J Vet Sci.
2016 Sep;17(3):431-433. 10.4142/jvs.2016.17.3.431.
Hyperammonemic hepatic encephalopathy management through L-ornithin-L-aspartate administration in dogs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Internal Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Korea. hyyoun@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Veterinary Internal Medicine and Institute of Veterinary Science, College of Veterinary Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 24341, Korea. chungjinyoung@kangwon.ac.kr
- KMID: 2413146
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2016.17.3.431
Abstract
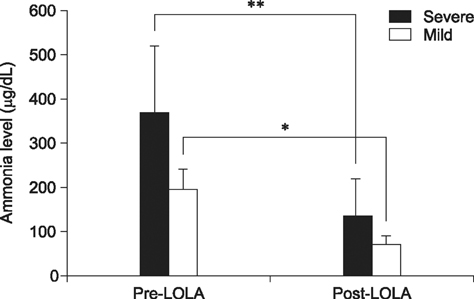
- Seventeen dogs were treated with L-ornithin-L-aspartate (LOLA; experimental group). Three dogs were treated with lactulose recognized therapy (control group). Following LOLA administration, 15 dogs experienced a significant decrease in ammonia level (p < 0.05) and showed clinical signs of improvement. However, there were no clinical signs of improvement in two dogs, even though the ammonia level decreased. Conversely, the clinical signs of the control group also improved and the ammonia level decreased, although these changes were not significant (p > 0.05). These results suggest that LOLA is an effective drug to treat hyperammonemia in veterinary medicine.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahmad I, Khan AA, Alam A, Dilshad A, Butt AK, Shafqat F, Malik K, Sarwar S. L-ornithine-L-aspartate infusion efficacy in hepatic encephalopathy. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2008; 18:684–687.2. Blei AT. Diagnosis and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2000; 14:959–974.
Article3. Czarnecki GL, Baker DH. Urea cycle function in the dog with emphasis on the role of arginine. J Nutr. 1984; 114:581–590.
Article4. Gerber T, Schomerus H. Hepatic encephalopathy in liver cirrhosis: pathogenesis, diagnosis and management. Drugs. 2000; 60:1353–1370.5. Häussinger D. Nitrogen metabolism in liver: structural and functional organization and physiological relevance. Biochem J. 1990; 267:281–290.
Article6. Häussinger D, Kircheis G, Fischer R, Schliess F, vom Dahl S. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: a clinical manifestation of astrocyte swelling and low-grade cerebral edema? J Hepatol. 2000; 32:1035–1038.
Article7. Jiang Q, Jiang XH, Zheng MH, Chen YP. L-Ornithine-L-aspartate in the management of hepatic encephalopathy: a meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 24:9–14.
Article8. Laflamme DP, Allen SW, Huber TL. Apparent dietary protein requirement of dogs with portosystemic shunt. Am J Vet Res. 1993; 54:719–723.9. Meyer HP, Legemate DA, van den Brom W, Rothuizen J. Improvement of chronic hepatic encephalopathy in dogs by the benzodiazepine-receptor partial inverse agonist sarmazenil, but not by the antagonist flumazenil. Metab Brain Dis. 1998; 13:241–251.10. Nusrat S, Khan MS, Fazili J, Madhoun MF. Cirrhosis and its complications: evidence based treatment. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:5442–5460.
Article11. Poo JL, Góngora J, Sánchez-Avila F, Aguilar-Castillo S, García-Ramos G, Fernández-Zertuche M, Rodríguez-Fragoso L, Uribe M. Efficacy of oral L-ornithine-L-aspartate in cirrhotic patients with hyperammonemic hepatic encephalopathy. Results of a randomized, lactulose-controlled study. Ann Hepatol. 2006; 5:281–288.
Article12. Reagan-Shaw S, Nihal M, Ahmad N. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J. 2008; 22:659–661.
Article13. Sharma K, Pant S, Misra S, Dwivedi M, Misra A, Narang S, Tewari R, Bhadoria AS. Effect of rifaximin, probiotics, and l-ornithine l-aspartate on minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized controlled trial. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:225–232.
Article14. van Straten G, van Steenbeek FG, Grinwis GCM, Favier RP, Kummeling A, van Gils IH, Fieten H, Groot Koerkamp MJA, Holstege FCP, Rothuizen J, Spee B. Aberrant expression and distribution of enzymes of the urea cycle and other ammonia metabolizing pathways in dogs with congenital portosystemic shunts. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e100077.
Article15. Wright G, Jalan R. Management of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2007; 21:95–110.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy with Features on Diffusion-Weighted Images: Report of Two Cases
- Anesthetic Management of Embolization for a Cerebral Aneurysm in Patient with Portal-systemic Encephalopathy: A case report
- Non-cirrhotic Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy with Portosystemic Shunt
- Therapeutic Dose Range of Valproate-Induced Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy: A Case Report
- Reversible Burst-suppression Pattern of Acute Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy