Ann Dermatol.
2018 Feb;30(1):13-19. 10.5021/ad.2018.30.1.13.
Mortality and Comorbidity Profiles of Patients with Bullous Pemphigoid in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. jbmlee@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2399749
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2018.30.1.13
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is a common autoimmune-mediated blistering skin disease that is significantly associated with mortality and morbidity. However, few studies regarding the mortality and comorbidity profiles of BP have been reported in Korea.
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate and compare the mortality, comorbidity profiles, and risk factors between patients with BP who visited our clinic and an age-matched general population of Korea.
METHODS
We retrospectively evaluated 103 patients diagnosed with BP between 2006 and 2013 at Chonnam National University Hospital in Gwangju, Korea.
RESULTS
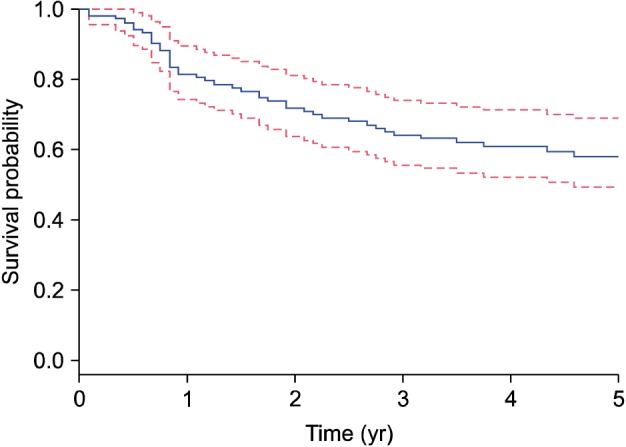
The 1-year, 2-year, and 5-year mortality rates of the patients were 18.44%, 28.16%, and 42.00%, respectively. The median age was 76 years (range, 41~96 years). The standardized mortality ratio of patients with BP was 1.83 times that of the age- and sex-matched general population of Korea. Old age at the time of diagnosis, cardiac disease and renal disease were associated with increased 5-year mortality. In addition, the prevalence of diabetes, stroke, dementia, and Parkinson's disease was higher among BP patients than in the general population.
CONCLUSION
The mortality rate of patients with BP is higher than that of the general Korean population. Korean patients with BP are more likely to have dementia, Parkinson's disease, diabetes, and stroke. Risk factors for increased 5-year mortality include old age at the time of diagnosis and medical comorbidities, especially cardiac disease and renal disease.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
2. Di Zenzo G, Marazza G, Borradori L. Bullous pemphigoid: physiopathology, clinical features and management. Adv Dermatol. 2007; 23:257–288. PMID: 18159905.
Article3. Ahmed AR, Maize JC, Provost TT. Bullous pemphigoid. Clinical and immunologic follow-up after successful therapy. Arch Dermatol. 1977; 113:1043–1046. PMID: 329769.
Article4. Bernard P, Enginger V, Venot J, Bedane C, Bonnetblanc JM. Survival prognosis in pemphigoid. A cohort analysis of 78 patients. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1995; 122:751–757. PMID: 8729818.5. Bernard P, Vaillant L, Labeille B, Bedane C, Arbeille B, Denoeux JP, et al. Incidence and distribution of subepidermal autoimmune bullous skin diseases in three French regions. Bullous Diseases French Study Group. Arch Dermatol. 1995; 131:48–52. PMID: 7826096.
Article6. Bernard P, Bedane C, Bonnetblanc JM. Anti-BP180 autoantibodies as a marker of poor prognosis in bullous pemphigoid: a cohort analysis of 94 elderly patients. Br J Dermatol. 1997; 136:694–698. PMID: 9205501.
Article7. Roujeau JC, Lok C, Bastuji-Garin S, Mhalla S, Enginger V, Bernard P. High risk of death in elderly patients with extensive bullous pemphigoid. Arch Dermatol. 1998; 134:465–469. PMID: 9554299.
Article8. Joly P, Roujeau JC, Benichou J, Picard C, Dreno B, Delaporte E, et al. A comparison of oral and topical corticosteroids in patients with bullous pemphigoid. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:321–327. PMID: 11821508.
Article9. Rzany B, Partscht K, Jung M, Kippes W, Mecking D, Baima B, et al. Risk factors for lethal outcome in patients with bullous pemphigoid: low serum albumin level, high dosage of glucocorticosteroids, and old age. Arch Dermatol. 2002; 138:903–908. PMID: 12071817.
Article10. Colbert RL, Allen DM, Eastwood D, Fairley JA. Mortality rate of bullous pemphigoid in a US medical center. J Invest Dermatol. 2004; 122:1091–1095. PMID: 15140208.
Article11. Bystryn JC, Rudolph JL. Why is the mortality of bullous pemphigoid greater in Europe than in the US? J Invest Dermatol. 2005; 124:xx–xxi. PMID: 15737186.
Article12. Garcia-Doval I, Conde Taboada A, Cruces Prado MJ. Sepsis associated with dermatologic hospitalization is not the cause of high mortality of bullous pemphigoid in Europe. J Invest Dermatol. 2005; 124:666–667. PMID: 15737212.13. Gudi VS, White MI, Cruickshank N, Herriot R, Edwards SL, Nimmo F, et al. Annual incidence and mortality of bullous pemphigoid in the Grampian Region of North-east Scotland. Br J Dermatol. 2005; 153:424–427. PMID: 16086760.
Article14. Joly P, Benichou J, Lok C, Hellot MF, Saiag P, Tancrede-Bohin E, et al. Prediction of survival for patients with bullous pemphigoid: a prospective study. Arch Dermatol. 2005; 141:691–698. PMID: 15967914.
Article15. Langan SM, Smeeth L, Hubbard R, Fleming KM, Smith CJ, West J. Bullous pemphigoid and pemphigus vulgaris--incidence and mortality in the UK: population based cohort study. BMJ. 2008; 337:a180. PMID: 18614511.
Article16. Parker SR, Dyson S, Brisman S, Pennie M, Swerlick RA, Khan R, et al. Mortality of bullous pemphigoid: an evaluation of 223 patients and comparison with the mortality in the general population in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008; 59:582–588. PMID: 18707800.
Article17. Marazza G, Pham HC, Schärer L, Pedrazzetti PP, Hunziker T, Trüeb RM, et al. Incidence of bullous pemphigoid and pemphigus in Switzerland: a 2-year prospective study. Br J Dermatol. 2009; 161:861–868. PMID: 19566661.
Article18. Risser J, Lewis K, Weinstock MA. Mortality of bullous skin disorders from 1979 through 2002 in the United States. Arch Dermatol. 2009; 145:1005–1008. PMID: 19770439.
Article19. Cortés B, Marazza G, Naldi L, Combescure C, Borradori L. Autoimmune Bullous Disease Swiss Study Group. Mortality of bullous pemphigoid in Switzerland: a prospective study. Br J Dermatol. 2011; 165:368–374. PMID: 21574978.
Article20. Cortés B, Khelifa E, Clivaz L, Cazzaniga S, Saurat JH, Naldi L, et al. Mortality rate in bullous pemphigoid: a retrospective monocentric cohort study. Dermatology. 2012; 225:320–325. PMID: 23257934.
Article21. Joly P, Baricault S, Sparsa A, Bernard P, Bédane C, Duvert-Lehembre S, et al. Incidence and mortality of bullous pemphigoid in France. J Invest Dermatol. 2012; 132:1998–2004. PMID: 22418872.
Article22. Li J, Zuo YG, Zheng HY. Mortality of bullous pemphigoid in China. JAMA Dermatol. 2013; 149:106–108. PMID: 23324774.
Article23. Zhang LM, Wu J, Xiao T, Jin GY, Li JH, Geng L, et al. Treatment and mortality rate of bullous pemphigoid in China: a hospital-based study. Eur J Dermatol. 2013; 23:94–98. PMID: 23419247.
Article24. Bernard P. Mortality of bullous pemphigoid in Asia: the same as in Europe? Br J Dermatol. 2014; 170:1216–1217.
Article25. Brick KE, Weaver CH, Lohse CM, Pittelkow MR, Lehman JS, Camilleri MJ, et al. Incidence of bullous pemphigoid and mortality of patients with bullous pemphigoid in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1960 through 2009. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014; 71:92–99. PMID: 24704091.
Article26. Cai SC, Allen JC, Lim YL, Chua SH, Tan SH, Tang MB. Mortality of bullous pemphigoid in Singapore: risk factors and causes of death in 359 patients seen at the National Skin Centre. Br J Dermatol. 2014; 170:1319–1326. PMID: 24372558.
Article27. Lee JH, Kim SC. Mortality of patients with bullous pemphigoid in Korea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014; 71:676–683. PMID: 24930586.28. Gual A, Mascaró JM Jr, Rojas-Farreras S, Guilabert A, Julià M, Iranzo P. Mortality of bullous pemphigoid in the first year after diagnosis: a retrospective study in a Spanish medical centre. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014; 28:500–506. PMID: 23279207.
Article29. Serwin AB, Musialkowska E, Piascik M. Incidence and mortality of bullous pemphigoid in north-east Poland (Podlaskie Province), 1999-2012: a retrospective bicentric cohort study. Int J Dermatol. 2014; 53:e432–e437. PMID: 25041554.
Article30. Försti AK, Jokelainen J, Timonen M, Tasanen K. Risk of death in bullous pemphigoid: a retrospective database study in Finland. Acta Derm Venereol. 2016; 96:758–761. PMID: 26806363.
Article31. Ren Z, Hsu DY, Brieva J, Silverberg NB, Langan SM, Silverberg JI. Hospitalization, inpatient burden and comorbidities associated with bullous pemphigoid in the U.S.A. Br J Dermatol. 2017; 176:87–99. PMID: 27343837.
Article32. Laffitte E, Burkhard PR, Fontao L, Jaunin F, Saurat JH, Chofflon M, et al. Bullous pemphigoid antigen 1 isoforms: potential new target autoantigens in multiple sclerosis? Br J Dermatol. 2005; 152:537–540. PMID: 15787824.
Article33. Groves RW, Liu L, Dopping-Hepenstal PJ, Markus HS, Lovell PA, Ozoemena L, et al. A homozygous nonsense mutation within the dystonin gene coding for the coiled-coil domain of the epithelial isoform of BPAG1 underlies a new subtype of autosomal recessive epidermolysis bullosa simplex. J Invest Dermatol. 2010; 130:1551–1557. PMID: 20164846.
Article34. Chen YJ, Wu CY, Lin MW, Chen TJ, Liao KK, Chen YC, et al. Comorbidity profiles among patients with bullous pemphigoid: a nationwide population-based study. Br J Dermatol. 2011; 165:593–599. PMID: 21517800.
Article35. Langan SM, Groves RW, West J. The relationship between neurological disease and bullous pemphigoid: a population-based case-control study. J Invest Dermatol. 2011; 131:631–636. PMID: 21085189.
Article36. Bastuji-Garin S, Joly P, Lemordant P, Sparsa A, Bedane C, Delaporte E, et al. Risk factors for bullous pemphigoid in the elderly: a prospective case-control study. J Invest Dermatol. 2011; 131:637–643. PMID: 20944650.
Article37. Cordel N, Chosidow O, Hellot MF, Delaporte E, Lok C, Vaillant L, et al. Neurological disorders in patients with bullous pemphigoid. Dermatology. 2007; 215:187–191. PMID: 17823513.
Article38. Taghipour K, Chi CC, Vincent A, Groves RW, Venning V, Wojnarowska F. The association of bullous pemphigoid with cerebrovascular disease and dementia: a case-control study. Arch Dermatol. 2010; 146:1251–1254. PMID: 21079062.
Article39. Jedlickova H, Hlubinka M, Pavlik T, Semradova V, Budinska E, Vlasin Z. Bullous pemphigoid and internal diseases-a case-control study. Eur J Dermatol. 2010; 20:96–101. PMID: 19797038.40. Bastuji-Garin S, Joly P, Picard-Dahan C, Bernard P, Vaillant L, Pauwels C, et al. Drugs associated with bullous pemphigoid. A case-control study. Arch Dermatol. 1996; 132:272–276. PMID: 8607630.
Article41. Lloyd-Lavery A, Chi CC, Wojnarowska F, Taghipour K. The associations between bullous pemphigoid and drug use: a UK case-control study. JAMA Dermatol. 2013; 149:58–62. PMID: 23324757.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Coexistence of Bullous Pemphigoid and Psoriasis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- A Case of Bullous Pemphigoid Associated with Prostate Adenocarcinoma
- A Case of Dyshidrosiform Pemphigoid
- Atypical Variant of Bullous Pemphigoid: Prolonged Eruptions of Papulourticarial Lesions
- Erythema Multiforme like Bullous Pemphigoid