Korean J Radiol.
2018 Apr;19(2):301-310. 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.2.301.
The Incidence of Various Types of Systemic Reactions Related to Epidural Steroid Injections: A Prospective Observational Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam 13620, Korea. joonwoo2@gmail.com
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam 13620, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam 13620, Korea.
- 4Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam 13620, Korea.
- 5Department of Radiology, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul 06973, Korea.
- KMID: 2404927
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.2.301
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the incidence, types and association of systemic reactions after an epidural steroid injection (ESI) with patient demographics, ESI factors and repeated occurrence of an ESI.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
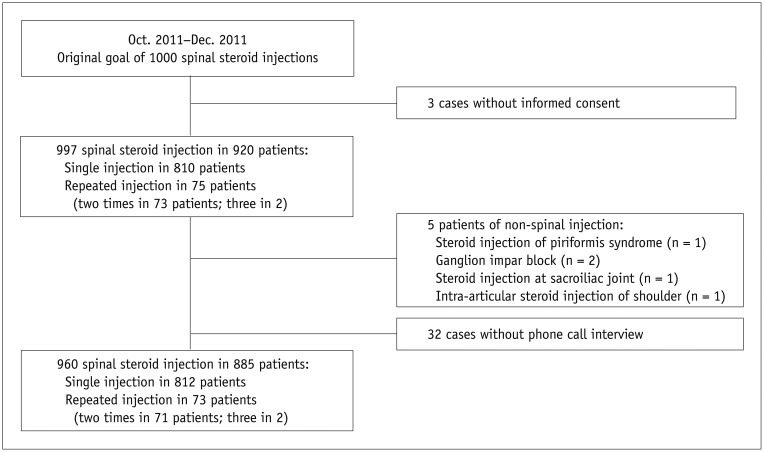
This prospective observational study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of our hospital, and written informed consent was obtained from all the participants. From October to December 2011, systemic reactions at 2 weeks after 960 ESIs among 885 patients were measured. Patients were evaluated by phone interviews to obtain the patients' demographics, history of previous ESI, ESI factors, and ESI reoccurrence. Statistical analyses were performed using the chi-square tests, Fisher's exact tests and a binary logistic regression analysis.
RESULTS
Overall, 557 types of systemic reactions occurred after 292 injections (30.4%) of a total of 960 ESIs in which facial flushing was most common (131/557, 23.5%) and 144 ESIs were followed by a mixed form of systemic reactions (49.3%). Age of 62 years or younger (odds ratio [OR], 2.361), female sex (OR, 1.674), and history of diabetes mellitus (OR, 1.681) were significant risk factors in the occurrence of systemic reactions after an ESI. In 73 patients with repeated ESI, 14 patients re-experienced systemic reactions (19.2%), of which twelve re-experienced the same systemic reaction as the previous one.
CONCLUSION
Systemic reactions followed about 30% of ESIs, and more commonly occurred in patients 62 years of age or younger, women, and diabetic patients. Half of the patients experienced a mixed form of systemic reactions. Patients with recurring systemic reactions tend to re-experience the same systemic reaction as the prior one after an ESI.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Systemic effects of fluoroscopically guided epidural steroid injection with dexamethasone
Woo Young Kang, Joon Woo Lee, Eugene Lee, Yusuhn Kang, Joong Mo Ahn, Heung Sik Kang
Korean J Pain. 2019;32(3):178-186. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2019.32.3.178.
Reference
-
1. Deyo RA, Mirza SK, Turner JA, Martin BI. Overtreating chronic back pain: time to back off? J Am Board Fam Med. 2009; 22:62–68. PMID: 19124635.
Article2. Manchikanti L, Pampati V, Falco FJ, Hirsch JA. Growth of spinal interventional pain management techniques: analysis of utilization trends and Medicare expenditures 2000 to 2008. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38:157–168. PMID: 22781007.3. Manchikanti L, Singh V, Pampati V, Smith HS, Hirsch JA. Analysis of growth of interventional techniques in managing chronic pain in the Medicare population: a 10-year evaluation from 1997 to 2006. Pain Physician. 2009; 12:9–34. PMID: 19165296.4. Buenaventura RM, Datta S, Abdi S, Smith HS. Systematic review of therapeutic lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injections. Pain Physician. 2009; 12:233–251. PMID: 19165306.5. Conn A, Buenaventura RM, Datta S, Abdi S, Diwan S. Systematic review of caudal epidural injections in the management of chronic low back pain. Pain Physician. 2009; 12:109–135. PMID: 19165299.6. Abdi S, Datta S, Trescot AM, Schultz DM, Adlaka R, Atluri SL, et al. Epidural steroids in the management of chronic spinal pain: a systematic review. Pain Physician. 2007; 10:185–212. PMID: 17256030.7. Boswell MV, Colson JD, Sehgal N, Dunbar EE, Epter R. A systematic review of therapeutic facet joint interventions in chronic spinal pain. Pain Physician. 2007; 10:229–253. PMID: 17256032.8. Waldman SD. Complications of cervical epidural nerve blocks with steroids: a prospective study of 790 consecutive blocks. Reg Anesth. 1989; 14:149–151. PMID: 2486595.9. Slipman CW, Meyers JS, Chou LH, Sterenfeld EB, Abrams S. Complications of fluoroscopically guided spinal injections (abstract). Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1995; 76:1032.10. Huston CW, Slipman CW, Meyers JS, Yang ST, Anghel BN. Side effects and complications of fluoroscopically guided nerve root injections (abstract). Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1996; 77:937.11. Botwin KP, Gruber RD, Bouchlas CG, Torres-Ramos FM, Freeman TL, Slaten WK. Complications of fluoroscopically guided transforaminal lumbar epidural injections. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2000; 81:1045–1050. PMID: 10943753.
Article12. Botwin KP, Gruber RD, Bouchlas CG, Torres-Ramos FM, Hanna A, Rittenberg J, et al. Complications of fluoroscopically guided caudal epidural injections. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2001; 80:416–424. PMID: 11399002.
Article13. Botwin KP, Castellanos R, Rao S, Hanna AF, Torres-Ramos FM, Gruber RD, et al. Complications of fluoroscopically guided interlaminar cervical epidural injections. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2003; 84:627–633. PMID: 12736872.
Article14. Derby R, Lee SH, Kim BJ, Chen Y, Seo KS. Complications following cervical epidural steroid injections by expert interventionalists in 2003. Pain Physician. 2004; 7:445–449. PMID: 16858486.15. Huston CW, Slipman CW, Garvin C. Complications and side effects of cervical and lumbosacral selective nerve root injections. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005; 86:277–283. PMID: 15706554.
Article16. Pobiel RS, Schellhas KP, Eklund JA, Golden MJ, Johnson BA, Chopra S, et al. Selective cervical nerve root blockade: prospective study of immediate and longer term complications. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 30:507–511. PMID: 19193762.
Article17. Karaman H, Kavak GO, Tüfek A, Yldrm ZB. The complications of transforaminal lumbar epidural steroid injections. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36:E819–E824. PMID: 21217425.
Article18. McGrath JM, Schaefer MP, Malkamaki DM. Incidence and characteristics of complications from epidural steroid injections. Pain Med. 2011; 12:726–731. PMID: 21392252.
Article19. Manchikanti L, Malla Y, Wargo BW, Cash KA, Pampati V, Fellows B. Complications of fluoroscopically directed facet joint nerve blocks: a prospective evaluation of 7,500 episodes with 43,000 nerve blocks. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:E143–E150. PMID: 22430660.20. Manchikanti L, Malla Y, Wargo BW, Cash KA, Pampati V, Fellows B. A prospective evaluation of complications of 10,000 fluoroscopically directed epidural injections. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:131–140. PMID: 22430650.21. von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gotzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Ann Intern Med. 2007; 147:573–577. PMID: 17938396.
Article22. Simopoulos TT, Kraemer JJ, Glazer P, Bajwa ZH. Vertebral osteomyelitis: a potentially catastrophic outcome after lumbar epidural steroid injection. Pain Physician. 2008; 11:693–697. PMID: 18850035.23. Ain RJ, Vance MB. Epidural hematoma after epidural steroid injection in a patient withholding enoxaparin per guidelines. Anesthesiology. 2005; 102:701–703.
Article24. Xu R, Bydon M, Gokaslan ZL, Wolinsky JP, Witham TF, Bydon A. Epidural steroid injection resulting in epidural hematoma in a patient despite strict adherence to anticoagulation guidelines. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009; 11:358–364. PMID: 19769520.
Article25. MacLean CA, Bachman DT. Documented arterial gas embolism after spinal epidural injection. Ann Emerg Med. 2001; 38:592–595. PMID: 11679875.
Article26. Ludwig MA, Burns SP. Spinal cord infarction following cervical transforaminal epidural injection: a case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:E266–E268. PMID: 15897816.27. Muro K, O'Shaughnessy B, Ganju A. Infarction of the cervical spinal cord following multilevel transforaminal epidural steroid injection: case report and review of the literature. J Spinal Cord Med. 2007; 30:385–388. PMID: 17853663.
Article28. Suresh S, Berman J, Connell DA. Cerebellar and brainstem infarction as a complication of CT-guided transforaminal cervical nerve root block. Skeletal Radiol. 2007; 36:449–452. PMID: 17216270.
Article29. Lyders EM, Morris PP. A case of spinal cord infarction following lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injection: MR imaging and angiographic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 30:1691–1693. PMID: 19369604.
Article30. Popescu A, Lai D, Lu A, Gardner K. Stroke following epidural injections--case report and review of literature. J Neuroimaging. 2013; 23:118–121. PMID: 21699610.
Article31. Kushner FH, Olson JC. Retinal hemorrhage as a consequence of epidural steroid injection. Arch Ophthalmol. 1995; 113:309–313. PMID: 7887844.
Article32. Young WF. Transient blindness after lumbar epidural steroid injection: a case report and literature review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27:E476–E477. PMID: 12439000.33. Browning DJ. Acute retinal necrosis following epidural steroid injections. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003; 136:192–194. PMID: 12834695.
Article34. Bhat AL, Chow DW, DePalma MJ, Garvan C, Chou L, Lenrow D, et al. Incidence of vocal cord dysfunction after fluoroscopically guided steroid injections in the axial skeleton. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005; 86:1330–1332. PMID: 16003659.
Article35. Everett CR, Baskin MN, Speech D, Novoseletsky D, Patel R. Flushing as a side effect following lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injection. Pain Physician. 2004; 7:427–429. PMID: 16858483.36. Abbasi A, Roque-Dang CM, Malhotra G. Persistent hiccups after interventional pain procedures: a case series and review. PM R. 2012; 4:144–151. PMID: 22373464.
Article37. Benyamin RM, Vallejo R, Kramer J, Rafeyan R. Corticosteroid induced psychosis in the pain management setting. Pain Physician. 2008; 11:917–920. PMID: 19057637.38. Sandberg DI, Lavyne MH. Symptomatic spinal epidural lipomatosis after local epidural corticosteroid injections: case report. Neurosurgery. 1999; 45:162–165. PMID: 10414580.
Article39. Goodman BS, Bayazitoglu M, Mallempati S, Noble BR, Geffen JF. Dural puncture and subdural injection: a complication of lumbar transforaminal epidural injections. Pain Physician. 2007; 10:697–705. PMID: 17876368.40. Candido KD, Katz JA, Chinthagada M, McCarthy RA, Knezevic NN. Incidence of intradiscal injection during lumbar fluoroscopically guided transforaminal and interlaminar epidural steroid injections. Anesth Analg. 2010; 110:1464–1467. PMID: 20418306.
Article41. Zufferey P, Bulliard C, Gremion G, Saugy M, So A. Systemic effects of epidural methylprednisolone injection on glucose tolerance in diabetic patients. BMC Res Notes. 2011; 4:552. PMID: 22185681.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of incidence of intravascular injections during transforaminal epidural steroid injection using different needle types
- Systemic effects of fluoroscopically guided epidural steroid injection with dexamethasone
- Persistent Hiccup after Epidural Steroid Injection: Case reports
- Clinical Analysis on the Efficacy of Epidural Injections in Low Back Pain Patient
- Hyperprolactinemia and Galactorrhea Following Single Epidural Steroid Injection