Blood Res.
2018 Mar;53(1):81-83. 10.5045/br.2018.53.1.81.
Pulmonary embolism presenting with acute abdominal pain in a girl with stable ankle fracture and inherited antithrombin deficiency
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Health Science Institute, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. howoo@gnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2414370
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2018.53.1.81
Abstract
- No abstract available.
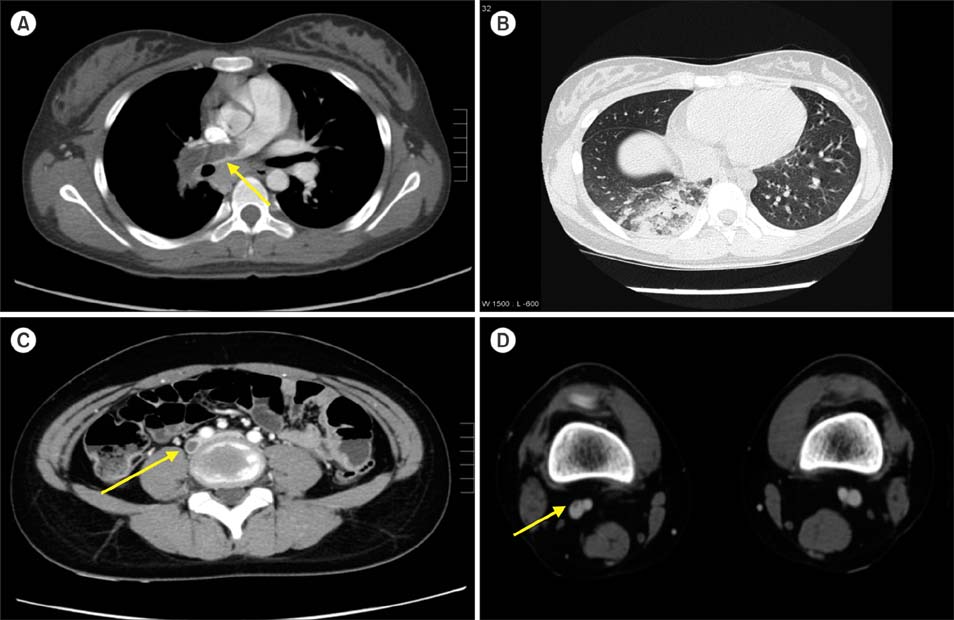
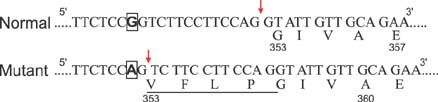
Figure
Reference
-
1. Andrew M, David M, Adams M, et al. Venous thromboembolic complications (VTE) in children: first analyses of the Canadian Registry of VTE. Blood. 1994; 83:1251–1257.
Article2. Nowak-Göttl U, Janssen V, Manner D, Kenet G. Venous thromboembolism in neonates and children-update 2013. Thromb Res. 2013; 131:Suppl 1. S39–S41.3. Klaassen IL, van Ommen CH, Middeldorp S. Manifestations and clinical impact of pediatric inherited thrombophilia. Blood. 2015; 125:1073–1077.
Article4. van Ommen CH, Heijboer H, Büller HR, Hirasing RA, Heijmans HS, Peters M. Venous thromboembolism in childhood: a prospective two-year registry in The Netherlands. J Pediatr. 2001; 139:676–681.
Article5. Tuckuviene R, Christensen AL, Helgestad J, Johnsen SP, Kristensen SR. Pediatric venous and arterial noncerebral thromboembolism in Denmark: a nationwide population-based study. J Pediatr. 2011; 159:663–669.
Article6. Patnaik MM, Moll S. Inherited antithrombin deficiency: a review. Haemophilia. 2008; 14:1229–1239.
Article7. Emmerich J, Vidaud D, Alhenc-Gelas M, et al. Three novel mutations of antithrombin inducing high-molecular-mass compounds. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994; 14:1958–1965.
Article8. Jochmans K, Lissens W, Yin T, et al. Molecular basis for type 1 antithrombin deficiency: identification of two novel point mutations and evidence for a de novo splice site mutation. Blood. 1994; 84:3742–3748.
Article9. Gouault-Heilmann M, Quetin P, Dreyfus M, et al. Massive thrombosis of venous cerebral sinuses in a 2-year-old boy with a combined inherited deficiency of antithrombin III and protein C. Thromb Haemost. 1994; 72:782–783.
Article10. Sansores-García L, Majluf-Cruz A. Arterial and venous thrombosis associated to combined deficiency of protein C and antithrombin III. Am J Hematol. 1998; 57:182–183.
Article11. Sethuraman U, Siadat M, Lepak-Hitch CA, Haritos D. Pulmonary embolism presenting as acute abdomen in a child and adult. Am J Emerg Med. 2009; 27:514.e1–514.e5.
Article12. Kerlin BA. Current and future management of pediatric venous thromboembolism. Am J Hematol. 2012; 87:Suppl 1. S68–S74.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recurrent Acute Pulmonary Embolism Associated With Protein S Deficiency
- A Case of Hereditary Antithrombin III Deficiency Manifested by Myocardial Infarction and Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Renal Infarction Concurrent with Multiple Venous Thrombosis in Association with Inherited Antithrombin Deficiency
- A Case of Anti-Thrombin III Deficiency Discovered by Myocardial Infarction
- A Case of Pulmonary Thromboembolism due to Congenital Antithrombin III Deficiency