Clin Orthop Surg.
2018 Jun;10(2):248-252. 10.4055/cios.2018.10.2.248.
Biportal Endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Arthroscopy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Andong Medical Center, Andong, Korea.
- 2Department of Spine Surgery, Barun Hospital, Jinju, Korea. djchoi9@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2411752
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.2.248
Abstract
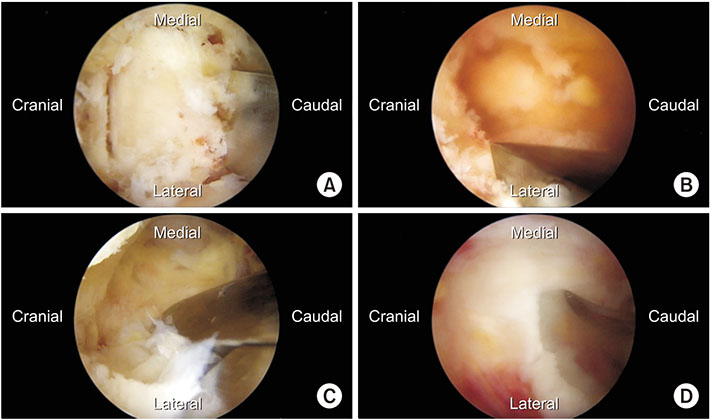
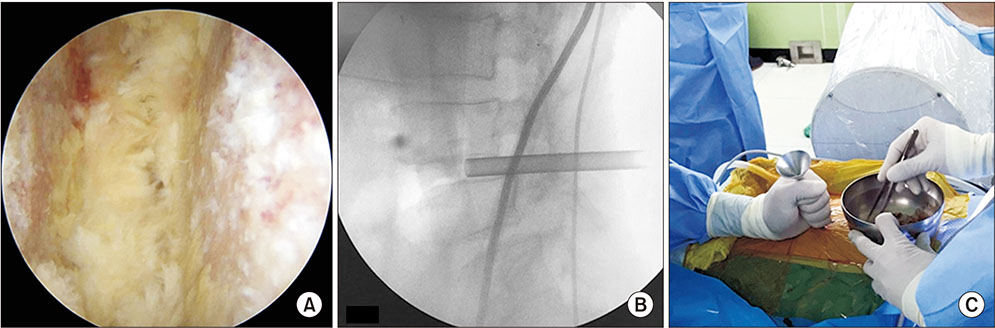
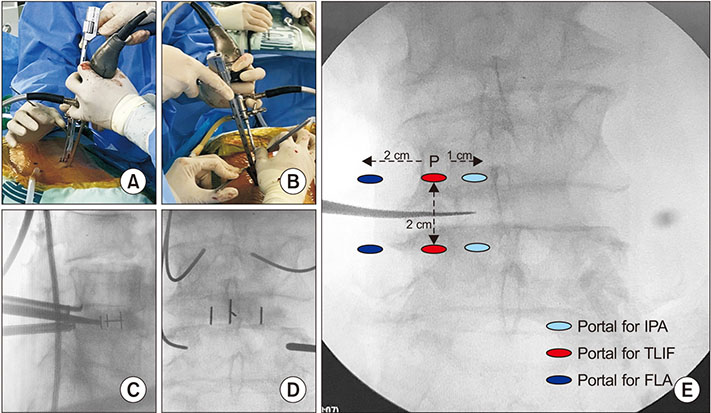
- Lumbar spine fusion has been widely accepted as a treatment for various spinal pathologies, including the degenerative spinal diseases. Transforaminal interbody fusion (TLIF) using minimally invasive surgery (MIS-TLIF) is well-known for reducing muscle damage. However, the need to use a tubular retractor during MIS-TLIF may contribute to some limitations of instrument handling, and a great deal of difficulty in confirming contralateral decompression and accurate endplate preparation. Several studies in spinal surgery have reported the use of the unilateral biportal endoscopic spinal surgery (technique for decompression or discectomy). The purpose of this study is to describe the process of and technical tips for TLIF using the biportal endoscopic spinal surgery technique. Biportal endoscopic TLIF is similar to MIS-TLIF except that there is no need for a tubular retractor. It is supposed to be another option for alternating open lumbar fusion and MIS fusion in degenerative lumbar disease that needs fusion surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Full-Endoscopic versus Minimally Invasive Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Degenerative Diseases : A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Seong Son, Byung Rhae Yoo, Sang Gu Lee, Woo Kyung Kim, Jong Myung Jung
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2022;65(4):539-548. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2021.0168.
Reference
-
1. Bagan B, Patel N, Deutsch H, et al. Perioperative complications of minimally invasive surgery (MIS): comparison of MIS and open interbody fusion techniques. Surg Technol Int. 2008; 17:281–286.2. Harms JG, Jeszenszky D. Die posteriore, lumbale, interkorporelle fusion in unilateraler transforaminaler technik. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 1998; 10(2):90–102.
Article3. Gejo R, Matsui H, Kawaguchi Y, Ishihara H, Tsuji H. Serial changes in trunk muscle performance after posterior lumbar surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999; 24(10):1023–1028.
Article4. Kawaguchi Y, Matsui H, Tsuji H. Back muscle injury after posterior lumbar spine surgery. Part 1: histologic and histochemical analyses in rats. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19(22):2590–2597.5. Foley KT, Holly LT, Schwender JD. Minimally invasive lumbar fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:15 Suppl. S26–S35.
Article6. Kim CW. Scientific basis of minimally invasive spine surgery: prevention of multifidus muscle injury during posterior lumbar surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35:26 Suppl. S281–S286.7. Choi CM, Chung JT, Lee SJ, Choi DJ. How I do it? Biportal endoscopic spinal surgery (BESS) for treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2016; 158(3):459–463.
Article8. Eum JH, Heo DH, Son SK, Park CK. Percutaneous biportal endoscopic decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis: a technical note and preliminary clinical results. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016; 24(4):602–607.
Article9. Sihvonen T, Herno A, Paljarvi L, Airaksinen O, Partanen J, Tapaninaho A. Local denervation atrophy of paraspinal muscles in postoperative failed back syndrome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993; 18(5):575–581.
Article10. Choi DJ, Choi CM, Jung JT, Lee SJ, Kim YS. Learning curve associated with complications in biportal endoscopic spinal surgery: challenges and strategies. Asian Spine J. 2016; 10(4):624–629.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Technique of Biportal Endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- The Use of Dual Direction Expandable Titanium Cage With Biportal Endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Technical Consideration With Preliminary Results
- Uniportal Endoscopic Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Selective Biportal Endoscopic Posterior Decompression for Multilevel Lumbar Degenerative Diseases
- Biportal Endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Double Cages: Surgical Techniques and Treatment Outcomes