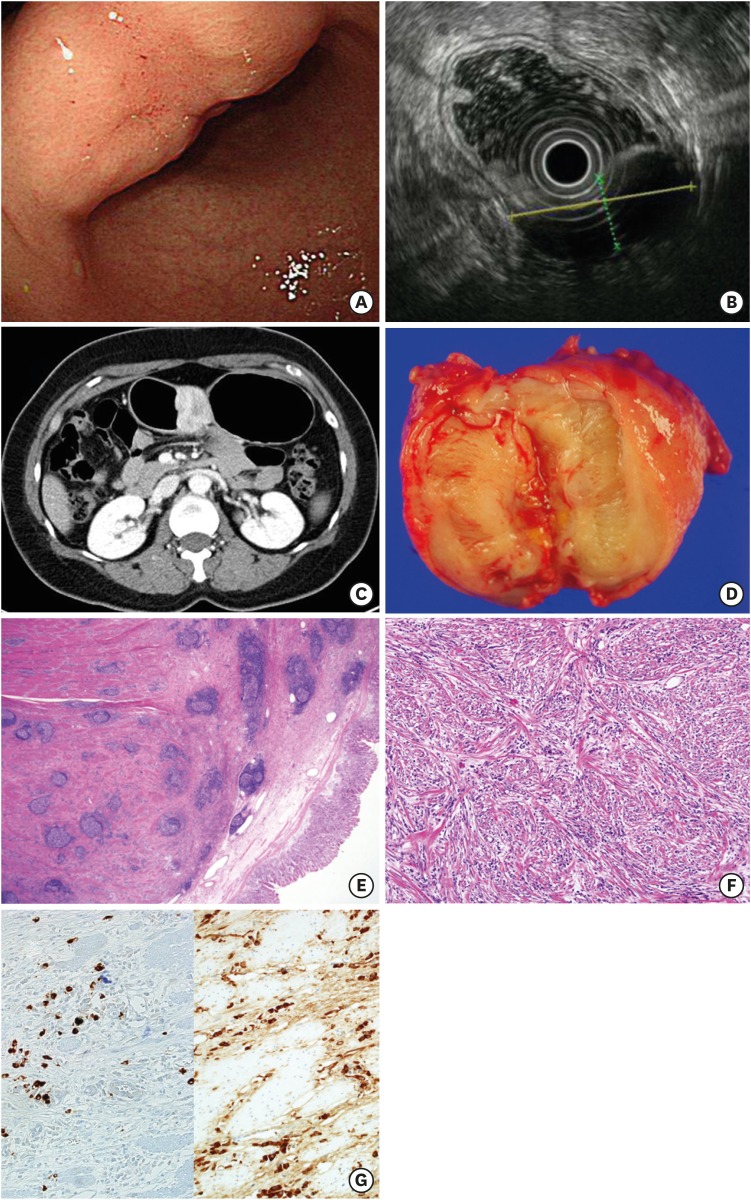
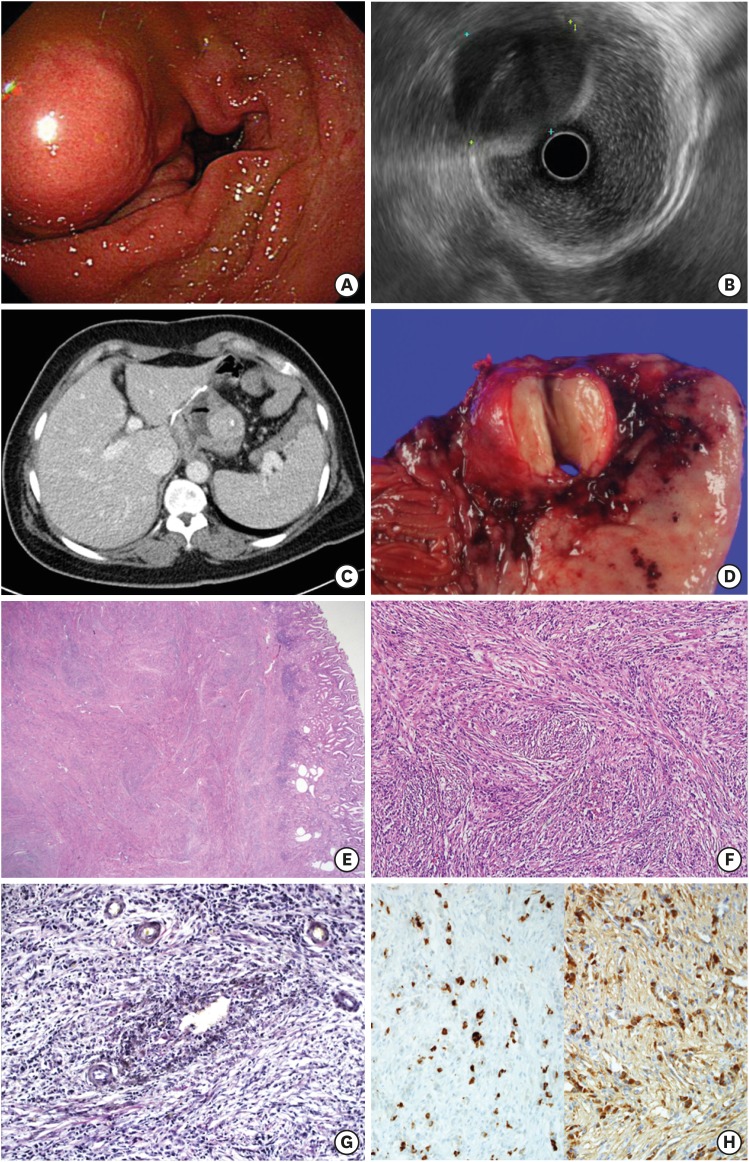
- Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is an immune-mediated fibro-inflammatory disorder characterized by specific pathological findings and elevated serum IgG4 level. IgG4-RD in the stomach is rare, and occasionally diagnosed as gastric subepithelial tumor (SET) by endoscopy or computed tomography scan. Two female patients in the age group of 40-50 years were diagnosed with 4 cm sized gastric SET. One underwent laparoscopic gastric wedge resection. Another one had a history of subtotal gastrectomy for early gastric cancer and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura with oral steroids administration. She underwent a completion total gastrectomy with splenectomy for the gastric SET and ITP. The pathology showed storiform fibrosis, and IgG4 was positive in immunohistochemistry (IHC) stain. IgG4-RD is known as a medical disease that could be treated with oral steroids. The difficulty in preoperative diagnosis of the disease occasionally causes unnecessary gastric resection. Thus, preoperative diagnostic methods for IgG4-RD such as deep biopsy with IHC stain or magnetic resonance imaging are needed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Gastric IgG4-related disease presenting as a mass lesion and masquerading as a gastrointestinal stromal tumor
Banumathi Ramakrishna, Rohan Yewale, Kavita Vijayakumar, Patta Radhakrishna, Balakrishnan Siddartha Ramakrishna
J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(3):258-262. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2020.02.10.
Reference
-
1. Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:539–551. PMID: 22316447.
Article2. Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y, Koike M, Tsuruta K, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003; 38:982–984. PMID: 14614606.
Article3. Inoue D, Zen Y, Abo H, Gabata T, Demachi H, Kobayashi T, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related lung disease: CT findings with pathologic correlations. Radiology. 2009; 251:260–270. PMID: 19221056.
Article4. Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:732–738. PMID: 11236777.
Article5. Zen Y. The pathology of IgG4-related disease in the bile duct and pancreas. Semin Liver Dis. 2016; 36:242–256. PMID: 27466794.
Article6. Kawano M, Yamada K. IgG4-related kidney disease and IgG4-related retroperitoneal fibrosis. Semin Liver Dis. 2016; 36:283–290. PMID: 27466797.
Article7. Perugino CA, Wallace ZS, Meyersohn N, Oliveira G, Stone JR, Stone JH. Large vessel involvement by IgG4-related disease. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e3344. PMID: 27428181.
Article8. Williams MM, Mashaly H, Puduvalli VK, Jin M, Mendel E. Immunoglobulin G4-related disease mimicking an epidural spinal cord tumor: case report. J Neurosurg Spine. 2017; 26:76–80. PMID: 27517527.
Article9. Kim JH, Byun JH, Lee SS, Kim HJ, Lee MG. Atypical manifestations of IgG4-related sclerosing disease in the abdomen: imaging findings and pathologic correlations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013; 200:102–112. PMID: 23255748.
Article10. Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease. Lancet. 2015; 385:1460–1471. PMID: 25481618.
Article11. Aalberse RC, Stapel SO, Schuurman J, Rispens T. Immunoglobulin G4: an odd antibody. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009; 39:469–477. PMID: 19222496.
Article12. Khosroshahi A, Wallace ZS, Crowe JL, Akamizu T, Azumi A, Carruthers MN, et al. International consensus guidance statement on the management and treatment of IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67:1688–1699. PMID: 25809420.
Article13. Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, Yi EE, Sato Y, Yoshino T, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012; 25:1181–1192. PMID: 22596100.
Article14. Inoue D, Yoshida K, Yoneda N, Ozaki K, Matsubara T, Nagai K, et al. IgG4-related disease: dataset of 235 consecutive patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e680. PMID: 25881845.15. Vlachou PA, Khalili K, Jang HJ, Fischer S, Hirschfield GM, Kim TK. IgG4-related sclerosing disease: autoimmune pancreatitis and extrapancreatic manifestations. Radiographics. 2011; 31:1379–1402. PMID: 21918050.
Article16. Takahashi N, Kawashima A, Fletcher JG, Chari ST. Renal involvement in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis: CT and MR imaging findings. Radiology. 2007; 242:791–801. PMID: 17229877.
Article17. Inoue D, Zen Y, Abo H, Gabata T, Demachi H, Yoshikawa J, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related periaortitis and periarteritis: CT findings in 17 patients. Radiology. 2011; 261:625–633. PMID: 21803920.
Article18. Inoue D, Yoneda N, Yoshida K, Nuka H, Kinoshita J, Fushida S, et al. Imaging and pathological features of gastric lesion of immunoglobulin G4-related disease: a case report and review of the recent literature. Mod Rheumatol. 2016; 1–5.
Article19. Shinji A, Sano K, Hamano H, Unno H, Fukushima M, Nakamura N, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis is closely associated with gastric ulcer presenting with abundant IgG4-bearing plasma cell infiltration. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 59:506–511. PMID: 15044886.
Article20. Fujita T, Ando T, Sakakibara M, Hosoda W, Goto H. Refractory gastric ulcer with abundant IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration: a case report. World J Gastroenterol. 2010; 16:2183–2186. PMID: 20440861.
Article21. Kaji R, Okabe Y, Ishida Y, Takedatsu H, Kawahara A, Aino H, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis presenting with IgG4-positive multiple gastric polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:420–422. PMID: 19846081.
Article22. Baez JC, Hamilton MJ, Bellizzi A, Mortele KJ. Gastric involvement in autoimmune pancreatitis: MDCT and histopathologic features. JOP. 2010; 11:610–613. PMID: 21068496.23. Chetty R, Serra S, Gauchotte G, Markl B, Agaimy A. Sclerosing nodular lesions of the gastrointestinal tract containing large numbers of IgG4 plasma cells. Pathology. 2011; 43:31–35. PMID: 21240062.
Article24. Rollins KE, Mehta SP, O'Donovan M, Safranek PM. Gastric IgG4-related autoimmune fibrosclerosing pseudotumour: a novel location. ISRN Gastroenterol. 2011; 2011:873087. PMID: 21991533.
Article25. Na KY, Sung JY, Jang JY, Lim SJ, Kim GY, Kim YW, et al. Gastric nodular lesion caused by IgG4-related disease. Pathol Int. 2012; 62:716–718. PMID: 23005600.
Article26. Bateman AC, Sommerlad M, Underwood TJ. Chronic gastric ulceration: a novel manifestation of IgG4-related disease? J Clin Pathol. 2012; 65:569–570. PMID: 22259178.
Article27. Kim DH, Kim J, Park DH, Lee JH, Choi KD, Lee GH, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related inflammatory pseudotumor of the stomach. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:451–452. PMID: 21981816.
Article28. Woo CG, Yook JH, Kim AY, Kim J. IgG4-related disease presented as a mural mass in the stomach. J Pathol Transl Med. 2016; 50:67–70. PMID: 26420251.
Article29. Yang L, Jin P, Sheng JQ. Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) affecting the esophagus, stomach, and liver. Endoscopy. 2015; 47(Suppl 1 UCTN):E96–E97. PMID: 25734809.
Article30. Inoue K, Okubo T, Kato T, Shimamura K, Sugita T, Kubota M, et al. IgG4-related stomach muscle lesion with a renal pseudotumor and multiple renal rim-like lesions: a rare manifestation of IgG4-related disease. Mod Rheumatol. 2018; 28:188–192. PMID: 26381653.
Article31. Cheong HR, Lee BE, Song GA, Kim GH, An SG, Lim W. Immunoglobulin G4-related inflammatory pseudotumor presenting as a solitary mass in the stomach. Clin Endosc. 2016; 49:197–201. PMID: 26867551.
Article32. Bulanov D, Arabadzhieva E, Bonev S, Yonkov A, Kyoseva D, Dikov T, et al. A rare case of IgG4-related disease: a gastric mass, associated with regional lymphadenopathy. BMC Surg. 2016; 16:37. PMID: 27255154.
Article33. Otsuka R, Kano M, Hayashi H, Hanari N, Gunji H, Hayano K, et al. Probable IgG4-related sclerosing disease presenting as a gastric submucosal tumor with an intense tracer uptake on PET/CT: a case report. Surg Case Rep. 2016; 2:33. PMID: 27059471.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gastric IgG4-related disease presenting as a mass lesion and masquerading as a gastrointestinal stromal tumor
- Synchronous Occurrence of a Gastric Adenocarcinoma and a GIST (Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor): A Case Report
- C-Kit-Negative Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor in the Stomach
- A Case of an Exoluminal Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor That Was Confused with a Metastatic Lymph Node in Early Gastric Cancer
- Exophytic Colon Cancer: Resemblance to a Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor of the Stomach: A Case Report