Ann Lab Med.
2018 Jan;38(1):23-31. 10.3343/alm.2018.38.1.23.
Comparison of Singleplex Specific IgE Detection Immunoassays: ImmunoCAP Phadia 250 and Immulite 2000 3gAllergy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Allergy and Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. white182@yuhs.ac
- 2Institute of Allergy, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Allergy, Asthma, and Clinical Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2397598
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2018.38.1.23
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The identification of clinically meaningful specific immunoglobulin E (sIgE) is important for the diagnosis and management of allergic diseases. Various in vitro sIgE detection methods are available worldwide. Depending on the number of antigens that can be tested simultaneously, there are two representative methods: singleplex and multiplex. Singleplex sIgE detection is mainly provided by Thermo Fisher (ImmunoCAP) and Siemens (Immulite). This study aimed to compare the diagnostic agreement of two singleplex sIgE detection assays.
METHODS
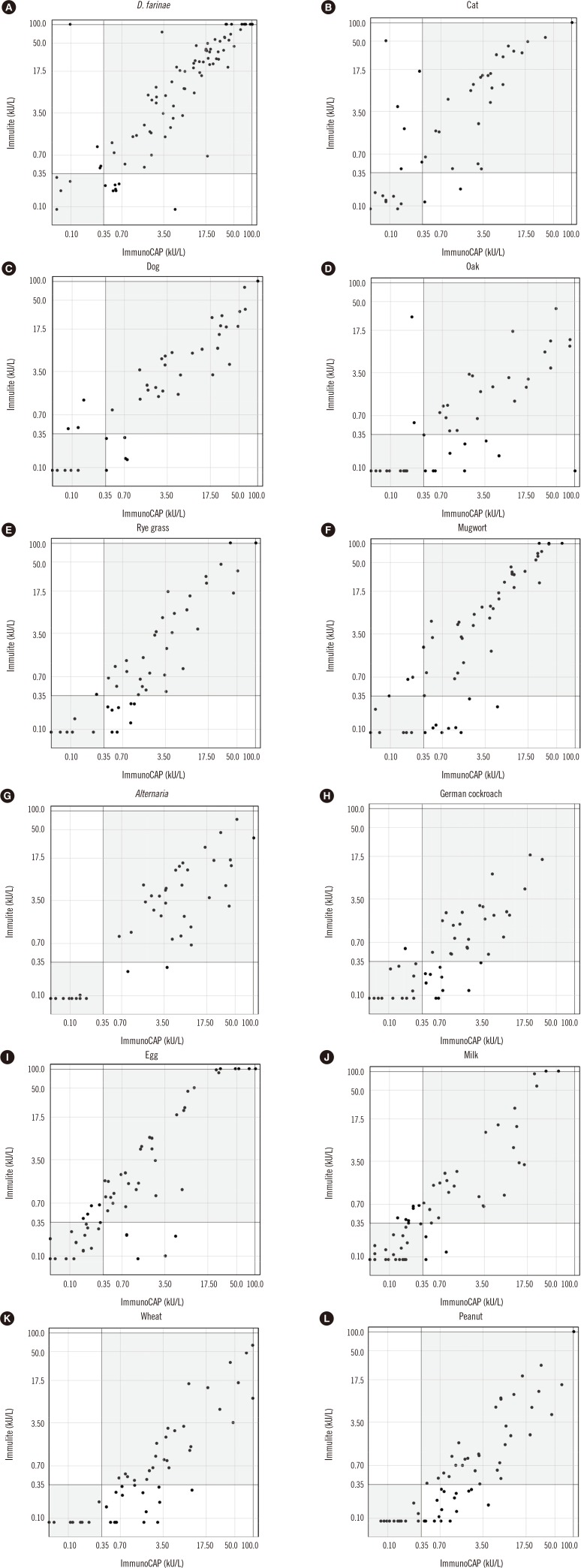
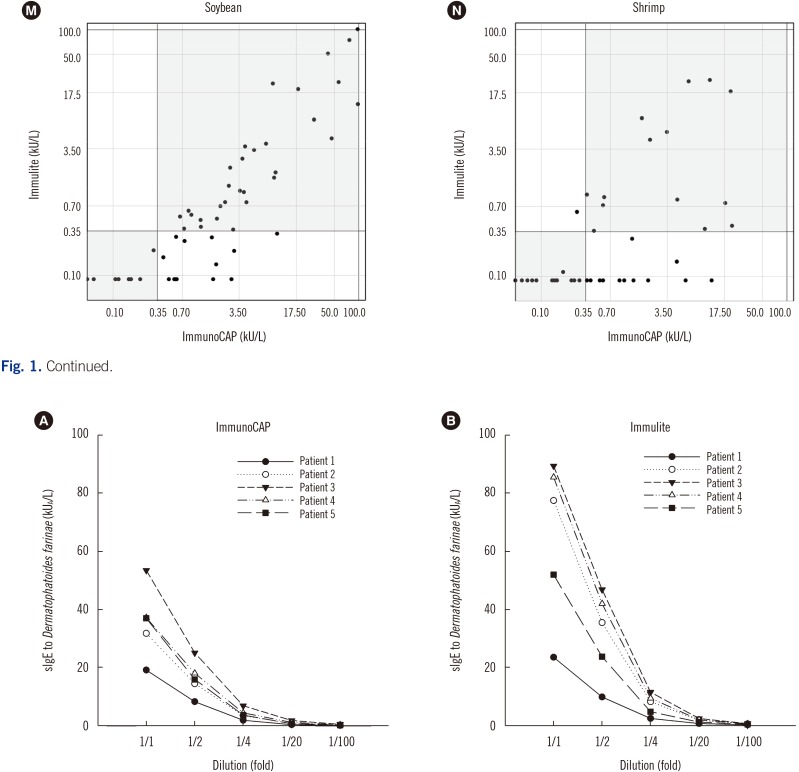
Sera from 209 Korean patients with allergic disease were used to compare the ImmunoCAP and Immulite assays with respect to the following allergens: inhalant allergens (Dermatophagoides farinae, cat and dog dander, oak, rye grass, mugwort, Alternaria, German cockroach) and food allergens (hen's egg white, cow's milk, wheat, peanut, soybean, and shrimp). Data from 902 paired comparison tests were included for comparisons. Qualitative, semi-quantitative, and quantitative comparisons were performed using statistical analyses.
RESULTS
In qualitative comparisons, the positivity and negativity agreements ranged from 75% (wheat, shrimp) to 96% (Alternaria). Class consistency (classes 0-6) was well matched. Spearman's rank correlation coefficients for all allergens except shrimp were over 0.7. In quantitative comparisons, all allergens excluding shrimp showed >0.7 intra-class correlation coefficients.
CONCLUSIONS
The ImmunoCAP and Immulite systems showed similar performances. However, clinicians should consider fundamental methodological differences between the assays.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Park KH, Lee J, Lee SC, Son YW, Sim DW, Lee JH, et al. Comparison of the ImmunoCAP Assay and AdvanSure AlloScreen Advanced Multiplex Specific IgE Detection Assay. Yonsei Med J. 2017; 58:786–792. PMID: 28540992.2. Lee JH, Park HJ, Park KH, Jeong KY, Park JW. Performance of the PROTIA (TM) Allergy-Q (R) System in the Detection of Allergen-specific IgE: A Comparison with the ImmunoCAP (R) System. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015; 7:565–572. PMID: 26333703.3. Bousquet J, Heinzerling L, Bachert C, Papadopoulos NG, Bousquet PJ, Burney PG, et al. Practical guide to skin prick tests in allergy to aeroallergens. Allergy. 2012; 67:18–24. PMID: 22050279.4. Celik-Bilgili S, Mehl A, Verstege A, Staden U, Nocon M, Beyer K, et al. The predictive value of specific immunoglobulin E levels in serum for the outcome of oral food challenges. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005; 35:268–273. PMID: 15784102.5. Williams PB, Barnes JH, Szeinbach SL, Sullivan TJ. Analytic precision and accuracy of commercial immunoassays for specific IgE: Establishing a standard. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000; 105:1221–1230. PMID: 10856158.6. Goikoetxea MJ, Sanz ML, Garcia BE, Mayorga C, Longo N, Gamboa PM, et al. Recommendations for the use of in vitro methods to detect specific immunoglobulin E: are they comparable? J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2013; 23:448–454.7. Lee JH, Park KH, Kim HS, Kim KW, Sohn MH, Kim CH, et al. Specific IgE measurement using AdvanSure (R) system: Comparison of detection performance with ImmunoCAP (R) system in Korean allergy patients. Clin Chim Acta. 2012; 413:914–919. PMID: 22394454.8. Crameri R. The crux with a reliable in vitro and in vivo diagnosis of allergy. Allergy. 2013; 68:693–694. PMID: 23621640.9. Lee YW, Sohn JH, Lee JH, Hong CS, Park JW. Allergen-specific IgE measurement with the IMMULITE 2000 system: intermethod comparison of detection performance for allergen-specific IgE antibodies from Korean allergic patients. Clin Chim Acta. 2009; 401:25–32. PMID: 19056369.10. Park HJ, Lee JH, Park KH, Ann HW, Jin MN, Choi SY, et al. A nationwide survey of inhalant allergens sensitization and levels of indoor major allergens in Korea. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:222–227. PMID: 24843797.11. Mukaka MM. Statistics Corner: A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Med J. 2012; 24:69–71. PMID: 23638278.12. Sae-Jung S, Jirarattanaphochai K, Sumananont C, Wittayapairoj K, Sukhonthamarn K. Interrater reliability of the postoperative epidural fibrosis classification: a histopathologic study in the rat model. Asian Spine J. 2015; 9:587–594. PMID: 26240719.13. Sidenius KE, Hallas TE, Poulsen LK, Mosbech H. Allergen cross-reactivity between house-dust mites and other invertebrates. Allergy. 2001; 56:723–733. PMID: 11488665.14. Park KH, Son YW, Lee SC, Jeong K, Sim DW, Park HJ, et al. Clinical significance of component allergens in fagales pollen-sensitized peanut allergy in Korea. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2016; 8:505–511. PMID: 27582401.15. Vereda A, van Hage M, Ahlstedt S, Ibanez MD, Cuesta-Herranz J, van Odijk J, et al. Peanut allergy: clinical and immunologic differences among patients from 3 different geographic regions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:603–607. PMID: 21093026.16. Moverare R, Westritschnig K, Svensson M, Hayek B, Bende M, Pauli G, et al. Different IgE reactivity profiles in birch pollen-sensitive patients from six European populations revealed by recombinant allergens: an imprint of local sensitization. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002; 128:325–335. PMID: 12218371.17. Park HJ, Lee JH, Park KH, Kim KR, Han MJ, Choe H, et al. A six-year study on the changes in airborne pollen counts and skin positivity rates in Korea: 2008-2013. Yonsei Med J. 2016; 57:714–720. PMID: 26996572.18. Byun JG, Lee WK, Kim M, Kwak DA, Kwak H, Park T, et al. Radial growth response of Pinus densiflora and Quercus spp. to topographic and climatic factors in South Korea. J Plant Ecol. 2013; 6:380–392.19. Jeong KY, Park JW, Hong CS. House dust mite allergy in Korea: the most important inhalant allergen in current and future. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:313–325. PMID: 23115727.20. Cox L, Williams B, Sicherer S, Oppenheimer J, Sher L, Hamilton R, et al. Pearls and pitfalls of allergy diagnostic testing: report from the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology/American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology Specific IgE Test Task Force. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008; 101:580–592. PMID: 19119701.21. Li TM, Chuang T, Tse S, Hovanec-Burns D, El Shami AS. Development and validation of a third generation allergen-specific IgE assay on the continuous random access IMMULITE (R) 2000 analyzer. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2004; 34:67–74. PMID: 15038670.22. Hamilton RG, Williams PB, Force SITT, Asthma ACA. Human IgE antibody serology: A primer for the practicing North American allergist/immunologist. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 126:33–38. PMID: 20451984.23. Wood RA, Segall N, Ahlstedt S, Williams PB. Accuracy of IgE antibody laboratory results. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2007; 99:34–41. PMID: 17650827.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Measurement of Hymenoptera venom specific IgE by the IMMULITE 3gAllergy in subjects with negative or positive results by ImmunoCAP
- Clinical validation of ImmuneCheck IgE for the rapid detection of serum total IgE
- Erratum: Measurement of Hymenoptera venom specific IgE by the IMMULITE 3gAllergy in subjects with negative or positive results by ImmunoCAP
- Diagnostic Value of Serum Specific IgE to Toxocara canis in Patients with Eosinophilia
- Comparison of Clinical Utility between Phadiatop Assay and AdvanSureTM AlloScreen