Asia Pac Allergy.
2015 Jul;5(3):156-162. 10.5415/apallergy.2015.5.3.156.
Immunoglobulin E to allergen components of house dust mite in Korean children with allergic disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul 137-701, Korea. pedjsyoon@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2397045
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5415/apallergy.2015.5.3.156
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
House dust mites (HDMs) are important sources of indoor allergens. Seventeen components have been identified from Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Der p).
OBJECTIVE
Our aim was to define the prevalence of specific IgE to components of Der p in Korea and investigate the clinical features of them in children with allergic disease.
METHODS
We performed a prospective evaluation of 80 HDM sensitized patients with history of allergic rhinitis (AR), atopic dermatitis (AD), asthma and urticaria (UC). Patients underwent ImmunoCAP for total IgE, Der p, Der f, Der p 1, Der p 2, and Der p 10.
RESULTS
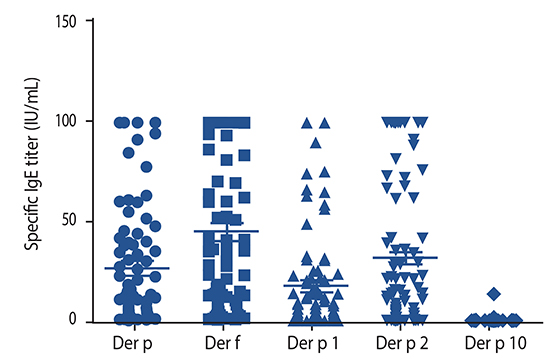
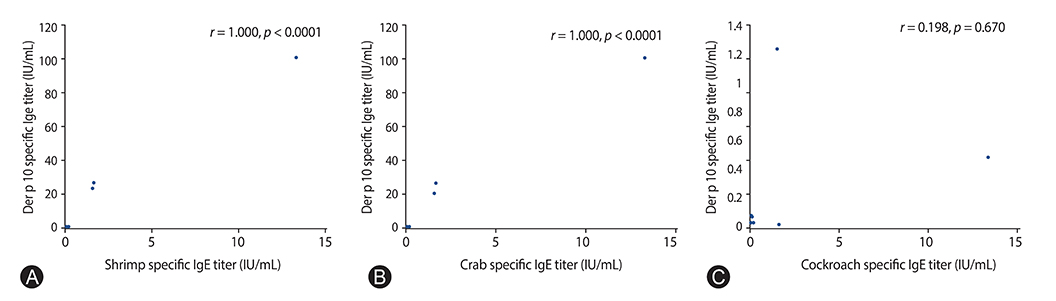
Seventy-nine patients had detectable serum IgE to Der p, 80 patients were sensitized to Der f, 66 patients were sensitized to Der p 1, 63 patients to Der p 2, and 7 patients were sensitized to Der p 10. Der p 1 specific IgE was significantly lower in the UC group compared with the AD and AR group. Total IgE was significantly higher in the Der p 10 sensitized group. Der p 10 serum IgE level was highly correlated with crab and shrimp specific IgE. There was a significant positive correlation between total IgE and specific IgE to Der p and its components and Der f.
CONCLUSION
Sensitization to HDM and its components in Korea is similar to previous studies from temperate climate. The determination of Der p 1, Der p 2, and Der p 10 specific IgE helps in obtaining additional information in regards to allergic disease.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Spieksma FT, Dieges PH. The history of the finding of the house dust mite. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:573–576.
Article2. Squillace SP, Sporik RB, Rakes G, Couture N, Lawrence A, Merriam S, Zhang J, Platts-Mills AE. Sensitization to dust mites as a dominant risk factor for asthma among adolescents living in central Virginia. Multiple regression analysis of a population-based study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997; 156:1760–1764.3. Arlian LG, Platts-Mills TA. The biology of dust mites and the remediation of mite allergens in allergic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 107:3 Suppl. S406–S413.
Article4. Thomas WR, Smith WA, Hales BJ, Mills KL, O'Brien RM. Characterization and immunobiology of house dust mite allergens. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002; 129:1–18.
Article5. Nomenclature subcommittee [Internet]. Kurfürstendamm (DE): International Union of Immunological Societies;c2015. cited 2014 Jun 7. Available from: http://www.iuisonline.org/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=47&Itemid=54.6. Van Der Veen MJ, Jansen HM, Aalberse RC, van der Zee JS. Der p 1 and Der p 2 induce less severe late asthmatic responses than native Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus extract after a similar early asthmatic response. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001; 31:705–714.
Article7. Gregory LG, Lloyd CM. Orchestrating house dust mite-associated allergy in the lung. Trends Immunol. 2011; 32:402–411.
Article8. Jacquet A. The role of innate immunity activation in house dust mite allergy. Trends Mol Med. 2011; 17:604–611.
Article9. Lambrecht BN, Hammad H. Biology of lung dendritic cells at the origin of asthma. Immunity. 2009; 31:412–424.
Article10. Miglino N, Roth M, Tamm M, Borger P. House dust mite extract down-regulates C/EBPα in asthmatic bronchial smooth muscle cells. Eur Respir J. 2011; 38:50–58.
Article11. Hongjia L, Qingling G, Meiying L, Weixuan W, Lihong Z, Yongsheng G, Yanli L, Jinxiang W, Liang D. House dust mite regulate the lung inflammation of asthmatic mice through TLR4 pathway in airway epithelial cells. Cell Biochem Funct. 2010; 28:597–603.
Article12. Trompette A, Divanovic S, Visintin A, Blanchard C, Hegde RS, Madan R, Thorne PS, Wills-Karp M, Gioannini TL, Weiss JP, Karp CL. Allergenicity resulting from functional mimicry of a Toll-like receptor complex protein. Nature. 2009; 457:585–588.
Article13. Resch Y, Weghofer M, Seiberler S, Horak F, Scheiblhofer S, Linhart B, Swoboda I, Thomas WR, Thalhamer J, Valenta R, Vrtala S. Molecular characterization of Der p 10: a diagnostic marker for broad sensitization in house dust mite allergy. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011; 41:1468–1477.
Article14. Lopata AL, Lehrer SB. New insights into seafood allergy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 9:270–277.
Article15. Reese G, Ayuso R, Lehrer SB. Tropomyosin: an invertebrate pan-allergen. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1999; 119:247–258.16. Jenkins JA, Breiteneder H, Mills EN. Evolutionary distance from human homologs reflects allergenicity of animal food proteins. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120:1399–1405.
Article17. Pittner G, Vrtala S, Thomas WR, Weghofer M, Kundi M, Horak F, Kraft D, Valenta R. Component-resolved diagnosis of house-dust mite allergy with purified natural and recombinant mite allergens. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004; 34:597–603.
Article18. Weghofer M, Thomas WR, Kronqvist M, Mari A, Purohit A, Pauli G, Horak F, Gronlund H, van Hage M, Valenta R, Vrtala S. Variability of IgE reactivity profiles among European mite allergic patients. Eur J Clin Invest. 2008; 38:959–965.
Article19. Kidon MI, Chiang WC, Liew WK, Ong TC, Tiong YS, Wong KN, Angus AC, Ong ST, Gao YF, Reginald K, Bi XZ, Shang HS, Chew FT. Mite component-specific IgE repertoire and phenotypes of allergic disease in childhood: the tropical perspective. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2011; 22:202–210.
Article20. Trombone AP, Tobias KR, Ferriani VP, Schuurman J, Aalberse RC, Smith AM, Chapman MD, Arruda LK. Use of a chimeric ELISA to investigate immunoglobulin E antibody responses to Der p 1 and Der p 2 in mite-allergic patients with asthma, wheezing and/or rhinitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002; 32:1323–1328.21. Hales BJ, Martin AC, Pearce LJ, Laing IA, Hayden CM, Goldblatt J, Le Souëf PN, Thomas WR. IgE and IgG anti-house dust mite specificities in allergic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 118:361–367.
Article22. Bardini G, Santos AC, Santos KS, Arruda LK. IgE reactivity profiles in patients with asthma and/or rhinitis allergic to cockroach and mites. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:2 Suppl. AB171.
Article23. Kidon MI, Chiang WC, Liew WK, Lim SH, See Y, Goh A, Tan JP, Chay OM, Balakrishnan A. Sensitization to dust mites in children with allergic rhinitis in Singapore: does it matter if you scratch while you sneeze? Clin Exp Allergy. 2005; 35:434–440.
Article24. Muraro A, Dreborg S, Halken S, Host A, Niggemann B, Aalberse R, Arshad SH, von Berg A, Carlsen KH, Duschen K, Eigenmann P, Hill D, Jones C, Mellon M, Oldeus G, Oranje A, Pascual C, Prescott S, Sampson H, Svartengren M, Vandenplas Y, Wahn U, Warner JA, Warner JO, Wickman M, Zeiger RS. Dietary prevention of allergic diseases in infants and small children. Part II. Evaluation of methods in allergy prevention studies and sensitization markers. Definitions and diagnostic criteria of allergic diseases. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2004; 15:196–205.
Article25. Zuberbier T, Aberer W, Asero R, Bindslev-Jensen C, Brzoza Z, Canonica GW, Church MK, Ensina LF, Gimenez-Arnau A, Godse K, Gonçalo M, Grattan C, Hebert J, Hide M, Kaplan A, Kapp A, Abdul Latiff AH, Mathelier-Fusade P, Metz M, Nast A, Saini SS, Sánchez-Borges M, Schmid-Grendelmeier P, Simons FE, Staubach P, Sussman G, Toubi E, Vena GA, Wedi B, Zhu XJ, Maurer M. European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. Global Allergy and Asthma European Network. European Dermatology Forum. World Allergy Organization. The EAACI/GA(2) LEN/EDF/WAO Guideline for the definition, classification, diagnosis, and management of urticaria: the 2013 revision and update. Allergy. 2014; 69:868–887.26. de Blay F, Pauli G, Velten M, Bessot JC. Influence of mite exposure on symptoms of mite-sensitive patients with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1994; 93(1 Pt 1):136–138.27. Bronnert M, Mancini J, Birnbaum J, Agabriel C, Liabeuf V, Porri F, Cleach I, Fabre A, Deneux I, Grandne V, Grob JJ, Berbis P, Charpin D, Bongrand P, Vitte J. Component-resolved diagnosis with commercially available D. pteronyssinus Der p 1, Der p 2 and Der p 10: relevant markers for house dust mite allergy. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012; 42:1406–1415.28. Fonseca P, Tavares-Ratado P, Tomaz CT. Interference of Dermatophagoides' specific immunoglobulins G in the quantification of mite's specific immunoglobulins E. J Immunoassay Immunochem. 2009; 30:338–347.29. Fernandes J, Reshef A, Patton L, Ayuso R, Reese G, Lehrer SB. Immunoglobulin E antibody reactivity to the major shrimp allergen, tropomyosin, in unexposed Orthodox Jews. Clin Exp Allergy. 2003; 33:956–961.
Article30. Aki T, Kodama T, Fujikawa A, Miura K, Shigeta S, Wada T, Jyo T, Murooka Y, Oka S, Ono K. Immunochemical characterization of recombinant and native tropomyosins as a new allergen from the house dust mite, Dermatophagoides farinae. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995; 96:74–83.31. Wang J, Calatroni A, Visness CM, Sampson HA. Correlation of specific IgE to shrimp with cockroach and dust mite exposure and sensitization in an inner-city population. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 128:834–837.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Nonspecific IgE and IgG Antibodies on Basophil Histamine Release mediated by Specific IgE Antibodies
- Two Cases of Atopic Dermatitis Improved by Combination Treatment of Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy and Histamine-Immunoglobulin Complex
- The Innate Immune Response in House Dust Mite-Induced Allergic Inflammation
- Correlation between House Dust Mite Allergen Concentrations in Scalp Dander and Clinical Severity of Atopic Dermatitis in Children
- House Dust Mite Allergic Rhinitis Model in C57BL/6 Mice