Arch Hand Microsurg.
2018 Mar;23(1):63-67. 10.12790/ahm.2018.23.1.63.
Bilateral Vulvar Reconstruction Using Two Different Types of Perforator Flap: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic Surgery, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. mdki1967@gmail.com
- 2Department of Plastic Surgery, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2412493
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.2018.23.1.63
Abstract
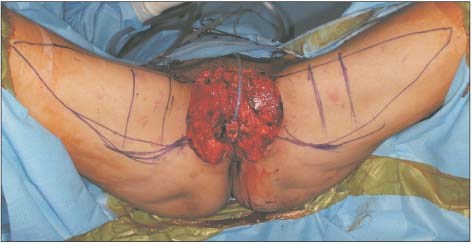
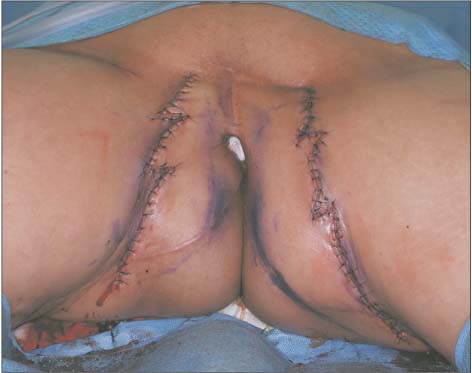
- We reconstructed an extensive vulvar defect with the internal pudendal artery and the anterior obturator artery perforator flap and compared the two types of flaps. A 57-year-old female patient had a 15×13 cm2 defect on both sides around the vagina after vulvectomy. Due to the injury in the internal pudendal artery, we used the internal pudendal artery perforator on the right side, and the anterior obturator artery perforator flap on the left side. The internal pudendal artery perforator flap could be rotated easily 120 degrees toward the vulvar defect. However, as the anterior obturator artery perforator flap was difficult to rotate, reconstruction was performed by rotation and advancement. The anterior obturator artery perforator flap is a viable alternative method that can be used when it is difficult to use the internal pudendal artery perforator flap during vulvar reconstruction.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Höckel M, Dornhöfer N. Vulvovaginal reconstruction for neoplastic disease. Lancet Oncol. 2008; 9:559–568.
Article2. Hashimoto I, Abe Y, Nakanishi H. The internal pudendal artery perforator flap: free-style pedicle perforator flaps for vulva, vagina, and buttock reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014; 133:924–933.3. Bodin F, Weitbruch D, Seigle-Murandi F, Volkmar P, Bruant-Rodier C, Rodier JF. Vulvar reconstruction by a “supra-fascial” lotus petal flap after surgery for malignancies. Gynecol Oncol. 2012; 125:610–613.
Article4. Al-Benna S, Tzakas E. Postablative reconstruction of vulvar defects with local fasciocutaneous flaps and superficial fascial system repair. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2012; 286:443–448.
Article5. Sawada M, Kimata Y, Kasamatsu T, et al. Versatile lotus petal flap for vulvoperineal reconstruction after gynecological ablative surgery. Gynecol Oncol. 2004; 95:330–335.
Article6. Tan BK, Kang GC, Tay EH, Por YC. Subunit principle of vulvar reconstruction: algorithm and outcomes. Arch Plast Surg. 2014; 41:379–386.
Article7. O'Dey DM, Bozkurt A, Pallua N. The anterior Obturator Artery Perforator (aOAP) flap: surgical anatomy and application of a method for vulvar reconstruction. Gynecol Oncol. 2010; 119:526–530.8. Lazzaro L, Guarneri GF, Rampino , et al. Vulvar reconstruction using a “V-Y” fascio-cutaneous gluteal flap: a valid reconstructive alternative in post-oncological loss of substance. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2010; 282:521–527.
Article9. Chen YC, Scaglioni MF, Kuo YR. Profunda artery perforator based V-Y rotation advancement flap for total vulvectomy defect reconstruction--A case report and literature review. Microsurgery. 2015; 35:668–671.
Article10. Lee JH, Shin JW, Kim SW, et al. Modified gluteal fold V-Y advancement flap for vulvovaginal reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2013; 71:571–574.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Perineal Reconstruction with the Perineal Perforator Based Island Flap
- Various Utility of Perforator Flaps in Head and Neck Reconstruction
- Reconstruction of the Soft Tissue Defect Using Thoracodorsal Artery Perforator Skin Flap
- Contribution of Perforator Flaps in the Flap Selection for Head and Neck Reconstruction
- Dual Perforator Flap for Reconstruction of Large Sacral Defects: Superior Gluteal Artery Perforator Super-Flap with Parasacral Perforator