J Rheum Dis.
2018 Jan;25(1):47-57. 10.4078/jrd.2018.25.1.47.
Prevalence and Associated Factors for Non-adherence in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Hanyang University Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Seoul, Korea. sungyk@hanyang.ac.kr, scbae@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Clinical Research Center for Rheumatoid Arthritis (CRCRA), Seoul, Korea.
- 3Kyung Hee University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Guri, Korea.
- 5Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 7Dong-A University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 8Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 9Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 10Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- 11Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2405020
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2018.25.1.47
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To estimate the prevalence of non-adherence to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) medication and identify the associated factors for non-adherence in RA patients.
METHODS
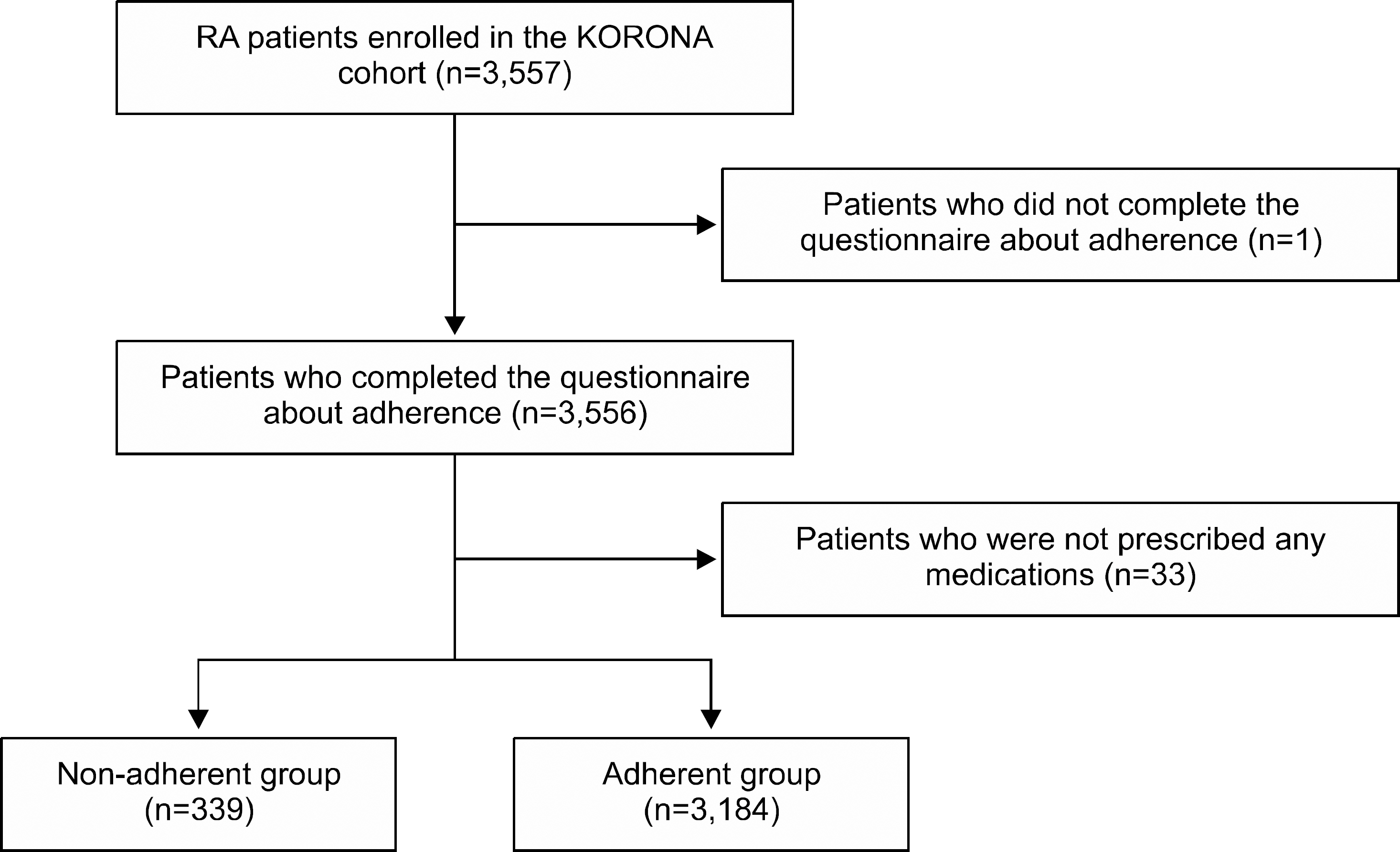
Among the KORean Observational study Network for Arthritis 3,523 patients who completed a questionnaire about the adherence to RA medication were analyzed. The patients were divided into two groups: 1) adherent group, patients who skipped medication ≤5 days within the past 2 months; and 2) non-adherent group, patients who skipped ≥6 days of medication. The baseline characteristics were compared, and multivariable regression analysis was performed to identify the associated factors for non-adherence.
RESULTS
The non-adherent group had 339 patients (9.6%). The common causes of non-adherence were forgetfulness (45.8%), absence of RA symptoms (24.7%), and discomfort with RA medication (13.1%). Younger age (odds ratio [OR] 1.02, p < 0.01) and higher income (OR 1.70, p < 0.01) were associated with an increased risk of non-adherence. Whereas higher functional disability (OR 0.68, p < 0.01) and oral corticosteroid use (OR 0.73, p=0.02) were associated with a decreased risk of non-adherence. The associated factors differed according to cause of non-adherence. Having adverse events (OR 2.65, p=0.02) was associated with the risk of non-adherence due to discomfort with RA medication while a higher level of education (OR 2.37, p=0.03) was associated with the risk of non-adherence due to an absence of RA symptoms.
CONCLUSION
The 9.6% of Korean RA patients were non-adherent to RA medication. The associated factors differed according to the cause of non-adherence. Therefore, an individualized approach will be needed to improve the adherence to RA medication.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of Drug Adherence on Treatment Outcome in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Yoon-Jeong Oh, Bumhee Park, Ki Won Moon
J Rheum Dis. 2019;26(4):264-272. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2019.26.4.264.
Reference
-
1. Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003; 423:356–61.
Article2. Singh JA, Furst DE, Bharat A, Curtis JR, Kavanaugh AF, Kremer JM, et al. 2012 update of the 2008 American College of Rheumatology recommendations for the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologic agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012; 64:625–39.
Article3. Kuriya B, Xiong J, Boire G, Haraoui B, Hitchon C, Pope J, et al. Earlier time to remission predicts sustained clinical remission in early rheumatoid arthritis–results from the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort (CATCH). J Rheumatol. 2014; 41:2161–6.4. Treharne GJ, Douglas KM, Iwaszko J, Panoulas VF, Hale ED, Mitton DL, et al. Polypharmacy among people with rheumatoid arthritis: the role of age, disease duration and comorbidity. Musculoskeletal Care. 2007; 5:175–90.
Article5. Contreras-Yáñez I, Ponce De León S, Cabiedes J, Rull-Gabayet M, Pascual-Ramos V. Inadequate therapy behavior is associated to disease flares in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who have achieved remission with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Am J Med Sci. 2010; 340:282–90.
Article6. Osterberg L, Blaschke T. Adherence to medication. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:487–97.
Article7. Horne R. Compliance, adherence, and concordance: implications for asthma treatment. Chest. 2006; 130(1 Suppl):65S–72S.8. Cramer JA, Roy A, Burrell A, Fairchild CJ, Fuldeore MJ, Ollendorf DA, et al. Medication compliance and persistence: terminology and definitions. Value Health. 2008; 11:44–7.
Article9. Salt E, Frazier SK. Adherence to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a narrative review of the literature. Orthop Nurs. 2010; 29:260–75.10. van den Bemt BJ, van den Hoogen FH, Benraad B, Hekster YA, van Riel PL, van Lankveld W. Adherence rates and associations with nonadherence in patients with rheumatoid arthritis using disease modifying antirheumatic drugs. J Rheumatol. 2009; 36:2164–70.
Article11. Waimann CA, Marengo MF, de Achaval S, Cox VL, Garcia-Gonzalez A, Reveille JD, et al. Electronic monitoring of oral therapies in ethnically diverse and economically dis-advantaged patients with rheumatoid arthritis: consequences of low adherence. Arthritis Rheum. 2013; 65:1421–9.
Article12. Cannon GW, Mikuls TR, Hayden CL, Ying J, Curtis JR, Reimold AM, et al. Merging Veterans Affairs rheumatoid arthritis registry and pharmacy data to assess methotrexate adherence and disease activity in clinical practice. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011; 63:1680–90.
Article13. Curtis JR, Bharat A, Chen L, Greenberg JD, Harrold L, Kremer JM, et al. Agreement between rheumatologist and patient-reported adherence to methotrexate in a US rheumatoid arthritis registry. J Rheumatol. 2016; 43:1027–9.
Article14. Park DC, Hertzog C, Leventhal H, Morrell RW, Leventhal E, Birchmore D, et al. Medication adherence in rheumatoid arthritis patients: older is wiser. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1999; 47:172–83.
Article15. Brus H, van de Laar M, Taal E, Rasker J, Wiegman O. Determinants of compliance with medication in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the importance of self-efficacy expectations. Patient Educ Couns. 1999; 36:57–64.
Article16. Treharne GJ, Lyons AC, Kitas GD. Medication adherence in rheumatoid arthritis: effects of psychosocial factors. Psychol Health Med. 2004; 9:337–49.
Article17. Viller F, Guillemin F, Briançon S, Moum T, Suurmeijer T, van den Heuvel W. Compliance to drug treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a 3 year longitudinal study. J Rheumatol. 1999; 26:2114–22.18. van den Bemt BJ, Zwikker HE, van den Ende CH. Medication adherence in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a critical appraisal of the existing literature. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2012; 8:337–51.
Article19. Sung YK, Cho SK, Choi CB, Park SY, Shim J, Ahn JK, et al. Korean Observational Study Network for Arthritis (KORONA): establishment of a prospective multicenter cohort for rheumatoid arthritis in South Korea. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012; 41:745–51.
Article20. Zwikker HE, van Dulmen S, den Broeder AA, van den Bemt BJ, van den Ende CH. Perceived need to take medication is associated with medication non-adherence in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2014; 8:1635–45.
Article21. DiBenedetti DB, Zhou X, Reynolds M, Ogale S, Best JH. Assessing methotrexate adherence in rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional survey. Rheumatol Ther. 2015; 2:73–84.
Article22. Pasma A, Schenk CV, Timman R, Busschbach JJ, van den Bemt BJ, Molenaar E, et al. Non-adherence to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs is associated with higher disease activity in early arthritis patients in the first year of the disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015; 17:281.
Article23. Kumar K, Raza K, Nightingale P, Horne R, Chapman S, Greenfield S, et al. Determinants of adherence to disease modifying antirheumatic drugs in White British and South Asian patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a cross sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015; 16:396.
Article24. De Cuyper E, De Gucht V, Maes S, Van Camp Y, De Clerck LS. Determinants of methotrexate adherence in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2016; 35:1335–9.
Article25. Brandstetter S, Riedelbeck G, Steinmann M, Loss J, Ehrenstein B, Apfelbacher C. Depression moderates the associations between beliefs about medicines and medication adherence in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Cross-sectional study. J Health Psychol. 2016 May 1; [Epub].DOI: DOI: 10.1177/1359105316646440.
Article26. Xia Y, Yin R, Fu T, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Guo G, et al. Treatment adherence to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2016; 10:735–42.27. Michetti P, Weinman J, Mrowietz U, Smolen J, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Louis E, et al. Impact of treatment-related beliefs on medication adherence in immunemediated inflammatory diseases: results of the global ALIGN study. Adv Ther. 2017; 34:91–108.
Article28. Pasma A, Schenk C, Timman R, van't Spijker A, Appels C, van der Laan WH, et al. Does non-adherence to DMARDs influence hospital-related healthcare costs for early arthritis in the first year of treatment? PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0171070.
Article29. Wabe N, Lee A, Wechalekar M, McWilliams L, Proudman S, Wiese M. Adherence to combination DMARD therapy and treatment outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis: a longitudinal study of new and existing DMARD users. Rheumatol Int. 2017; 37:897–904.
Article30. Koneru S, Shishov M, Ware A, Farhey Y, Mongey AB, Graham TB, et al. Effectively measuring adherence to medications for systemic lupus erythematosus in a clinical setting. Arthritis Rheum. 2007; 57:1000–6.
Article31. Rapoff MA, Belmont JM, Lindsley CB, Olson NY. Electronically monitored adherence to medications by newly diagnosed patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 53:905–10.
Article32. Tuncay R, Eksioglu E, Cakir B, Gurcay E, Cakci A. Factors affecting drug treatment compliance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2007; 27:743–6.
Article33. Welsing PM, van Gestel AM, Swinkels HL, Kiemeney LA, van Riel PL. The relationship between disease activity, joint destruction, and functional capacity over the course of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001; 44:2009–17.
Article34. Choi SC, Ingale SL, Kim JS, Park YK, Kwon IK, Chae BJ. An antimicrobial peptide-A3: effects on growth performance, nutrient retention, intestinal and faecal microflora and intestinal morphology of broilers. Br Poult Sci. 2013; 54:738–46.
Article35. Wawruch M, Zatko D, Wimmer G Jr, Luha J, Hricak V Jr, Murin J, et al. Patient-related characteristics associated with non-persistence with statin therapy in elderly patients following an ischemic stroke. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2017; 26:201–7.
Article