Ann Dermatol.
2017 Aug;29(4):422-426. 10.5021/ad.2017.29.4.422.
Gene Expression Analysis of Inflammatory Cytokines in Korean Psoriatic Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea. cjpark777smp@gmail.com
- KMID: 2388939
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.4.422
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Although phenotypic heterogeneity of psoriasis is suggested by the alternate activation of either T-helper (Th)1-related or Th17-related cytokines, little is known about the mRNA levels of inflammatory cytokines.
OBJECTIVE
To investigate whether there is differential expression of Th1-related and Th17-related inflammatory cytokine genes 1) between psoriatic patients and healthy controls, and 2) between patients with different psoriasis phenotypes.
METHODS
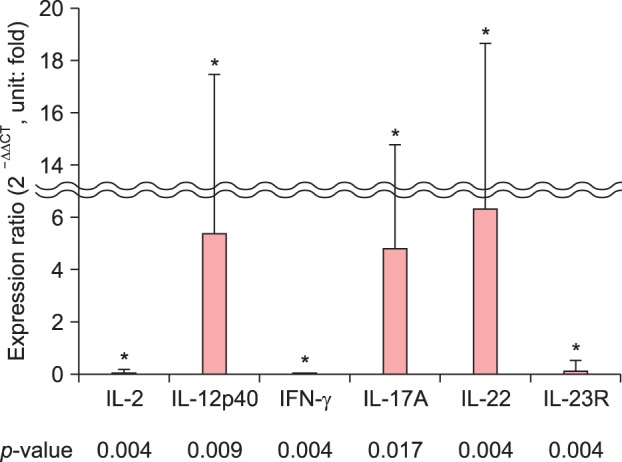
Twenty-five patients with psoriasis (10 with guttate psoriasis and 15 with plaque psoriasis) and 5 healthy volunteers were enrolled in this study. The mRNA levels of circulating cytokines (interleukin [IL]-2, IL-12p40, interferon-γ, IL-17A, IL-22, and IL-23R) were measured by real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.
RESULTS
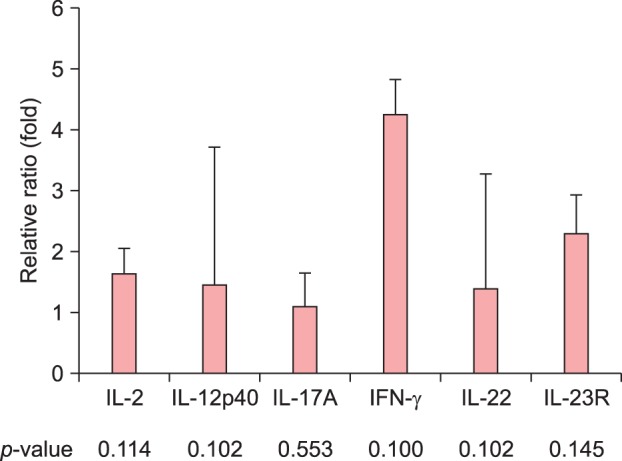
The comparison between psoriatic and healthy control samples revealed that IL-12p40, IL-17A, and IL-22 mRNA levels were significantly higher (approximately 4∼6 folds) in the patients with psoriasis. The mRNA levels of these six cytokines in the blood did not differ between the guttate and plaque psoriasis groups.
CONCLUSION
We found that the mRNA levels of blood inflammatory cytokines (IL-12p40, IL-17A, and IL-22) were significantly elevated in patients with psoriasis compared to the levels in healthy controls, but they did not significantly differ between patients with guttate and plaque type psoriasis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nestle FO, Kaplan DH, Barker J. Psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:496–509. PMID: 19641206.
Article2. Wrone-Smith T, Nickoloff BJ. Dermal injection of immunocytes induces psoriasis. J Clin Invest. 1996; 98:1878–1887. PMID: 8878440.
Article3. Bos JD. The pathomechanisms of psoriasis; the skin immune system and cyclosporin. Br J Dermatol. 1988; 118:141–155. PMID: 3279998.
Article4. Rustin MH. Long-term safety of biologics in the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: review of current data. Br J Dermatol. 2012; 167(Suppl 3):3–11. PMID: 23082810.
Article5. Christophers E. Explaining phenotype heterogeneity in patients with psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2008; 158:437–441. PMID: 18047519.
Article6. Pietrzak AT, Zalewska A, Chodorowska G, Krasowska D, Michalak-Stoma A, Nockowski P, et al. Cytokines and anticytokines in psoriasis. Clin Chim Acta. 2008; 394:7–21. PMID: 18445484.
Article7. Griffiths CE, Christophers E, Barker JN, Chalmers RJ, Chimenti S, Krueger GG, et al. A classification of psoriasis vulgaris according to phenotype. Br J Dermatol. 2007; 156:258–262. PMID: 17223864.
Article8. Williams RC, Mckenzie AW, Roger JH, Joysey VC. HL-A antigens in patients with guttate psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 1976; 95:163–167. PMID: 952752.
Article9. Choe YB, Hwang YJ, Hahn HJ, Jung JW, Jung HJ, Lee YW, et al. A comparison of serum inflammatory cytokines according to phenotype in patients with psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2012; 167:762–767. PMID: 22564054.
Article10. Hwang YJ, Jung HJ, Kim MJ, Roh NK, Jung JW, Lee YW, et al. Serum levels of LL-37 and inflammatory cytokines in plaque and guttate psoriasis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014; 2014:268257. PMID: 25197165.
Article11. Roh NK, Han SH, Youn HJ, Kim YR, Lee YW, Choe YB, et al. Tissue and serum inflammatory cytokine levels in Korean psoriasis patients: a comparison between plaque and guttate psoriasis. Ann Dermatol. 2015; 27:738–743. PMID: 26719644.
Article12. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001; 25:402–408. PMID: 11846609.13. Lee E, Zarei M, Lasenna C, Villada G, Romanelli P. Psoriasis targeted therapy: characterization of interleukin 17A expression in subtypes of psoriasis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015; 14:1133–1136. PMID: 26461825.14. Yilmaz SB, Cicek N, Coskun M, Yegin O, Alpsoy E. Serum and tissue levels of IL-17 in different clinical subtypes of psoriasis. Arch Dermatol Res. 2012; 304:465–469. PMID: 22426986.
Article15. Nakajima H, Nakajima K, Tarutani M, Morishige R, Sano S. Kinetics of circulating Th17 cytokines and adipokines in psoriasis patients. Arch Dermatol Res. 2011; 303:451–455. PMID: 21681565.
Article16. Takahashi H, Tsuji H, Hashimoto Y, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Iizuka H. Serum cytokines and growth factor levels in Japanese patients with psoriasis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010; 35:645–649. PMID: 19843085.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Interleukin-8 Expression in Psoriatic Skin of Different Disease Activities
- Psoriatic Serum Induce an Abnormal Inflammatory Phenotype and a Decreased Immunosuppressive Function of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- A Global Gene Expression Analysis of the Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Reveals the Gene Expression Signature in Psoriasis
- Expression of Neuropeptides and Their Receptors in Psoriatic Lesions
- Gene Expression Profile Analysis by cDNA Array in the Subacromial Bursa of Patients with Rotator Cuff Disease