Clin Endosc.
2017 Sep;50(5):464-472. 10.5946/ce.2016.161.
Carbon Dioxide versus Air Insufflation in Gastric Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hurley Medical Center/Michigan State University, Flint, MI, USA.
- KMID: 2394746
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.161
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) with air insufflation is commonly used for the staging and treatment of early gastric carcinoma. However, carbon dioxide (CO2) use has been shown to cause less post-procedural pain and fewer adverse events. The objective of this study was to compare the post-procedural pain and adverse events associated with COâ‚‚ and air insufflation in ESD.
METHODS
A systematic search was conducted for randomized control trials (RCTs) comparing the two approaches in ESD. The Mantel-Haenszel method was used to analyze the data. The mean difference (MD) and odds ratio (OR) were used for continuous and categorical variables, respectively.
RESULTS
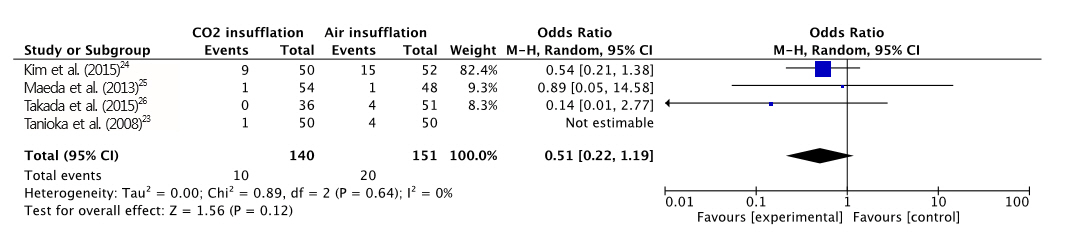
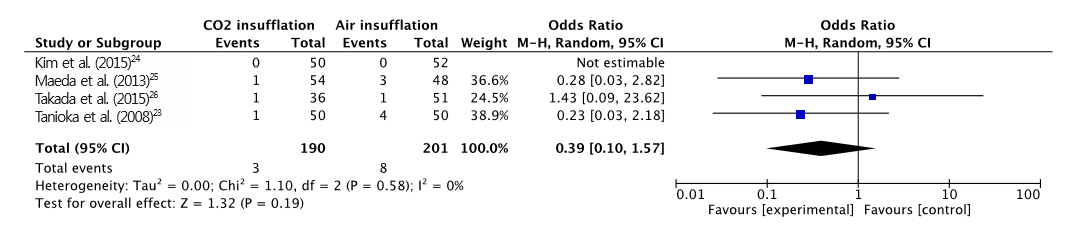
Four RCTs with a total of 391 patients who underwent ESD were included in our meta-analysis. The difference in maximal post-procedural pain between the two groups was statistically significant (MD, -7.41; 95% confidence interval [CI], -13.6 - -1.21; p=0.020). However, no significant differences were found in the length of procedure, end-tidal CO2, rate of perforation, and postprocedural hemorrhage between the two groups. The incidence of overall adverse events was significantly lower in the CO2 group (OR, 0.51; CI, 0.32-0.84; p=0.007).
CONCLUSIONS
: CO2 insufflation in gastric ESD is associated with less post-operative pain and discomfort, and a lower risk of overall adverse events compared with air insufflation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Effectiveness of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Healing of Ulcers after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Eunju Jeong, In kyung Yoo, Ozlem Ozer Cakir, Hee Kyung Kim, Won Hee Kim, Sung Pyo Hong, Joo Young Cho
Clin Endosc. 2019;52(5):472-478. doi: 10.5946/ce.2018.152.Carbon Dioxide Insufflation in Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection: Is It an Urgent Need?
Chang Seok Bang, Gwang Ho Baik
Clin Endosc. 2017;50(5):407-409. doi: 10.5946/ce.2017.127.
Reference
-
1. National Cancer Institute. Cancer stat facts: stomach cancer [Internet]. Rockville (MD): National Cancer Institute;c2016. [cited 2016 Nov 1]. Available from: http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/stomach.html.2. World Health Organization. Cancer [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization;c2017. [updated 2017 Feb; cited 2016 Nov 1]. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en/.3. Noguchi Y, Yoshikawa T, Tsuburaya A, Motohashi H, Karpeh MS, Brennan MF. Is gastric carcinoma different between Japan and the United States? Cancer. 2000; 89:2237–2246.
Article4. Gotoda T, Jung HY. Endoscopic resection (endoscopic mucosal resection/ endoscopic submucosal dissection) for early gastric cancer. Dig Endosc. 2013; 25 Suppl 1:55–63.
Article5. Gotoda T, Yamamoto H, Soetikno RM. Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol. 2006; 41:929–942.
Article6. Oda I, Saito D, Tada M, et al. A multicenter retrospective study of endoscopic resection for early gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2006; 9:262–270.
Article7. Oka S, Tanaka S, Kaneko I, et al. Advantage of endoscopic submucosal dissection compared with EMR for early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 64:877–883.
Article8. Watanabe K, Ogata S, Kawazoe S, et al. Clinical outcomes of EMR for gastric tumors: historical pilot evaluation between endoscopic submucosal dissection and conventional mucosal resection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:776–782.
Article9. Onozato Y, Ishihara H, Iizuka H, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancers and large flat adenomas. Endoscopy. 2006; 38:980–986.
Article10. Fujishiro M. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for stomach neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:5108–5112.
Article11. Takano A, Kobayashi M, Takeuchi M, et al. Capnographic monitoring during endoscopic submucosal dissection with patients under deep sedation: a prospective, crossover trial of air and carbon dioxide insufflations. Digestion. 2011; 84:193–198.
Article12. Sumanac K, Zealley I, Fox BM, et al. Minimizing postcolonoscopy abdominal pain by using CO2 insufflation: a prospective, randomized, double blind, controlled trial evaluating a new commercially available CO2 delivery system. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 56:190–194.13. Church J, Delaney C. Randomized, controlled trial of carbon dioxide insufflation during colonoscopy. Dis Colon Rectum. 2003; 46:322–326.
Article14. Nonaka S, Saito Y, Takisawa H, Kim Y, Kikuchi T, Oda I. Safety of carbon dioxide insufflation for upper gastrointestinal tract endoscopic treatment of patients under deep sedation. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24:1638–1645.
Article15. Bretthauer M, Thiis-Evensen E, Huppertz-Hauss G, et al. NORCCAP (Norwegian colorectal cancer prevention): a randomised trial to assess the safety and efficacy of carbon dioxide versus air insufflation in colonoscopy. Gut. 2002; 50:604–607.
Article16. Maeda Y, Hirasawa D, Fujita N, et al. A pilot study to assess mediastinal emphysema after esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection with carbon dioxide insufflation. Endoscopy. 2012; 44:565–571.
Article17. Saltzman HA, Sieker HO. Intestinal response to changing gaseous environments: normobaric and hyperbaric observations. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968; 150:31–39.
Article18. Beller EM, Glasziou PP, Altman DG, et al. PRISMA for abstracts: reporting systematic reviews in journal and conference abstracts. PLoS Med. 2013; 10:e1001419.
Article19. Wright RW, Brand RA, Dunn W, Spindler KP. How to write a systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 455:23–29.
Article20. Mori H, Kobara H, Muramatsu A, et al. Comparison of postoperative complications after endoscopic submucosal dissection: differences of insufflations and anesthesias. Diagn Ther Endosc. 2011; 2011:709237.
Article21. Suzuki T, Minami H, Komatsu T, et al. Prolonged carbon dioxide insufflation under general anesthesia for endoscopic submucosal dissection. Endoscopy. 2010; 42:1021–1029.
Article22. Takada J, Araki H, Onogi F, et al. Safety of carbon dioxide insufflation during gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection in patients with pulmonary dysfunction under conscious sedation. Surg Endosc. 2015; 29:1963–1969.
Article23. Tanioka D, Kawahara Y, Okada H, et al. Safety and efficacy of carbon dioxide (CO2) insufflation during endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for gastric cancer under propofol sedation: a randomized, controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 67:AB279.24. Kim SY, Chung JW, Park DK, Kwon KA, Kim KO, Kim YJ. Efficacy of carbon dioxide insufflation during gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection: a randomized, double-blind, controlled, prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 82:1018–1024.
Article25. Maeda Y, Hirasawa D, Fujita N, et al. A prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial on the efficacy of carbon dioxide insufflation in gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection. Endoscopy. 2013; 45:335–341.
Article26. Takada J, Araki H, Onogi F, et al. Safety and efficacy of carbon dioxide insufflation during gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection. World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21:8195–8202.
Article27. Verhagen AP, de Vet HC, de Bie RA, et al. The Delphi list: a criteria list for quality assessment of randomized clinical trials for conducting systematic reviews developed by Delphi consensus. J Clin Epidemiol. 1998; 51:1235–1241.28. Kontopantelis E, Springate DA, Reeves D. A re-analysis of the cochrane library data: the dangers of unobserved heterogeneity in meta-analyses. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e69930.
Article29. Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2005; 5:13.
Article30. Hawker GA, Mian S, Kendzerska T, French M. Measures of adult pain: visual analog scale for pain (VAS Pain), numeric rating scale for pain (NRS Pain), McGill pain questionnaire (MPQ), short-form McGill pain questionnaire (SF-MPQ), chronic pain grade scale (CPGS), short form-36 bodily pain scale (SF-36 BPS), and measure of intermittent and constant osteoarthritis pain (ICOAP). Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011; 63 Suppl 11:S240–S252.31. Wang WL, Wu ZH, Sun Q, et al. Meta-analysis: the use of carbon dioxide insufflation vs. room air insufflation for gastrointestinal endoscopy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 35:1145–1154.
Article32. ASGE Technology Committee, Lo SK, Fujii-Lau LL, et al. The use of carbon dioxide in gastrointestinal endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83:857–865.
Article33. Dellon ES, Hawk JS, Grimm IS, Shaheen NJ. The use of carbon dioxide for insufflation during GI endoscopy: a systematic review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:843–849.
Article34. Maple JT, Keswani RN, Hovis RM, et al. Carbon dioxide insufflation during ERCP for reduction of postprocedure pain: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 70:278–283.
Article35. Bretthauer M, Seip B, Aasen S, Kordal M, Hoff G, Aabakken L. Carbon dioxide insufflation for more comfortable endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: a randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. Endoscopy. 2007; 39:58–64.
Article36. Bretthauer M, Hoff G, Thiis-Evensen E, et al. Carbon dioxide insufflation reduces discomfort due to flexible sigmoidoscopy in colorectal cancer screening. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2002; 37:1103–1107.
Article37. Stevenson GW, Wilson JA, Wilkinson J, Norman G, Goodacre RL. Pain following colonoscopy: elimination with carbon dioxide. Gastrointest Endosc. 1992; 38:564–567.
Article38. Wong JC, Yau KK, Cheung HY, Wong DC, Chung CC, Li MK. Towards painless colonoscopy: a randomized controlled trial on carbon dioxide-insufflating colonoscopy. ANZ J Surg. 2008; 78:871–874.
Article39. Shi H, Chen S, Swar G, Wang Y, Ying M. Carbon dioxide insufflation during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: a review and meta-analysis. Pancreas. 2013; 42:1093–1100.40. Kikuchi T, Fu KI, Saito Y, et al. Transcutaneous monitoring of partial pressure of carbon dioxide during endoscopic submucosal dissection of early colorectal neoplasia with carbon dioxide insufflation: a prospective study. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24:2231–2235.
Article41. Saito Y, Uraoka T, Matsuda T, et al. A pilot study to assess the safety and efficacy of carbon dioxide insufflation during colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection with the patient under conscious sedation. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 65:537–542.
Article42. Yoshida M, Imai K, Hotta K, et al. Carbon dioxide insufflation during colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection for patients with obstructive ventilatory disturbance. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2014; 29:365–371.
Article43. Maeda Y, Hirasawa D, Fujita N, et al. Carbon dioxide insufflation in esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection reduces mediastinal emphysema: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. World J Gastroenterol. 2016; 22:7373–7382.
Article44. Rai A, Iftikhar S. Tension pneumothorax complicating diagnostic upper endoscopy: a case report. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999; 94:845–847.
Article45. Green BT, Tendler DA. Cerebral air embolism during upper endoscopy: case report and review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 61:620–623.
Article46. Hayakawa M, Gando S, Kameue T, Morimoto Y, Kemmotsu O. Abdominal compartment syndrome and intrahepatic portal venous gas: a possible complication of endoscopy. Intensive Care Med. 2002; 28:1680–1681.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Carbon Dioxide Insufflation in Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection: Is It an Urgent Need?
- Insufflation of Carbon Dioxide versus Air During Colonoscopy Among Pediatric Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Difficult colonoscopy: air, carbon dioxide, or water insufflation?
- Can water insufflation and carbon dioxide overcome the difficulties of colonoscope insertion?
- Clinical Trial of Tracheal Gas Insufflation to Control Hypercapnia Occured during Laparoscopic Surgery: A Case Report