Ann Dermatol.
2018 Feb;30(1):100-101. 10.5021/ad.2018.30.1.100.
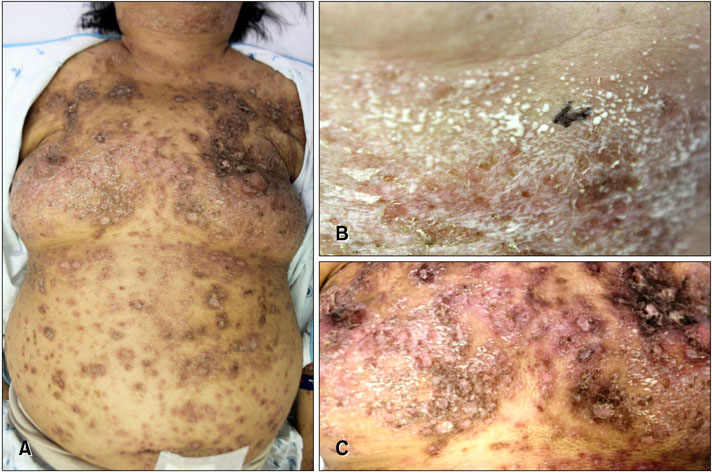
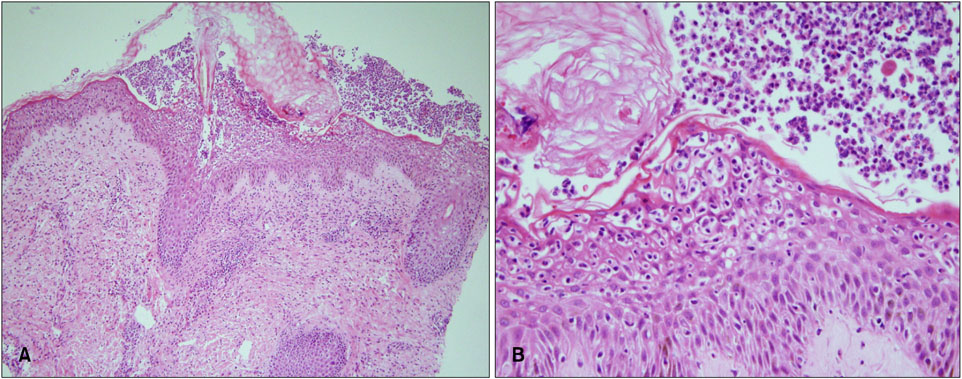
A Case of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis after Injection of an Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agent
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. nmcderma@daum.net
- 2Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2399766
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2018.30.1.100
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Del Vecchio L, Locatelli F. An overview on safety issues related to erythropoiesis-stimulating agents for the treatment of anaemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2016; 15:1021–1030.
Article2. Halevy S. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 9:322–328.
Article3. Schmutz JL, Barbaud A, Trechot P. Epoetin alpha-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis and desensitisation. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2010; 137:761–762.4. Hamdi NM, Al-Hababi FH, Eid AE. HLA class I and class II associations with ESRD in Saudi Arabian population. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e111403.
Article5. Casadevall N, Rossert J. Importance of biologic follow-ons: experience with EPO. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2005; 18:381–387.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis with Hemodynamic Instability Induced by Ingestion of Lacquer Chicken
- A Case of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Possibly Induced by Ritodrine
- Two Cases of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis
- Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Caused by Diltiazem
- Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis