Higher Prevalence and Progression Rate of Chronic Kidney Disease in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University School of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. imdrksk@cha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2413985
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0065
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
To evaluate the prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and progression rate to CKD in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
METHODS
We investigated the medical records of 190 elderly patients (65 years or older) with T2DM from 2005 to 2011 in 6-month increments. Mean follow-up duration was 64.5 months. CKD was defined as estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) < 60 mL/min/1.73 m² and/or the presence of albuminuria.
RESULTS
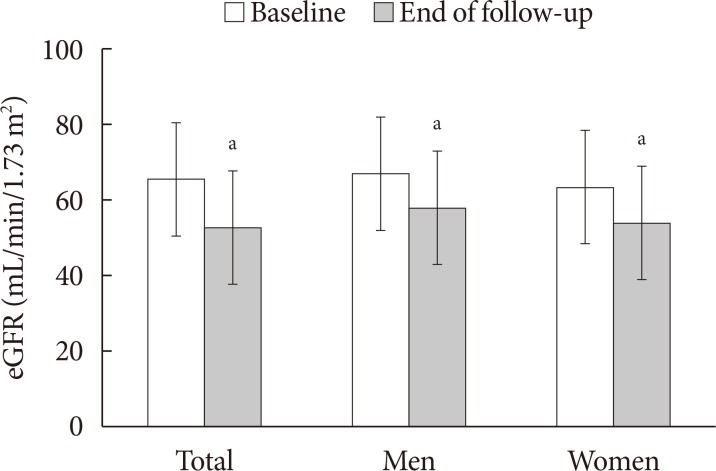
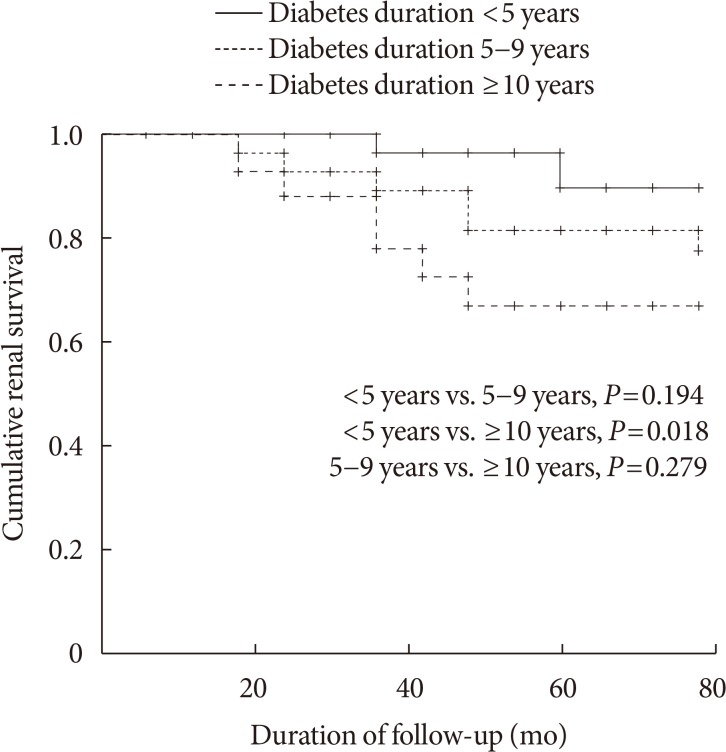
The mean age was 70.4 years and mean diabetes duration was 10.6 years. Among all the participants, 113 patients (59.5%) had CKD. The eGFR was significantly decreased between baseline (65.7±15.0 mL/min/1.73 m²) and the end of follow-up (52.7±17.5 mL/min/1.73 m², P < 0.001). At the end of follow-up, the prevalence of eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m² had increased by 61.6% (at baseline, 44.2%). Furthermore, in patients with eGFR ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m², the progression rate to more than CKD stage 3 was 39.6% at the end of follow-up; 30.2% of elderly diabetic patients had progressed to albuminuria from normoalbuminuria. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that the time interval to worsening nephropathy was significantly shorter in elderly patients with diabetes duration ≥10 years than in those with diabetes duration < 5 years (P=0.018).
CONCLUSION
CKD was commonly observed in older patients with T2DM, and the progression rate to CKD is also high. Consequently, it is important to identify and manage CKD as early as possible in elderly patients with T2DM, especially in those with diabetes duration ≥10 years.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Metformin Treatment for Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology Consensus Statement
Kyu Yeon Hur, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung Hyun Ko, Miyeun Han, Dong Won Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, ,
Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):3-10. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0004.Gemigliptin Attenuates Renal Fibrosis Through Down-Regulation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome
Jung Beom Seo, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Hye-In Woo, Yun-A Jung, Sungwoo Lee, Seunghyeong Lee, Mihyang Park, In-Kyu Lee, Gwon-Soo Jung, Keun-Gyu Park
Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(6):830-839. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0181.The Beneficial Effect of Glycemic Control against Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
Dong-Hwa Lee
Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):484-486. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0165.
Reference
-
1. Meguid El Nahas A, Bello AK. Chronic kidney disease: the global challenge. Lancet. 2005; 365:331–340. PMID: 15664230.2. Levey AS, Atkins R, Coresh J, Cohen EP, Collins AJ, Eckardt KU, Nahas ME, Jaber BL, Jadoul M, Levin A, Powe NR, Rossert J, Wheeler DC, Lameire N, Eknoyan G. Chronic kidney disease as a global public health problem: approaches and initiatives: a position statement from Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes. Kidney Int. 2007; 72:247–259. PMID: 17568785.3. Zhou XJ, Rakheja D, Yu X, Saxena R, Vaziri ND, Silva FG. The aging kidney. Kidney Int. 2008; 74:710–720. PMID: 18614996.
Article4. de Boer IH, Rue TC, Hall YN, Heagerty PJ, Weiss NS, Himmelfarb J. Temporal trends in the prevalence of diabetic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA. 2011; 305:2532–2539. PMID: 21693741.
Article5. Afkarian M, Sachs MC, Kestenbaum B, Hirsch IB, Tuttle KR, Himmelfarb J, de Boer IH. Kidney disease and increased mortality risk in type 2 diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013; 24:302–308. PMID: 23362314.
Article6. Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004; 351:1296–1305. PMID: 15385656.
Article7. Shlipak MG, Sarnak MJ, Katz R, Fried LF, Seliger SL, Newman AB, Siscovick DS, Stehman-Breen C. Cystatin C and the risk of death and cardiovascular events among elderly persons. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:2049–2060. PMID: 15901858.
Article8. Sarnak MJ, Levey AS, Schoolwerth AC, Coresh J, Culleton B, Hamm LL, McCullough PA, Kasiske BL, Kelepouris E, Klag MJ, Parfrey P, Pfeffer M, Raij L, Spinosa DJ, Wilson PW. American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: a statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation. 2003; 108:2154–2169. PMID: 14581387.9. O'Hare AM, Choi AI, Bertenthal D, Bacchetti P, Garg AX, Kaufman JS, Walter LC, Mehta KM, Steinman MA, Allon M, McClellan WM, Landefeld CS. Age affects outcomes in chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007; 18:2758–2765. PMID: 17855638.10. Iglesias P, Heras M, Diez JJ. Diabetes mellitus and kidney disease in the elderly. Nefrologia. 2014; 34:285–292. PMID: 24798557.11. Lee SW, Kim YC, Oh SW, Koo HS, Na KY, Chae DW, Kim S, Chin HJ. Trends in the prevalence of chronic kidney disease, other chronic diseases and health-related behaviors in an adult Korean population: data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011; 26:3975–3980. PMID: 21454352.
Article12. Wasen E, Isoaho R, Mattila K, Vahlberg T, Kivela SL, Irjala K. Renal impairment associated with diabetes in the elderly. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:2648–2653. PMID: 15505000.13. Sheen YJ, Sheu WH. Risks of rapid decline renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes. World J Diabetes. 2014; 5:835–846. PMID: 25512785.
Article14. Afkarian M, Zelnick LR, Hall YN, Heagerty PJ, Tuttle K, Weiss NS, de Boer IH. Clinical manifestations of kidney disease among US adults with diabetes, 1988–2014. JAMA. 2016; 316:602–610. PMID: 27532915.
Article15. Lou Arnal LM, Campos Gutierrez B, Cuberes Izquierdo M, Gracia Garcia O, Turon Alcaine JM, Bielsa Garcia S, Gimeno Orna JA, Boned Juliani B, Sanjuan Hernandez-French A. Grupo de Investigacion ERC Aragon. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated in primary care. Nefrologia. 2010; 30:552–556. PMID: 20882094.16. Coresh J, Astor BC, Greene T, Eknoyan G, Levey AS. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and decreased kidney function in the adult US population: third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003; 41:1–12. PMID: 12500213.
Article17. Fox CS, Larson MG, Leip EP, Culleton B, Wilson PW, Levy D. Predictors of new-onset kidney disease in a community-based population. JAMA. 2004; 291:844–850. PMID: 14970063.
Article18. Kim S, Lim CS, Han DC, Kim GS, Chin HJ, Kim SJ, Cho WY, Kim YH, Kim YS. The prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and the associated factors to CKD in urban Korea: a population-based cross-sectional epidemiologic study. J Korean Med Sci. 2009; 24(Suppl):S11–S21. PMID: 19194539.
Article19. Yun KJ, Kim HJ, Kim MK, Kwon HS, Baek KH, Roh YJ, Song KH. Risk factors for the development and progression of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and advanced diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Metab J. 2016; 40:473–481. PMID: 27766790.
Article20. Levey AS, Inker LA, Coresh J. Chronic kidney disease in older people. JAMA. 2015; 314:557–558. PMID: 26023868.
Article21. Kirkman MS, Briscoe VJ, Clark N, Florez H, Haas LB, Halter JB, Huang ES, Korytkowski MT, Munshi MN, Odegard PS, Pratley RE, Swift CS. Diabetes in older adults. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:2650–2664. PMID: 23100048.
Article22. Sinclair A, Morley JE, Rodriguez-Manas L, Paolisso G, Bayer T, Zeyfang A, Bourdel-Marchasson I, Vischer U, Woo J, Chapman I, Dunning T, Meneilly G, Rodriguez-Saldana J, Gutierrez Robledo LM, Cukierman-Yaffe T, Gadsby R, Schernthaner G, Lorig K. Diabetes mellitus in older people: position statement on behalf of the International Association of Gerontology and Geriatrics (IAGG), the European Diabetes Working Party for Older People (EDWPOP), and the International Task Force of Experts in Diabetes. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2012; 13:497–502. PMID: 22748719.
Article23. National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002; 39(2 Suppl 1):S1–S266. PMID: 11904577.24. Hwang SJ, Lin MY, Chen HC, Hwang SC, Yang WC, Hsu CC, Chiu HC, Mau LW. Increased risk of mortality in the elderly population with late-stage chronic kidney disease: a cohort study in Taiwan. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008; 23:3192–3198. PMID: 18450830.
Article25. Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea 2016. cited 2018 Apr 11. Available from: http://www.diabetes.or.kr/temp/KDA_fact_sheet%202016.pdf.26. Lundstrom UH, Gasparini A, Bellocco R, Qureshi AR, Carrero JJ, Evans M. Low renal replacement therapy incidence among slowly progressing elderly chronic kidney disease patients referred to nephrology care: an observational study. BMC Nephrol. 2017; 18:59. PMID: 28187786.
Article27. Anderson S, Halter JB, Hazzard WR, Himmelfarb J, Horne FM, Kaysen GA, Kusek JW, Nayfield SG, Schmader K, Tian Y, Ashworth JR, Clayton CP, Parker RP, Tarver ED, Woolard NF, High KP. workshop participants. Prediction, progression, and outcomes of chronic kidney disease in older adults. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009; 20:1199–1209. PMID: 19470680.
Article28. Arora P, Jalal K, Gupta A, Carter RL, Lohr JW. Progression of kidney disease in elderly stage 3 and 4 chronic kidney disease patients. Int Urol Nephrol. 2017; 49:1033–1040. PMID: 28236138.
Article29. Hemmelgarn BR, Zhang J, Manns BJ, Tonelli M, Larsen E, Ghali WA, Southern DA, McLaughlin K, Mortis G, Culleton BF. Progression of kidney dysfunction in the community-dwelling elderly. Kidney Int. 2006; 69:2155–2161. PMID: 16531986.
Article30. Costacou T, Orchard TJ. Cumulative kidney complication risk by 50 years of type 1 diabetes: the effects of sex, age, and calendar year at onset. Diabetes Care. 2018; 41:426–433. PMID: 28931542.
Article31. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998; 352:837–853. PMID: 9742976.32. Baid-Agrawal S, Reinke P, Schindler R, Tullius S, Frei U. WCN 2003 satellite symposium on kidney transplantation in the elderly, Weimar, Germany, June 12-14, 2003. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004; 19:43–46. PMID: 14671037.
Article