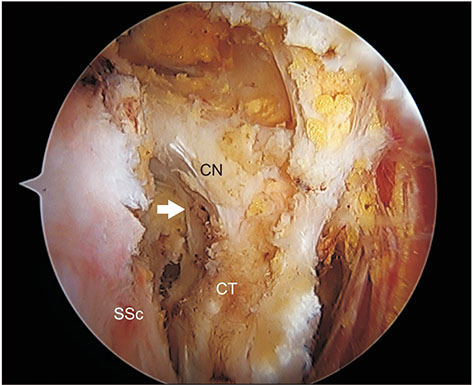
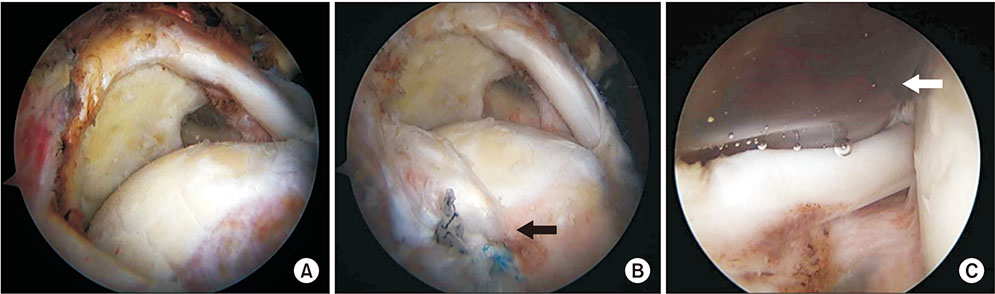
Clin Orthop Surg.
2018 Jun;10(2):119-134. 10.4055/cios.2018.10.2.119.
Treatment Strategy for Irreparable Rotator Cuff Tears
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. nanbin82@naver.com
- KMID: 2411736
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.2.119
Abstract
- Recently, patients with shoulder pain have increased rapidly. Of all shoulder disorders, rotator cuff tears (RCTs) are most prevalent in the middle-aged and older adults, which is the primary reason for shoulder surgery in the population. Some authors have reported that up to 30% of total RCTs can be classified as irreparable due to the massive tear size and severe muscle atrophy. In this review article, we provide an overview of treatment methods for irreparable massive RCTs and discuss proper surgical strategies for RCTs that require operative management.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chung SW, Kim JY, Kim MH, Kim SH, Oh JH. Arthroscopic repair of massive rotator cuff tears: outcome and analysis of factors associated with healing failure or poor postoperative function. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41(7):1674–1683.2. Warner JJ. Management of massive irreparable rotator cuff tears: the role of tendon transfer. Instr Course Lect. 2001; 50:63–71.3. Neri BR, Chan KW, Kwon YW. Management of massive and irreparable rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009; 18(5):808–818.
Article4. Levy O, Mullett H, Roberts S, Copeland S. The role of anterior deltoid reeducation in patients with massive irreparable degenerative rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008; 17(6):863–870.
Article5. Yian EH, Sodl JF, Dionysian E, Schneeberger AG. Anterior deltoid reeducation for irreparable rotator cuff tears revisited. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017; 26(9):1562–1565.
Article6. Gialanella B, Bertolinelli M. Corticosteroids injection in rotator cuff tears in elderly patient: pain outcome prediction. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2013; 13(4):993–1001.
Article7. Maman E, Yehuda C, Pritsch T, et al. Detrimental effect of repeated and single subacromial corticosteroid injections on the intact and injured rotator cuff: a biomechanical and imaging study in rats. Am J Sports Med. 2016; 44(1):177–182.
Article8. Rockwood CA Jr, Williams GR Jr, Burkhead WZ Jr. Debridement of degenerative, irreparable lesions of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77(6):857–866.9. Kempf JF, Gleyze P, Bonnomet F, et al. A multicenter study of 210 rotator cuff tears treated by arthroscopic acromioplasty. Arthroscopy. 1999; 15(1):56–66.
Article10. Veado MA, Rodrigues AU. Functional evaluation of patients who have undergone arthroscopic debridement to treat massive and irreparable tears of the rotator cuff. Rev Bras Ortop. 2010; 45(5):426–431.
Article11. Fenlin JM Jr, Chase JM, Rushton SA, Frieman BG. Tuberoplasty: creation of an acromiohumeral articulation-a treatment option for massive, irreparable rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002; 11(2):136–142.
Article12. Scheibel M, Lichtenberg S, Habermeyer P. Reversed arthroscopic subacromial decompression for massive rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2004; 13(3):272–278.
Article13. Verhelst L, Vandekerckhove PJ, Sergeant G, Liekens K, Van Hoonacker P, Berghs B. Reversed arthroscopic subacromial decompression for symptomatic irreparable rotator cuff tears: mid-term follow-up results in 34 shoulders. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010; 19(4):601–608.
Article14. Lee BG, Cho NS, Rhee YG. Results of arthroscopic decompression and tuberoplasty for irreparable massive rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27(10):1341–1350.
Article15. Park JG, Cho NS, Song JH, Baek JH, Rhee YG. Long-term outcome of tuberoplasty for irreparable massive rotator cuff tears: is tuberoplasty really applicable? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016; 25(2):224–231.
Article16. Burkhart SS, Esch JC, Jolson RS. The rotator crescent and rotator cable: an anatomic description of the shoulder's “suspension bridge”. Arthroscopy. 1993; 9(6):611–616.
Article17. Burkhart SS, Nottage WM, Ogilvie-Harris DJ, Kohn HS, Pachelli A. Partial repair of irreparable rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy. 1994; 10(4):363–370.
Article18. Kim SJ, Lee IS, Kim SH, Lee WY, Chun YM. Arthroscopic partial repair of irreparable large to massive rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy. 2012; 28(6):761–768.
Article19. Galasso O, Riccelli DA, De Gori M, et al. Quality of life and functional results of arthroscopic partial repair of irreparable rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy. 2017; 33(2):261–268.
Article20. Iagulli ND, Field LD, Hobgood ER, Ramsey JR, Savoie FH 3rd. Comparison of partial versus complete arthroscopic repair of massive rotator cuff tears. Am J Sports Med. 2012; 40(5):1022–1026.
Article21. Berth A, Neumann W, Awiszus F, Pap G. Massive rotator cuff tears: functional outcome after debridement or arthroscopic partial repair. J Orthop Traumatol. 2010; 11(1):13–20.
Article22. Oh JH, McGarry MH, Jun BJ, et al. Restoration of shoulder biomechanics according to degree of repair completion in a cadaveric model of massive rotator cuff tear: importance of margin convergence and posterior cuff fixation. Am J Sports Med. 2012; 40(11):2448–2453.
Article23. Bigliani LU, Cordasco FA, McLlveen SJ, Musso ES. Operative repair of massive rotator cuff tears: long-term results. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1992; 1(3):120–130.
Article24. Tauro JC. Arthroscopic “interval slide” in the repair of large rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy. 1999; 15(5):527–530.
Article25. Anley CM, Chan SK, Snow M. Arthroscopic treatment options for irreparable rotator cuff tears of the shoulder. World J Orthop. 2014; 5(5):557–565.
Article26. Lo IK, Burkhart SS. Arthroscopic repair of massive, contracted, immobile rotator cuff tears using single and double interval slides: technique and preliminary results. Arthroscopy. 2004; 20(1):22–33.
Article27. Kim SJ, Kim SH, Lee SK, Seo JW, Chun YM. Arthroscopic repair of massive contracted rotator cuff tears: aggressive release with anterior and posterior interval slides do not improve cuff healing and integrity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013; 95(16):1482–1488.28. Berdusco R, Trantalis JN, Nelson AA, et al. Arthroscopic repair of massive, contracted, immobile tears using interval slides: clinical and MRI structural follow-up. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015; 23(2):502–507.
Article29. Burkhart SS, Athanasiou KA, Wirth MA. Margin convergence: a method of reducing strain in massive rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy. 1996; 12(3):335–338.
Article30. Burkhart SS. The principle of margin convergence in rotator cuff repair as a means of strain reduction at the tear margin. Ann Biomed Eng. 2004; 32(1):166–170.
Article31. Shindle MK, Nho SJ, Nam D, et al. Technique for margin convergence in rotator cuff repair. HSS J. 2011; 7(3):208–212.
Article32. Mazzocca AD, Bollier M, Fehsenfeld D, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of margin convergence. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27(3):330–338.
Article33. Liu J, Hughes RE, O'Driscoll SW, An KN. Biomechanical effect of medial advancement of the supraspinatus tendon: a study in cadavera. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998; 80(6):853–859.
Article34. Yamamoto N, Itoi E, Tuoheti Y, et al. Glenohumeral joint motion after medial shift of the attachment site of the supraspinatus tendon: a cadaveric study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007; 16(3):373–378.
Article35. Kim YK, Jung KH, Won JS, Cho SH. Medialized repair for retracted rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017; 26(8):1432–1440.
Article36. Soler JA, Gidwani S, Curtis MJ. Early complications from the use of porcine dermal collagen implants (Permacol) as bridging constructs in the repair of massive rotator cuff tears: a report of 4 cases. Acta Orthop Belg. 2007; 73(4):432–436.37. Sclamberg SG, Tibone JE, Itamura JM, Kasraeian S. Six-month magnetic resonance imaging follow-up of large and massive rotator cuff repairs reinforced with porcine small intestinal submucosa. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2004; 13(5):538–541.
Article38. Iannotti JP, Codsi MJ, Kwon YW, Derwin K, Ciccone J, Brems JJ. Porcine small intestine submucosa augmentation of surgical repair of chronic two-tendon rotator cuff tears: a randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88(6):1238–1244.
Article39. Encalada-Diaz I, Cole BJ, Macgillivray JD, et al. Rotator cuff repair augmentation using a novel polycarbonate polyurethane patch: preliminary results at 12 months' follow-up. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011; 20(5):788–794.
Article40. Ciampi P, Scotti C, Nonis A, et al. The benefit of synthetic versus biological patch augmentation in the repair of posterosuperior massive rotator cuff tears: a 3-year follow-up study. Am J Sports Med. 2014; 42(5):1169–1175.
Article41. Neviaser JS, Neviaser RJ, Neviaser TJ. The repair of chronic massive ruptures of the rotator cuff of the shoulder by use of a freeze-dried rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978; 60(5):681–684.
Article42. Nasca RJ. The use of freeze-dried allografts in the management of global rotator cuff tears. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; (228):218–226.
Article43. Moore DR, Cain EL, Schwartz ML, Clancy WG Jr. Allograft reconstruction for massive, irreparable rotator cuff tears. Am J Sports Med. 2006; 34(3):392–396.
Article44. Barber FA, Burns JP, Deutsch A, Labbe MR, Litchfield RB. A prospective, randomized evaluation of acellular human dermal matrix augmentation for arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. Arthroscopy. 2012; 28(1):8–15.
Article45. Rhee SM, Oh JH. Bridging graft in irreparable massive rotator cuff tears: Autogenic Biceps Graft versus Allogenic Dermal Patch Graft. Clin Orthop Surg. 2017; 9(4):497–505.
Article46. Yoon JP, Chung SW, Kim JY, et al. Outcomes of combined bone marrow stimulation and patch augmentation for massive rotator cuff tears. Am J Sports Med. 2016; 44(4):963–971.
Article47. Chung SW, Song BW, Kim YH, Park KU, Oh JH. Effect of platelet-rich plasma and porcine dermal collagen graft augmentation for rotator cuff healing in a rabbit model. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41(12):2909–2918.
Article48. Neviaser JS. Ruptures of the rotator cuff of the shoulder: new concepts in the diagnosis and operative treatment of chronic ruptures. Arch Surg. 1971; 102(5):483–485.49. Rhee YG, Cho NS, Lim CT, Yi JW, Vishvanathan T. Bridging the gap in immobile massive rotator cuff tears: augmentation using the tenotomized biceps. Am J Sports Med. 2008; 36(8):1511–1518.
Article50. Cho NS, Yi JW, Rhee YG. Arthroscopic biceps augmentation for avoiding undue tension in repair of massive rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy. 2009; 25(2):183–191.
Article51. Ji JH, Shafi M, Jeong JJ, Park SE. Arthroscopic repair of large and massive rotator cuff tears using the biceps-incorporating technique: mid-term clinical and anatomical results. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014; 24(8):1367–1374.
Article52. Oh JH, Tilan J, Chen YJ, Chung KC, McGarry MH, Lee TQ. Biomechanical effect of latissimus dorsi tendon transfer for irreparable massive cuff tear. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013; 22(2):150–157.
Article53. Aoki M, Okamura K, Fukushima S, Takahashi T, Ogino T. Transfer of latissimus dorsi for irreparable rotator-cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996; 78(5):761–766.
Article54. Gerber C, Maquieira G, Espinosa N. Latissimus dorsi transfer for the treatment of irreparable rotator cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88(1):113–120.
Article55. Werner CM, Zingg PO, Lie D, Jacob HA, Gerber C. The biomechanical role of the subscapularis in latissimus dorsi transfer for the treatment of irreparable rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006; 15(6):736–742.
Article56. Grimberg J, Kany J, Valenti P, Amaravathi R, Ramalingam AT. Arthroscopic-assisted latissimus dorsi tendon transfer for irreparable posterosuperior cuff tears. Arthroscopy. 2015; 31(4):599–607.e1.
Article57. El-Azab HM, Rott O, Irlenbusch U. Long-term follow-up after latissimus dorsi transfer for irreparable posterosuperior rotator cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015; 97(6):462–469.
Article58. Henseler JF, Nagels J, Nelissen RG, de Groot JH. Does the latissimus dorsi tendon transfer for massive rotator cuff tears remain active postoperatively and restore active external rotation? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014; 23(4):553–560.
Article59. Resch H, Povacz P, Ritter E, Matschi W. Transfer of the pectoralis major muscle for the treatment of irreparable rupture of the subscapularis tendon. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000; 82(3):372–382.
Article60. Gavriilidis I, Kircher J, Magosch P, Lichtenberg S, Habermeyer P. Pectoralis major transfer for the treatment of irreparable anterosuperior rotator cuff tears. Int Orthop. 2010; 34(5):689–694.
Article61. Jost B, Puskas GJ, Lustenberger A, Gerber C. Outcome of pectoralis major transfer for the treatment of irreparable subscapularis tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85(10):1944–1951.
Article62. Mihata T, McGarry MH, Pirolo JM, Kinoshita M, Lee TQ. Superior capsule reconstruction to restore superior stability in irreparable rotator cuff tears: a biomechanical cadaveric study. Am J Sports Med. 2012; 40(10):2248–2255.
Article63. Mihata T, Lee TQ, Watanabe C, et al. Clinical results of arthroscopic superior capsule reconstruction for irreparable rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy. 2013; 29(3):459–470.
Article64. Denard PJ, Brady PC, Adams CR, Tokish JM, Burkhart SS. Preliminary results of arthroscopic superior capsule reconstruction with dermal allograft. arthroscopy. 2018; 34(1):93–99.
Article65. Senekovic V, Poberaj B, Kovacic L, et al. The biodegradable spacer as a novel treatment modality for massive rotator cuff tears: a prospective study with 5-year follow-up. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017; 137(1):95–103.
Article66. Holschen M, Brand F, Agneskirchner JD. Subacromial spacer implantation for massive rotator cuff tears: clinical outcome of arthroscopically treated patients. Obere Extrem. 2017; 12(1):38–45.67. Deranlot J, Herisson O, Nourissat G, et al. Arthroscopic subacromial spacer implantation in patients with massive irreparable rotator cuff tears: clinical and radiographic results of 39 retrospectives cases. Arthroscopy. 2017; 33(9):1639–1644.
Article68. Gervasi E, Cautero E, Dekel A. Fluoroscopy-guided implantation of subacromial “biodegradable spacer” using local anesthesia in patients with irreparable rotator cuff tear. Arthrosc Tech. 2014; 3(4):e455–e458.
Article69. Savarese E, Romeo R. New solution for massive, irreparable rotator cuff tears: the subacromial “biodegradable spacer”. Arthrosc Tech. 2012; 1(1):e69–e74.
Article70. Senekovic V, Poberaj B, Kovacic L, Mikek M, Adar E, Dekel A. Prospective clinical study of a novel biodegradable subacromial spacer in treatment of massive irreparable rotator cuff tears. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013; 23(3):311–316.
Article71. Bozkurt M, Akkaya M, Gursoy S, Isik C. Augmented fixation with biodegradable subacromial spacer after repair of massive rotator cuff tear. Arthrosc Tech. 2015; 4(5):e471–e474.
Article72. Goldberg SS, Bell JE, Kim HJ, Bak SF, Levine WN, Bigliani LU. Hemiarthroplasty for the rotator cuff-deficient shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90(3):554–559.
Article73. Zuckerman JD, Scott AJ, Gallagher MA. Hemiarthroplasty for cuff tear arthropathy. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2000; 9(3):169–172.
Article74. Visotsky JL, Basamania C, Seebauer L, Rockwood CA, Jensen KL. Cuff tear arthropathy: pathogenesis, classification, and algorithm for treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86:Suppl 2. 35–40.75. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Cofield RH, Rowland CM. Shoulder hemiarthroplasty for glenohumeral arthritis associated with severe rotator cuff deficiency. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001; 83(12):1814–1822.
Article76. Baulot E, Sirveaux F, Boileau P. Grammont's idea: the story of Paul Grammont's functional surgery concept and the development of the reverse principle. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011; 469(9):2425–2431.
Article77. Sirveaux F, Favard L, Oudet D, Huquet D, Walch G, Mole D. Grammont inverted total shoulder arthroplasty in the treatment of glenohumeral osteoarthritis with massive rupture of the cuff: results of a multicentre study of 80 shoulders. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86(3):388–395.78. Frankle M, Levy JC, Pupello D, et al. The reverse shoulder prosthesis for glenohumeral arthritis associated with severe rotator cuff deficiency: a minimum two-year follow-up study of sixty patients surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:Suppl 1 Pt 2. 178–190.
Article79. Favard L, Levigne C, Nerot C, Gerber C, De Wilde L, Mole D. Reverse prostheses in arthropathies with cuff tear: are survivorship and function maintained over time? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011; 469(9):2469–2475.
Article80. Ek ET, Neukom L, Catanzaro S, Gerber C. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for massive irreparable rotator cuff tears in patients younger than 65 years old: results after five to fifteen years. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013; 22(9):1199–1208.
Article81. Boileau P, Gonzalez JF, Chuinard C, Bicknell R, Walch G. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty after failed rotator cuff surgery. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009; 18(4):600–606.
Article82. Mulieri P, Dunning P, Klein S, Pupello D, Frankle M. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of irreparable rotator cuff tear without glenohumeral arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92(15):2544–2556.
Article83. Zumstein MA, Pinedo M, Old J, Boileau P. Problems, complications, reoperations, and revisions in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: a systematic review. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011; 20(1):146–157.
Article84. Oh JH, Kim SH, Shin SH, et al. Outcome of rotator cuff repair in large-to-massive tear with pseudoparalysis: a comparative study with propensity score matching. Am J Sports Med. 2011; 39(7):1413–1420.
Article85. Denard PJ, Ladermann A, Jiwani AZ, Burkhart SS. Functional outcome after arthroscopic repair of massive rotator cuff tears in individuals with pseudoparalysis. Arthroscopy. 2012; 28(9):1214–1219.
Article86. Denard PJ, Ladermann A, Brady PC, et al. Pseudoparalysis from a massive rotator cuff tear is reliably reversed with an arthroscopic rotator cuff repair in patients without preoperative glenohumeral arthritis. Am J Sports Med. 2015; 43(10):2373–2378.
Article87. Miyazaki AN, Fregoneze M, Santos PD, et al. Functional evaluation of arthroscopic repair of rotator cuff injuries in patients with pseudoparalysis. Rev Bras Ortop. 2014; 49(2):178–182.
Article88. Werner CM, Steinmann PA, Gilbart M, Gerber C. Treatment of painful pseudoparesis due to irreparable rotator cuff dysfunction with the Delta III reverse-ball-and-socket total shoulder prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87(7):1476–1486.
Article89. Vourazeris JD, Wright TW, Struk AM, King JJ, Farmer KW. Primary reverse total shoulder arthroplasty outcomes in patients with subscapularis repair versus tenotomy. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017; 26(3):450–457.
Article90. Friedman RJ, Flurin PH, Wright TW, Zuckerman JD, Roche CP. Comparison of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty outcomes with and without subscapularis repair. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017; 26(4):662–668.
Article91. Werner BC, Wong AC, Mahony GT, et al. Clinical outcomes after reverse shoulder arthroplasty with and without subscapularis repair: the importance of considering glenosphere lateralization. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2018; 26(5):e114–e119.92. Rhee YG, Cho NS, Moon SC. Effects of humeral component retroversion on functional outcomes in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for cuff tear arthropathy. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015; 24(10):1574–1581.
Article93. Cabezas AF, Krebes K, Hussey MM, et al. Morphologic variability of the shoulder between the populations of North American and East Asian. Clin Orthop Surg. 2016; 8(3):280–287.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Concepts and Recent Trends in Arthroscopic Treatment of Large to Massive Rotator Cuff Tears: A Review
- Arthroscopic supraspinatus advancement for retracted rotator cuff tears: a technical note
- Tendon Transfer for Irreparable Massive Rotator Cuff Tear
- The best options in superior capsular reconstruction
- Treatment of Massive Rotator Cuff Tears: Focusing on Arthroscopic Approach