J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2018 Apr;44(2):86-90. 10.5125/jkaoms.2018.44.2.86.
Modified two flap palatoplasty in asymptomatic transsphenoidal encephalocele: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Richardsons Dental and Craniofacial Hospital, Nagercoil, India. sunilrichardson145@gmail.com
- 2Department of Surgery, Azeezia Medical College, Kollam, India.
- 3Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Private Practitioner, Krishnagiri, India.
- KMID: 2410585
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2018.44.2.86
Abstract
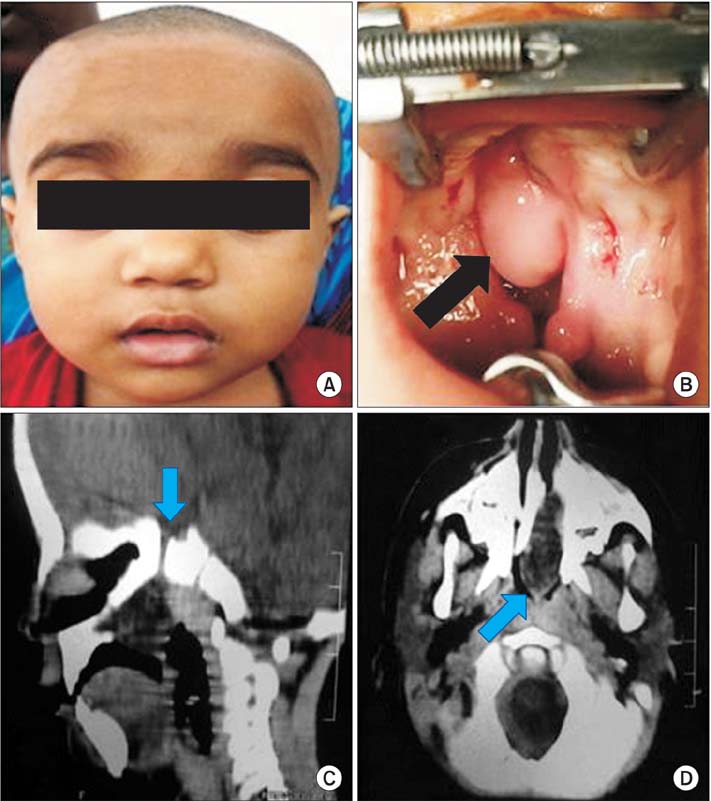
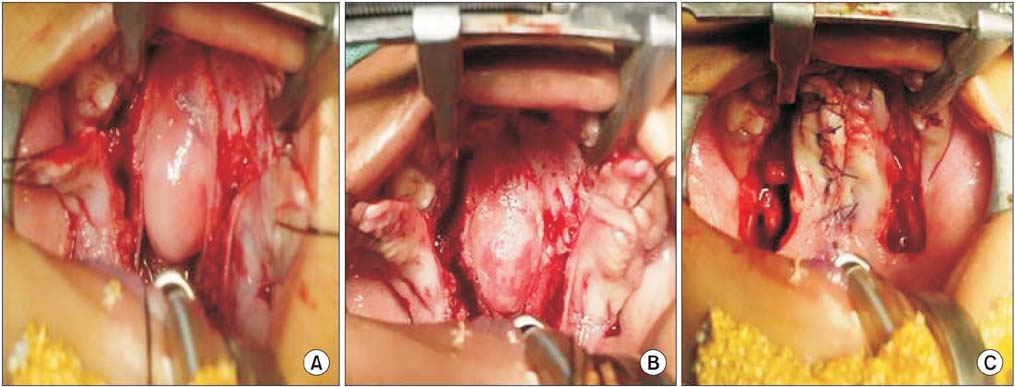
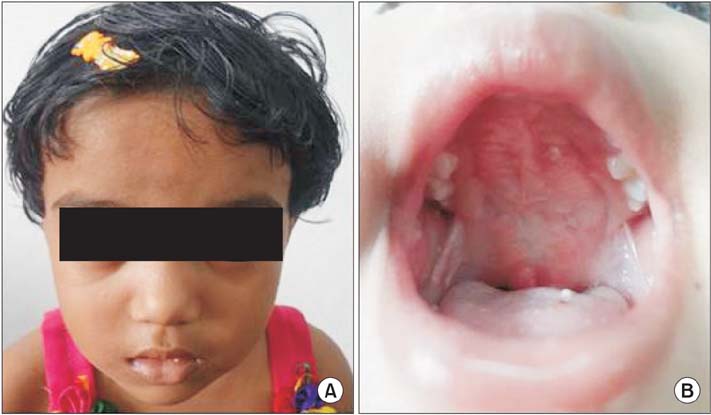
- About one-third of patients with transsphenoidal basal encephaloceles have associated congenital anomalies, including cleft palate. Moreover, they are often plagued by symptomatic exacerbations in the form of upper respiratory obstructions, cerebrospinal fluid leaks, meningitis, etc., with few patients being asymptomatic. We herein present a rare asymptomatic case of transsphenoidal basal encephalocele in an 18-month-old child with cleft palate and highlight a modified version of two-flap palatoplasty.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Siffel C, Wong LY, Olney RS, Correa A. Survival of infants diagnosed with encephalocele in Atlanta, 1979-98. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2003; 17:40–48.
Article2. McLone DG. Congenital malformations of the central nervous system. Clin Neurosurg. 2000; 47:346–377.3. Hashemi B, Kazemei T, Bayat A. Large sphenoethmoidal encephalocele associated with agenesis of corpus callosum and cleft palate. Iran J Med Sci. 2010; 35:154–156.4. Teng E, Heller J, Lazareff J, Kawamoto H, Wasson K, Garri JI, et al. Caution in treating transsphenoidal encephalocele with concomitant Moyamoya disease. J Craniofac Surg. 2006; 17:1004–1009.
Article5. Modesti LM, Glasauer FE, Terplan KL. Sphenoethmoidal encephalocele: a case report with review of literature. Childs Brain. 1977; 3:140–153.6. Rathore YS, Sinha S, Mahapatra AK. Transsellar transsphenoidal encephalocele: a series of four cases. Neurol India. 2011; 59:289–292.
Article7. Mahapatra AK. Anterior encephaloceles. Indian J Pediatr. 1997; 64:699–704.
Article8. Raman Sharma R, Mahapatra AK, Pawar SJ, Thomas C, Al-Ismaily M. Trans-sellar trans-sphenoidal encephaloceles: report of two cases. J Clin Neurosci. 2002; 9:89–92.
Article9. Morioka M, Marubayashi T, Masumitsu T, Miura M, Ushio Y. Basal encephaloceles with morning glory syndrome, and progressive hormonal and visual disturbances: case report and review of literature. Brain Dev. 1995; 17:196–201.
Article10. Acherman DS, Bosman DK, van der Horst CM. Sphenoethmoidal encephalocele: a case report. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2003; 40:329–333.
Article11. Macfarlane R, Rutka JT, Armstrong D, Phillips J, Posnick J, Forte V, et al. Encephaloceles of the anterior cranial fossa. Pediatr Neurosurg. 1995; 23:148–158.
Article12. Bano S, Chaudhary V, Yadav SN, Garga UC. Occult spontaneous lateral intrasphenoidal encephalocele: a rare presentation. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2013; 4:Suppl 1. S109–S111.
Article13. Waseem M, Upadhyay R, Al-Husayni H, Agyare S. Intrasphenoidal encephalocele: an incidental finding in emergency department. Int J Emerg Med. 2013; 6:45.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Repair of Complete Cleft Palate by Modified 2-Flap Palatoplasty
- A case of Spontaneous Transsphenoidal Encephalocele with Recurrent Bacterial Meningitis
- Columellar Flap for Transsphenoidal Approach
- Comparison of Two-Flap Palatoplasty and Pushback Palatoplasty: Complication Rates
- 2-Flap Palatoplasty for Troublesome Cleft Palate