Successful introduction of Model for End-stage Liver Disease scoring in deceased donor liver transplantation in Korea: analysis of first 1 year experience at a high-volume transplantation center
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shwang@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2397799
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2017.21.4.199
Abstract
- BACKGROUNDS/AIMS
Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) score was adopted in June 2016 in Korea.
METHODS
We analyzed changes in volumes and outcomes of deceased donor liver transplantation (DDLT) for 1 year before and after introduction of MELD scoring at Asan Medical Center.
RESULTS
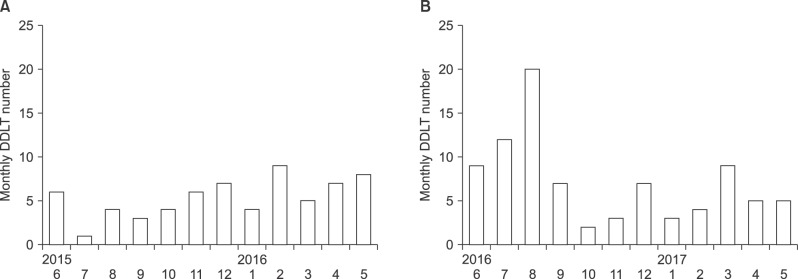
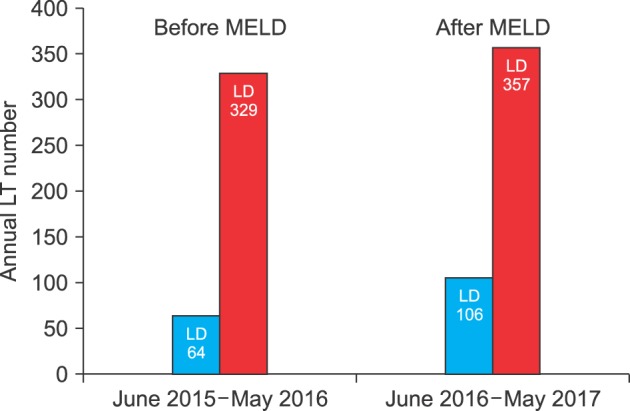
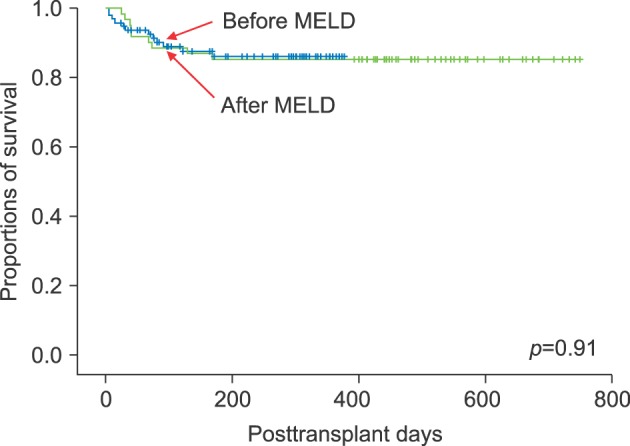
There were 64 cases of DDLT in 1 year before MELD introduction and 106 in 1 year after MELD introduction, an increase of 65%. The volume of DDLTs abruptly increased during first 3 months, but then returned to its usual level before MELD introduction, which indicated 3-month depletion of accumulated recipient pool with high MELD scores. The number of pediatric DDLT cases increased from 3 before MELD introduction to 11 after it, making up 21.4% and 47.8% of all cases of pediatric liver transplantation, respectively. The number of cases of retransplanted DDLTs increased from 4 to 27, representing 6.3% and 25.5% of all DDLT cases, respectively. The number of status 1 DDLT cases increased from 5 to 12, being 7.8% and 11.3% of all cases. Patient survival outcomes were similar before and after MELD introduction.
CONCLUSIONS
The number of DDLTs temporarily increased after adoption of MELD scoring due to accumulated recipient pool with high MELD scores. The numbers of retransplanted and pediatric DDLT cases significantly increased. Patient survival in adult and pediatric DDLT was comparable before and after adoption of MELD scoring. These results imply that Korean MELD score-based allocation system was successfully established within its first year.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Changes in the indications for living donor liver transplantation: single-institution experience of 3,145 cases over 10 years
Sang-Hyun Kang, Shin Hwang, Chul-Soo Ahn, Ki-Hun Kim, Deok-Bog Moon, Tae-Yong Ha, Gi-Won Song, Dong-Hwan Jung, Gil-Chun Park, Jung-Man Namgoong, Young-In Yoon, Hui-Dong Cho, Jae-Hyun Kwon, Yong-Kyu Chung, Jin-Uk Choi, Sung-Gyu Lee
Korean J Transplant. 2020;34(1):47-54. doi: 10.4285/kjt.2020.34.1.47.Prognosis of Split Liver Transplantation Compared with Whole Liver Transplantation in Adult Patients: Single-center Results under the Korean MELD Score-based Allocation Policy
Gil-Chun Park, Shin Hwang, Gi-Won Song, Dong-Hwan Jung, Tae-Yong Ha, Chul-Soo Ahn, Deok-Bog Moon, Ki-Hun Kim, Young-In Yoon, Woo-Hyoung Kang, Hwui-Dong Cho, Jin Uk Choi, Minjae Kim, Byeong-Gon Na, Sang Hoon Kim, Sung-Gyu Lee
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(37):e304. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e304.Is renal replacement therapy necessary in deceased donor liver transplantation candidates with hepatorenal syndrome?: a 2-year experience at a high-volume center
Gil-Chun Park, Shin Hwang, Dong-Hwan Jung, Gi-Won Song, Chul-Soo Ahn, Ki-Hun Kim, Deok-Bog Moon, Tae-Yong Ha, Young-In Yoon, Hui-Dong Cho, Jae-Hyun Kwon, Yong-Kyu Chung, Sang-Hyun Kang, I-Ji Jung, Jin Uk Choi, Sung-Gyu Lee
Ann Surg Treat Res. 2020;98(2):102-109. doi: 10.4174/astr.2020.98.2.102.Deceased donor liver transplantation under the Korean model for end-stage liver disease score-based liver allocation system: 2-year allocation results at a high-volume transplantation center
Hea-Seon Ha, Jung-Ja Hong, In-Ok Kim, Sae-Rom Lee, Ah-Young Lee, Tae-Yong Ha, Gi-Won Song, Dong-Hwan Jung, Gil-Chun Park, Chul-Soo Ahn, Deok-Bog Moon, Ki-Hun Kim, Sung-Gyu Lee, Shin Hwang
Korean J Transplant. 2019;33(4):112-117. doi: 10.4285/jkstn.2019.33.4.112.
Reference
-
1. Bollinger RR, Cho WH. Organ allocation for transplantation in the USA and Korea: the changing roles of equity and utility. Yonsei Med J. 2004; 45:1035–1042. PMID: 15627294.
Article2. Hwang S, Ahn CS, Kim KH, Moon DB, Ha TY, Song GW, et al. Survival rates among patients awaiting deceased donor liver transplants at a single high-volume Korean center. Transplant Proc. 2013; 45:2995–2996. PMID: 24157021.
Article3. Min SI, Ahn C, Han DJ, Kim SI, Chung SY, Lee SK, et al. To achieve national self-sufficiency: recent progresses in deceased donation in Korea. Transplantation. 2015; 99:765–770. PMID: 25226175.4. Lee SG, Moon DB, Hwang S, Ahn CS, Kim KH, Song GW, et al. Liver transplantation in Korea: past, present, and future. Transplant Proc. 2015; 47:705–708. PMID: 25891715.
Article5. Jung BH, Hwang S, Song GW, Jung DH, Ha TY, Park GC, et al. Updated status of deceased-donor liver graft allocation for high-urgency adult patients in a Korean high-volume liver transplantation center. Transplant Proc. 2015; 47:580–583. PMID: 25891690.
Article6. Korean Association for the Study of the Liver. KASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2016; 22:18–75. PMID: 27044762.7. Moon DB, Lee SG, Hwang S, Kim KH, Ahn CS, Ha TY, et al. Toward more than 400 liver transplantations a year at a single center. Transplant Proc. 2013; 45:1937–1941. PMID: 23769078.
Article8. Massie AB, Chow EK, Wickliffe CE, Luo X, Gentry SE, Mulligan DC, et al. Early changes in liver distribution following implementation of Share 35. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15:659–667. PMID: 25693474.
Article9. Washburn K, Harper A, Baker T, Edwards E. Changes in liver acceptance patterns after implementation of Share 35. Liver Transpl. 2016; 22:171–177. PMID: 26437266.
Article10. Hwang S, Ahn CS, Kim KH, Moon DB, Ha TY, Song GW, et al. Liver retransplantation for adult recipients. Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2013; 17:1–7. PMID: 26155206.
Article11. Oh SH, Kim KM, Kim DY, Song SM, Kim T, Hwang S, et al. Clinical experience of more than 200 cases of pediatric liver transplantation at a single center: improved patient survival. Transplant Proc. 2012; 44:484–486. PMID: 22410052.
Article12. Cuenca AG, Kim HB, Vakili K. Pediatric liver transplantation. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2017; 26:217–223. PMID: 28964477.
Article13. Moon DB, Lee SG, Kang WH, Song GW, Jung DH, Park GC, et al. Adult living donor liver transplantation for acute-on-chronic liver failure in high-model for end-stage liver disease score patients. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17:1833–1842. PMID: 28097804.
Article14. Yadav SK, Saraf N, Saigal S, Choudhary NS, Goja S, Rastogi A, et al. High MELD score does not adversely affect outcome of living donor liver transplantation: Experience in 1000 recipients. Clin Transplant. 2017; 31:DOI: 10.1111/ctr.13006.
Article15. Freeman RB, Wiesner RH, Edwards E, Harper A, Merion R, Wolfe R. Results of the first year of the new liver allocation plan. Liver Transpl. 2004; 10:7–15. PMID: 14755772.
Article16. Ben-Haim M, Carmiel M, Katz P, Shabtai E, Oren R, Nakache R. Is the model of end-stage liver disease (MELD) valid in Israel? A critical analysis of liver transplant waiting list mortality. Isr Med Assoc J. 2006; 8:605–609. PMID: 17058408.17. Castro RS, Deisanti D, Seva-Pereira T, Almeida JR, Yamanaka A, Boin IF, et al. Survival before and after model for end-stage liver disease score introduction on the Brazilian liver transplant waiting list. Transplant Proc. 2010; 42:412–416. PMID: 20304153.
Article18. Chaib E, Figueira ER, Brunheroto A, Gatti AP, Fernandes DV, D'Albuquerque LA. Does the patient selection with MELD score improve short-term survival in liver transplantation? Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2013; 26:324–327. PMID: 24510043.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Status of Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation for Alcoholic Liver Disease in Korea in MELD Era
- A study on differences in deceased donor liver transplantation before and after the introduction of the model for end-stage liver disease system: three low volume centers, multi-center trial
- Liver Transplantation
- Liver transplantation: a 10-year low-volume transplant center experience in Kazakhstan
- Simultaneous liver-kidney transplantation: a single-center experience in Korea