Nutr Res Pract.
2016 Aug;10(4):424-432. 10.4162/nrp.2016.10.4.424.
Perception and practice regarding allergen labeling: focus on food-related employees
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Foodservice Management and Nutrition, Sangmyung University, 20 Hongjimun 2-gil, Jongno-gu, Seoul 03016, Korea. wshong@smu.ac.kr
- 2Research Institute of Natural Science, Sangmyung University, Seoul 03016, Korea.
- 3Department of Food and Nutrition, Yonsei University, Seoul 03722, Korea.
- KMID: 2390146
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2016.10.4.424
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
Most consumers are able to recognize allergenic foods. However, the frequency of checking such foods is reportedly low, resulting in higher prevalence of food-related allergic reactions in Korea compared to other countries. Thus, this study was performed to investigate the overall perception of allergenic food labeling and its practice level in food manufacturing company employees.
SUBJECTS/METHODS
The survey was administered to food safety employees and food development teams at food companies located in metropolitan areas. A total of 399 (93.8%) valid samples were used in the final analysis. Statistical analyses, including Frequency Analysis, t-test, Anova, PCA (Principal Component Analysis), and Pearson Correlation Analysis using SPSS ver. 21.0, were performed.
RESULTS
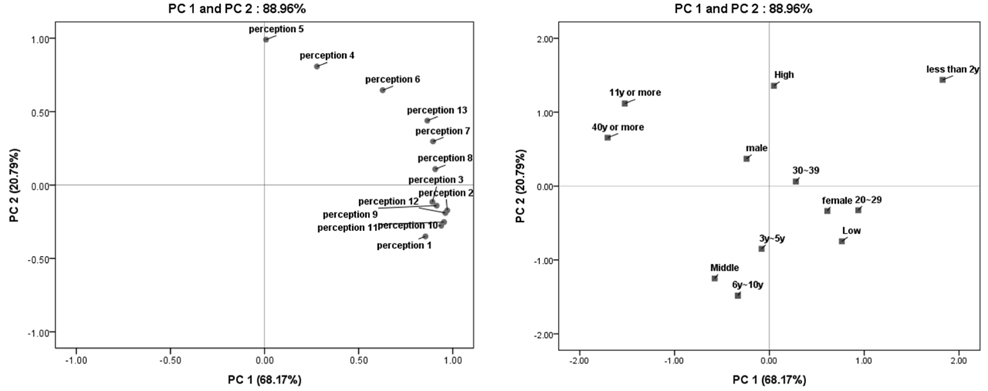
The correct answer rate in the analysis of allergy-related knowledge level ranged from 15.0% to 89.7%. Analysis of differences in allergy-related perception by knowledge level showed significant differences in introduction of a food recall system, strengthening of relevant laws and regulations, content labeling, description of substitutional food, and differentiated package by age.
CONCLUSIONS
It can be concluded that labeling of allergenic foods should be made easier and more convenient for checking by employees, developers, and consumers, and it is necessary to provide contents through the development of publicity, guidelines, or APP along with labeling.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Branum AM, Lukacs SL. Food allergy among U.S. children: trends in prevalence and hospitalizations. NCHS Data Brief. 2008; 10:1–8.2. Kanny G, Moneret-Vautrin DA, Flabbee J, Beaudouin E, Morisset M, Thevenin F. Population study of food allergy in France. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108:133–140.
Article3. Sicherer SH. Epidemiology of food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:594–602.
Article4. Seo WH, Jang EY, Han YS, Ahn KM, Jung JT. Management of food allergies in young children at a child care center and hospital in Korean. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2011; 21:32–38.
Article5. Sicherer SH, Sampson HA. Food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:S116–S125.
Article6. Kim WK. Diagnosis and treatment of food allergy in children. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2006; 16:274–283.7. Sampson HA, Muñoz-Furlong A, Campbell RL, Adkinson NF Jr, Bock SA, Branum A, Brown SG, Camargo CA Jr, Cydulka R, Galli SJ, Gidudu J, Gruchalla RS, Harlor AD Jr, Hepner DL, Lewis LM, Lieberman PL, Metcalfe DD, O'Connor R, Muraro A, Rudman A, Schmitt C, Scherrer D, Simons FE, Thomas S, Wood JP, Decker WW. Second symposium on the definition and management of anaphylaxis: summary report Second National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease/Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Network symposium. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 117:391–397.
Article8. Hong SJ, Ahn KM, Lee SY, Kim KE. The prevalences of asthma and allergic diseases in Korean children. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:343–350.
Article9. Oh JW, Pyun BY, Choung JT, Ahn KM, Kim CH, Song SW, Son JA, Lee SY, Lee SI. Epidemiological change of atopic dermatitis and food allergy in school-aged children in Korea between 1995 and 2000. J Korean Med Sci. 2004; 19:716–723.
Article10. Lee SI, Shin MH, Lee HB, Lee JS, Son BK, Koh YY, Kim KE, Ahn YO. Prevalences of symptoms of asthma and other allergic diseases in Korean children: a nationwide questionnaire survey. J Korean Med Sci. 2001; 16:155–164.
Article11. Hong SJ. Korean ISAAC Study Group of Korean Association of Allergy and Respiratory Diseases: report of Korean ISAAC epidemiologic study for asthma and allergic diseases in children. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2007; 17:S55–S66.12. Ewan PW, Clark AT. Long-term prospective observational study of patients with peanut and nut allergy after participation in a management plan. Lancet. 2001; 357:111–115.
Article13. U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition. Food Allergen Labeling and Consumer Protection Act of 2004 (Public Law 108-282, Title II). Silver Spring (MD): U.S. Food and Drug Administration;2004.14. Mills EN, Valovirta E, Madsen C, Taylor SL, Vieths S, Anklam E, Baumgartner S, Koch P, Crevel RW, Frewer L. Information provision for allergic consumers--where are we going with food allergen labelling? Allergy. 2004; 59:1262–1268.
Article15. Korea Food and Drug Administration. Allergenic Food Labeling Act 2003-27. Seoul: Korea Food and Drug Administration;2003.16. Sampson HA. Food allergy. Part 1: immunopathogenesis and clinical disorders. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 103:717–728.
Article17. Lee AH, Kim KE, Lee KE, Kim SH, Wang TW, Kim KW, Kwak TK. Prevalence of food allergy and perceptions on food allergen labeling in school foodservice among Korean students. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:227–234.
Article18. Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (KR). Perception of Allergenic School Food Manual. Seoul: Ministry of Education, Science and Technology;2012.19. Gendel SM. Comparison of international food allergen labeling regulations. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2012; 63:279–285.
Article20. Ministry of Education (KR). Statistics on School Foodservice. Seoul: Ministry of Education;2011.21. Kwak TK, Chung MS, Park SE, Paik JK, Hong WS. Understanding and importance-performance analysis of food allergen labeling system. Korean J Food Cookery Sci. 2014; 30:325–332.
Article22. Lee SY, Kim KW, Ahn K, Kim HH, Pyun BY, Park YM, Kim KE. Consumer's use and satisfaction of allergic food labels. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2011; 21:294–301.
Article23. Yang SH, Kim EJ, Kim YN, Seong KS, Kim SS, Han CK, Lee BH. Comparison of eating habits and dietary intake patterns between people with and without allergy. Korean J Nutr. 2009; 42:523–535.
Article24. Kim YM, Heo YR, Ro HK. Perception and practices regarding food allergy of elementary and middle school nutritionists in the Jeonnam area. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2014; 43:151–161.
Article25. Han JS, Hong SO, Kim JS, Han JP, Kim NS. Frequency of food allergy in Korea and the causative food allergens. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 1997; 26:1–9.26. Park JY, Park GY, Han YS, Shin MY. Survey of food allergy in elementary school children in Bucheon-city and relationship between food allergy and other allergic diseases. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:266–273.
Article27. Choi JH, Rajagopal L. Food allergy knowledge, attitudes, practices, and training of foodservice workers at a university foodservice operation in the midwestern united states. Food Contr. 2013; 31:474–481.
Article28. Kim MJ. Consumer research for improve the food allergy labeling [master's thesis]. Seoul: Sookmyung Women's University;2013.29. Kim CJ. Study of Detection Methods for Food Allergen: Standardization of Detection Method for Food Allergen and Research on the Actual Condition of Egg Allergen in Processed Food. Seoul: Korea Food and Drug Administration;2007. p. 5–8.30. Youn SM. Guidance on allergen labeling and the requirements in regulation in U.K. BRC (British Retail Consortium). Health Welf Policy Forum. 2013; 201:80–93.31. Ajala AR, Cruz AG, Faria JA, Walter EH, Granato D, Sant'Ana AS. Food allergens: knowledge and practices of food handlers in restaurants. Food Contr. 2010; 21:1318–1321.
Article32. Cornelisse-Vermaat JR, Voordouw J, Yiakoumaki V, Theodoridis G, Frewer LJ. Food-allergic consumers' labelling preferences: a cross-cultural comparison. Eur J Public Health. 2008; 18:115–120.
Article33. Goossens NJ, Flokstra-de Blok BM, van der Meulen GN, Botjes E, Burgerhof HG, Gupta RS, Springston EE, Smith B, Duiverman EJ, Dubois AE. Food allergy knowledge of parents - is ignorance bliss? Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2013; 24:567–573.
Article34. Gupta RS, Kim JS, Springston EE, Smith B, Pongracic JA, Wang X, Holl J. Food allergy knowledge, attitudes, and beliefs in the United States. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2009; 103:43–50.
Article35. Park JH. Perception analysis of food allergen labeling system for consumers and parents of food-allergenic children [master's thesis]. Seoul: Yonsei University;2015.36. Choi JH. Food allergy perception providing safe meals: food and nutrition and childhood education students. Korean J Community Living Sci. 2015; 26:63–74.
Article37. Marietta AB, Welshimer KJ, Anderson SL. Knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors of college students regarding the 1990 Nutrition Labeling Education Act food labels. J Am Diet Assoc. 1999; 99:445–449.
Article38. Satia JA, Galanko JA, Neuhouser ML. Food nutrition label use is associated with demographic, behavioral, and psychosocial factors and dietary intake among African Americans in North Carolina. J Am Diet Assoc. 2005; 105:392–402.
Article39. Misra R. Knowledge, attitudes, and label use among college students. J Am Diet Assoc. 2007; 107:2130–2134.
Article40. Prasad A, Strijnev A, Zhang Q. What can grocery basket data tell us about health consciousness? Int J Res Mark. 2008; 25:301–309.
Article41. Simons FE. Anaphylaxis: Recent advances in assessment and treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:625–636.
Article42. Mofidi S. Nutritional management of pediatric food hypersensitivity. Pediatrics. 2003; 111:1645–1653.
Article43. Fiocchi A, Martelli A. Dietary management of food allergy. Pediatr Ann. 2006; 35:755–756.
Article44. Kim E, Ham S, Yang IS, Choi JG. The roles of attitude, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control in the formation of consumers' behavioral intentions to read menu labels in the restaurant industry. Int J Hosp Manag. 2013; 35:203–213.
Article45. Kwon KI, Yoon SW, Kim SJ, Kang H, Kim HN, Kim JY, Kim SY, Kim K, Lee JH, Jung SM, Ock SW, Lee EJ, Kim JW, Kim MC, Park HK. A survey on customers' perceptions of nutrition labeling for processed food and restaurant meal. Korean J Nutr. 2010; 43:181–188.
Article46. Kim HY. Consumers' perceptions and behavioral intentions toward menu labeling for restaurants [master's thesis]. Seoul: Yonsei University;2014.47. Choi Y, Ju S, Chang H. Food allergy knowledge, perception of food allergy labeling, and level of dietary practice: A comparison between children with and without food allergy experience. Nutr Res Pract. 2015; 9:92–98.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Perceptions of Food Allergen Labeling in School Meal Service among Middle School Girls in Incheon
- Prevalence of food allergy and perceptions on food allergen labeling in school foodservice among Korean students
- A study on the consumer's perception of front-of-pack nutrition labeling
- Food allergy knowledge, perception of food allergy labeling, and level of dietary practice: A comparison between children with and without food allergy experience
- Perception on Nutrition Labeling of the Processed Food among Elementary School Teachers in Busan