Asia Pac Allergy.
2016 Jan;6(1):16-28. 10.5415/apallergy.2016.6.1.16.
A stepwise approach in the management of chronic spontaneous urticaria in children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Pharmacy Department, Kandang Kerbau Women's and Children's Hospital, Singapore 229899, Singapore.
- 2Allergy Service, Kandang Kerbau Women's and Children's Hospital, Singapore 229899, Singapore. Chiang.Wen.Chin@kkh.com.sg
- 3Duke-NUS Graduate Medical School Singapore, Singapore 169857, Singapore.
- KMID: 2396966
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5415/apallergy.2016.6.1.16
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
There is limited literature in the management of chronic urticaria in children. Treatment algorithms are generally extrapolated from adult studies.
OBJECTIVE
Utility of a weight and age-based algorithm for antihistamines in management of chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) in childhood. To document associated factors that predict for step of control of CSU and time taken to attain control of symptoms in children.
METHODS
A workgroup comprising of allergists, nurses, and pharmacists convened to develop a stepwise treatment algorithm in management of children with CSU. Sequential patients presenting to the paediatric allergy service with CSU were included in this observational, prospective study.
RESULTS
Ninety-eight patients were recruited from September 2012 to September 2013. Majority were male, Chinese with median age 4 years 7 months. A third of patients with CSU had a family history of acute urticaria. Ten point two percent had previously resolved CSU, 25.5% had associated angioedema, and 53.1% had a history of atopy. A total of 96.9% of patients achieved control of symptoms, of which 91.8% achieved control with cetirizine. Fifty percent of all the patients were controlled on step 2 or higher. Forty-seven point eight percent of those on step 2 or higher were between 2 to 6 years of age compared to 32.6% and 19.6% who were 6 years and older and lesser than 2 years of age respectively. Eighty percent of those with previously resolved CSU required an increase to step 2 and above to achieve chronic urticaria control.
CONCLUSION
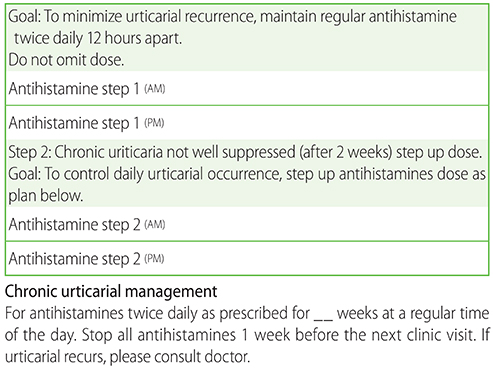
We propose a weight- and age-based titration algorithm for different antihistamines for CSU in children using a stepwise approach to achieve control. This algorithm may improve the management and safety profile for paediatric CSU patients and allow for review in a more systematic manner for physicians dealing with CSU in children.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Asia Pacific Allergy: it's been five years!
Yoon-Seok Chang
Asia Pac Allergy. 2016;6(1):1-2. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2016.6.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Asero R. Chronic unremitting urticaria: is the use of antihistamines above the licensed dose effective? A preliminary study of cetirizine at licensed and above-licensed doses. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2007; 32:34–38.
Article2. Khakoo G, Sofianou-Katsoulis A, Perkin MR, Lack G. Clinical features and natural history of physical urticaria in children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2008; 19:363–366.
Article3. Tuchinda M, Srimaruta N, Habanananda S, Vareenil J, Assatherawatts A. Urticaria in Thai children. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 1986; 4:41–45.4. Kaplan AP. Angioedema. World Allergy Organ J. 2008; 1:103–113.
Article5. Kaplan AP. Chronic urticaria: pathogenesis and treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 114:465–474.
Article6. Volonakis M, Katsarou-Katsari A, Stratigos J. Etiologic factors in childhood chronic urticaria. Ann Allergy. 1992; 69:61–65.7. Sheikh J. Autoantibodies to the high-affinity IgE receptor in chronic urticaria: how important are they? Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 5:403–407.
Article8. Levy Y, Segal N, Weintrob N, Danon YL. Chronic urticaria: association with thyroid autoimmunity. Arch Dis Child. 2003; 88:517–519.
Article9. Sharma M, Bennett C, Cohen SN, Carter B. H1-antihistamines for chronic spontaneous urticaria. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014; 11:CD006137.
Article10. Nolen TM. Sedative effects of antihistamines: safety, performance, learning, and quality of life. Clin Ther. 1997; 19:39–55.
Article11. Zuberbier T, Asero R, Bindslev-Jensen C, Walter Canonica G, Church MK, Giménez-Arnau AM, Grattan CE, Kapp A, Maurer M, Merk HF, Rogala B, Saini S, Sánchez-Borges M, Schmid-Grendelmeier P, Schünemann H, Staubach P, Vena GA, Wedi B. Dermatology Section of the European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology. Global Allergy and Asthma European Network. European Dermatology Forum. World Allergy Organization. EAACI/GA(2)LEN/EDF/WAO guideline: management of urticaria. Allergy. 2009; 64:1427–1443.12. Powell RJ, Du Toit GL, Siddique N, Leech SC, Dixon TA, Clark AT, Mirakian R, Walker SM, Huber PA, Nasser SM. British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology (BSACI). BSACI guidelines for the management of chronic urticaria and angio-oedema. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007; 37:631–650.
Article13. Młynek A, Zalewska-Janowska A, Martus P, Staubach P, Zuberbier T, Maurer M. How to assess disease activity in patients with chronic urticaria? Allergy. 2008; 63:777–780.
Article14. Kilic G, Guler N, Suleyman A, Tamay Z. Chronic urticaria and autoimmunity in children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010; 21:837–842.
Article15. Kanani A, Schellenberg R, Warrington R. Urticaria and angioedema. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2011; 7:Suppl 1. S9.
Article16. Sussman G, Hebert J, Gulliver W, Lynde C, Waserman S, Kanani A, Ben-Shoshan M, Horemans S, Barron C, Betschel S, Yang WH, Dutz J, Shear N, Lacuesta G, Vadas P, Kobayashi K, Lima H, Simons FE. Insights and advances in chronic urticaria: a Canadian perspective. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2015; 11:7.
Article17. Jirapongsananuruk O, Pongpreuksa S, Sangacharoenkit P, Visitsunthorn N, Vichyanond P. Identification of the etiologies of chronic urticaria in children: a prospective study of 94 patients. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010; 21:508–514.
Article18. Kim S, Baek S, Shin B, Yoon SY, Park SY, Lee T, Lee YS, Bae YJ, Kwon HS, Cho YS, Moon HB, Kim TB. Influence of initial treatment modality on long-term control of chronic idiopathic urticaria. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e69345.
Article19. Tay YK, Kong KH, Khoo L, Goh CL, Giam YC. The prevalence and descriptive epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in Singapore school children. Br J Dermatol. 2002; 146:101–106.
Article20. Hiragun M, Hiragun T, Mihara S, Akita T, Tanaka J, Hide M. Prognosis of chronic spontaneous urticaria in 117 patients not controlled by a standard dose of antihistamine. Allergy. 2013; 68:229–235.
Article21. Asero R. Intolerance to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs might precede by years the onset of chronic urticaria. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 111:1095–1098.
Article22. Lee AJ, Shek LP. Food allergy in Singapore: opening a new chapter. Singapore Med J. 2014; 55:244–247.
Article23. Kidon MI, Kang LW, Chin CW, Hoon LS, See Y, Goh A, Lin JT, Chay OM. Early presentation with angioedema and urticaria in cross-reactive hypersensitivity to nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs among young, Asian, atopic children. Pediatrics. 2005; 116:e675–e680.
Article24. Kidon MI, Liew WK, Chiang WC, Lim SH, Goh A, Tang JP, Chay OM. Hypersensitivity to paracetamol in Asian children with early onset of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug allergy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2007; 144:51–56.
Article25. Lam WY, Yau EK. Reports on Scientific Meetings: 19th Regional Conference of Dermatology. Hongkong J Dermatol Venereol. 2011; 19:35–39.26. Sahiner UM, Civelek E, Tuncer A, Yavuz ST, Karabulut E, Sackesen C, Sekerel BE. Chronic urticaria: etiology and natural course in children. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2011; 156:224–230.
Article