Kosin Med J.
2017 Dec;32(2):233-239. 10.7180/kmj.2017.32.2.233.
IgG4-Related Disease with lymphadenopathy Presenting as a Cervical lymph node enlargement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Konyang University, Daejeon, Korea. dycho@kyuh.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Konyang University, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2400267
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2017.32.2.233
Abstract
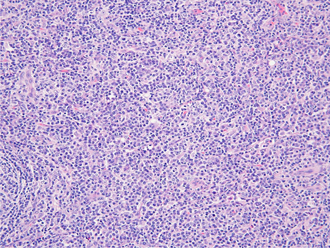
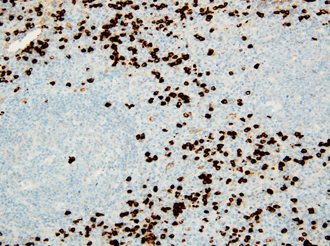
- During the course of evaluation and management of neck masses, consideration for Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) should be given. IgG4-RD is relatively a new growing entity of immune-mediated origin, characterized by a mass-forming lesion, the infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells and occasionally elevated serum IgG4. The most common manifestations are parotid and lacrimal swelling, lymphadenopathy and autoimmune pancreatitis. A previously healthy 72-year-old man was referred to our clinic with a 2-month history of left cervical lymph node enlargement without systemic manifestations . A cervical lymph node biopsy was planned because of elevated serum IgG4 levels. Pathological findings showed prominent infiltration of IgG4-postive plasma cells in the lymph node. After steroid therapy, a computed tomography scan revealed a decrease in the cervical lymph node size. This case illustrates the importance of including IgG4-RD in the differential diagnosis of a cervical lymph node enlargement.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Habermann TM, Steensma DP. Lymphadenopathy. Mayo Clin Proc. 2000; 75:723–732.
Article2. Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease. Lancet. 2015; 385:1460–1471.
Article3. Khosroshahi A, Stone JH. Treatment approaches to IgG4-related systemic disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011; 23:67–71.
Article4. Nizar AH, Toubi E. IgG4-related disease: case report and literature review. Auto Immun Highlights. 2015; 6:7–15.
Article5. Zen Y, Nakanuma Y. IgG4-related disease: a cross-sectional study of 114 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010; 34:1812–1819.6. Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M, Yamamoto M, Saeki T, et al. A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details. Mod Rheumatol. 2012; 22:1–14.
Article7. Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:539–551.
Article8. Ghably JG, Borthwick T, O'Neil TJ, Youngberg GA, Datta AA, Krishnaswamy G. IgG4-related disease: a primer on diagnosis and management. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015; 114:447–454.
Article9. Cornell LD. IgG4-related kidney disease. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2012; 29:245–250.
Article10. Shimosegawa T, Chari ST, Frulloni L, Kamisawa T, Kawa S, Mino-kenudson M, et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis: guidelines of the International Association of Pancreatology. Pancreas. 2011; 40:352–358.
Article11. Khosroshahi A, Bloch DB, Deshpande V, Stone JH. Rituximab therapy leads to rapid decline of serum IgG4 levels and prompt clinical improvement in IgG4-related systemic disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62:1755–1762.
Article12. Cheuk W, Chan JK. Lymphadenopathy of IgG4-related disease: an underdiagnosed and overdiagnosed entity. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2012; 29:226–234.
Article13. Kamisawa T, Nakajima H, Egawa N, Funata N, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A. IgG4-related sclerosing disease incorporating sclerosing pancreatitis, cholangitis, sialadenitis and retroperitoneal fibrosis with lymphadenopathy. Pancreatology. 2006; 6:132–137.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mikulicz's Disease with Progressively Transformed Germinal Centers-type Immunoglobulin G4-related Lymphadenopathy Mimicking Sjogren's Syndrome
- Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Cervical Lymph Nodes
- MRI Findings of Cervical Lymphadenopathy: Preliminary Study
- A Case of Rosai-Dorfman Disease Presented with Neck Mass
- CD68 Positive Histiocytic Necrotizing Lymphadenitis