Restor Dent Endod.
2015 Aug;40(3):241-248. 10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.241.
Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with three roots and seven root canals with the aid of cone-beam computed tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Institute of Dental Sciences, Bareilly, UP, India. gurudutt_nayak@hotmail.com
- 2Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Kanti Devi Dental College and Hospital, Mathura, UP, India.
- KMID: 2396469
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.241
Abstract
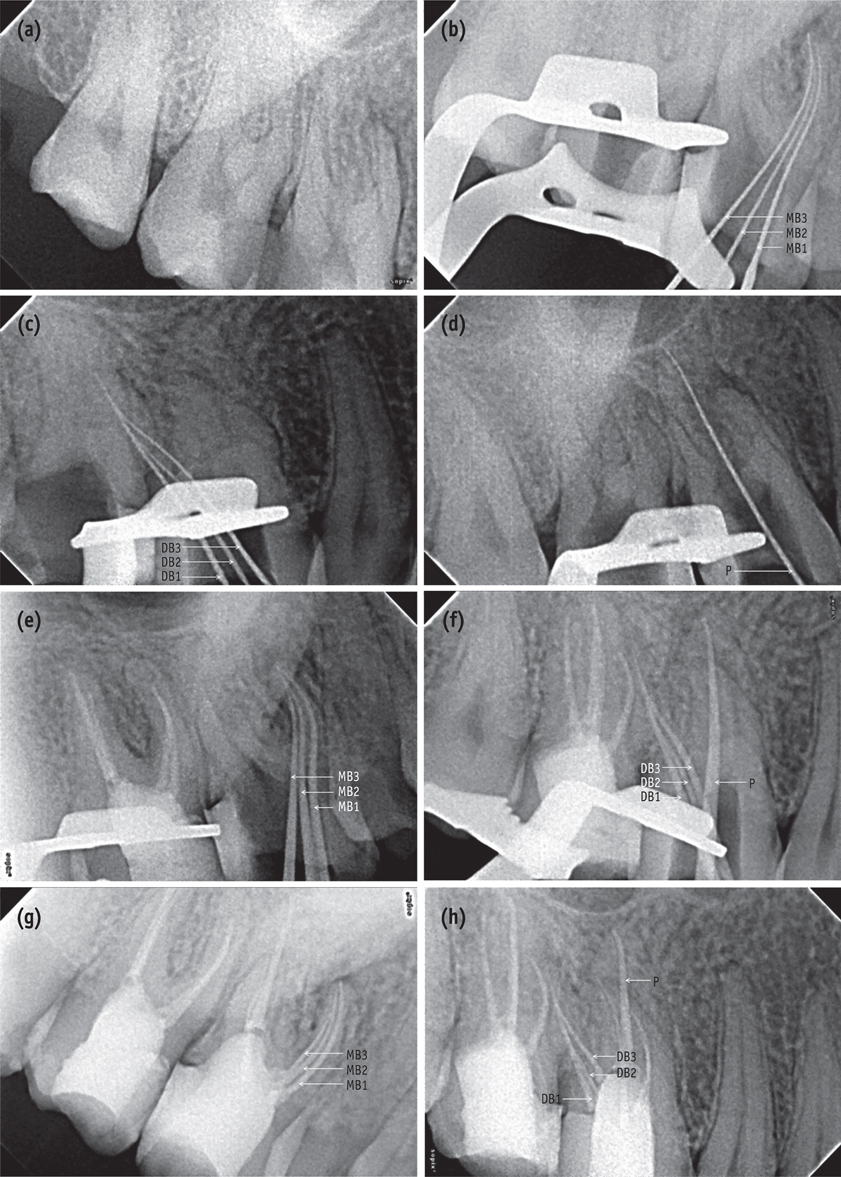
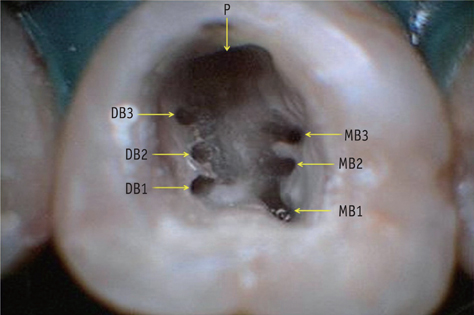
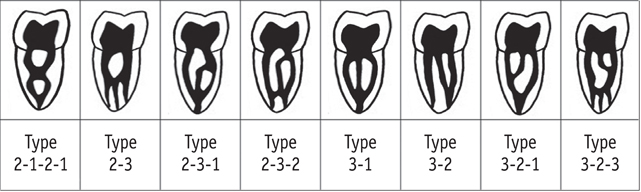
- Variation in root canal morphology, especially in maxillary first molar presents a constant challenge for a clinician in their detection and management. This case report describes the successful root canal treatment of a three rooted right maxillary first molar presenting with three canals each in the mesiobuccal and distobuccal roots and one canal in the palatal root. The clinical detection of this morphologic aberration was made using a dental operating microscope, and the canal configuration was established after correlating and computing the clinical, radiographic and cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan findings. CBCT images confirmed the configuration of the canals in the mesiobuccal and distobuccal roots to be Al-Qudah and Awawdeh type (3-2) and type (3-2-1), respectively, whereas the palatal root had a Vertucci type I canal pattern. This report reaffirms the importance of careful examination of the floor of the pulp chamber with a dental operating microscope and the use of multiangled preoperative radiographs along with advanced diagnostic aids such as CBCT in identification and successful management of aberrant canal morphologies.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Maxillary first molar with 7 root canals diagnosed using cone-beam computed tomography
Evaldo Rodrigues, Antônio Henrique Braitt, Bruno Ferraz Galvão, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
Restor Dent Endod. 2017;42(1):60-64. doi: 10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.60.
Reference
-
1. Slowey RR. Radiographic aids in the detection of extra root canals. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1974; 37:762–772.
Article2. Hartwell G, Bellizzi R. Clinical investigation of in vivo endodontically treated mandibular and maxillary molars. J Endod. 1982; 8:555–557.
Article3. Kulild JC, Peters DD. Incidence and configuration of canal systems in the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first and second molars. J Endod. 1990; 16:311–317.
Article4. Calişkan MK, Pehlivan Y, Sepetçioçlu F, Türkün M, Tuncer SS. Root canal morphology of human permanent teeth in a Turkish population. J Endod. 1995; 21:200–204.
Article5. Sert S, Bayirli GS. Evaluation of the root canal configurations of the mandibular and maxillary permanent teeth by gender in the Turkish population. J Endod. 2004; 30:391–398.
Article6. Kumar R. Report of a rare case: a maxillary first molar with seven canals confirmed with cone-beam computed tomography. Iran Endod J. 2014; 9:153–157.7. Badole GP, Warhadpande MM, Shenoi PR, Lachure C, Badole SG. A rare root canal configuration of bilateral maxillary first molar with 7 root canals diagnosed using cone-beam computed tomographic scanning: a case. J Endod. 2014; 40:296–301.
Article8. Kaushik M, Mehra N. Maxillary first molars with six canals diagnosed with the aid of cone beam computed tomography: a report of two cases. Case Rep Dent. 2013; 2013:406923.
Article9. Kakkar P, Singh A. Maxillary first molar with three mesiobuccal canals confirmed with spiral computer tomography. J Clin Exp Dent. 2012; 4:e256–e259.
Article10. Zhang P, Mao LS. Left maxillary first molar with three mesiobuccal canals: a case report. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 2011; 43:919–920.11. Ayranci LB, Arslan H, Topcuoglu HS. Maxillary first Molar with three canal orifices in MesioBuccal root. J Conserv Dent. 2011; 14:436–437.
Article12. Kottoor J, Velmurugan N, Surendran S. Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with eight root canal systems evaluated using cone-beam computed tomography scanning: a case report. J Endod. 2011; 37:715–719.
Article13. Du Y, Soo I, Zhang CF. A case report of six canals in a maxillary first molar. Chin J Dent Res. 2011; 14:151–153.14. Ma L, Yu J, Sun JJ. Maxillary first molar with three mesiobuccal root canals: a case report. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011; 29:102–103.15. Kottoor J, Velmurugan N, Sudha R, Hemamalathi S. Maxillary first molar with seven root canals diagnosed with cone-beam computed tomography scanning: a case report. J Endod. 2010; 36:915–921.
Article16. Garg AK, Tewari RK, Kumar A, Agrawal N. Endodontic treatment of a maxillary first molar having three mesiobuccal canals with the aid of spiral computed tomography: a case report. J Oral Sci. 2010; 52:495–499.
Article17. Favieri A, Barros FG, Campos LC. Root canal therapy of a maxillary first molar with five root canals: case report. Braz Dent J. 2006; 17:75–78.
Article18. Ferguson DB, Kjar KS, Hartwell GR. Three canals in the mesiobuccal root of a maxillary first molar: a case report. J Endod. 2005; 31:400–402.
Article19. Beatty RG. A five-canal maxillary first molar. J Endod. 1984; 10:156–157.
Article20. Martínez-Berná A, Ruiz-Badanelli P. Maxillary first molars with six canals. J Endod. 1983; 9:375–381.
Article21. Karthikeyan K, Mahalaxmi S. New nomenclature for extra canals based on four reported cases of maxillary first molars with six canals. J Endod. 2010; 36:1073–1078.
Article22. Maggiore F, Jou YT, Kim S. A six-canal maxillary first molar: case report. Int Endod J. 2002; 35:486–491.
Article23. Wong M. Maxillary first molar with three palatal canals. J Endod. 1991; 17:298–299.
Article24. Baratto Filho F, Zaitter S, Haragushiku GA, de Campos EA, Abuabara A, Correr GM. Analysis of the internal anatomy of maxillary first molars by using different methods. J Endod. 2009; 35:337–342.
Article25. Martins JN. Endodontic treatment of a maxillary first molar with seven root canals confirmed with cone beam computer tomography - case report. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014; 8:ZD13–ZD15.26. Al-Qudah AA, Awawdeh LA. Root and canal morphology of mandibular first and second molar teeth in a Jordanian population. Int Endod J. 2009; 42:775–784.
Article27. Cleghorn BM, Christie WH, Dong CC. Root and root canal morphology of the human permanent maxillary first molar: a literature review. J Endod. 2006; 32:813–821.
Article28. Degerness RA, Bowles WR. Dimension, anatomy and morphology of the mesiobuccal root canal system in maxillary molars. J Endod. 2010; 36:985–989.
Article29. Lee JH, Kim KD, Lee JK, Park W, Jeong JS, Lee Y, Gu Y, Chang SW, Son WJ, Lee WC, Baek SH, Bae KS, Kum KY. Mesiobuccal root canal anatomy of Korean maxillary first and second molars by cone-beam computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011; 111:785–791.
Article30. Kim Y, Lee SJ, Woo J. Morphology of maxillary first and second molars analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography in a Korean population: variations in the number of roots and canals and the incidence of fusion. J Endod. 2012; 38:1063–1068.
Article31. Verma P, Love RM. A Micro CT study of the mesiobuccal root canal morphology of the maxillary first molar tooth. Int Endod J. 2011; 44:210–217.
Article32. Kim Y, Chang SW, Lee JK, Chen IP, Kaufman B, Jiang J, Cha BY, Zhu Q, Safavi KE, Kum KY. A micro-computed tomography study of canal configuration of multiple-canalled mesiobuccal root of maxillary first molar. Clin Oral Investig. 2013; 17:1541–1546.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Management of a permanent maxillary first molar with unusual crown and root anatomy: a case report
- Detection of maxillary second molar with two palatal roots using cone beam computed tomography: a case report
- A cone-beam computed tomographic study of C-shaped root and root canal in maxillary molars
- Endodontic management of a C-shaped maxillary first molar with three independent buccal root canals by using cone-beam computed tomography
- Assessment of Root and Root Canal Morphology of Human Primary Molars using CBCT