J Korean Soc Transplant.
2017 Jun;31(2):87-90. 10.4285/jkstn.2017.31.2.87.
Late Onset Renal Vein Thrombosis after Kidney Transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine and Keimyung University Kidney Institute, Daegu, Korea. hansy@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2385534
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/jkstn.2017.31.2.87
Abstract
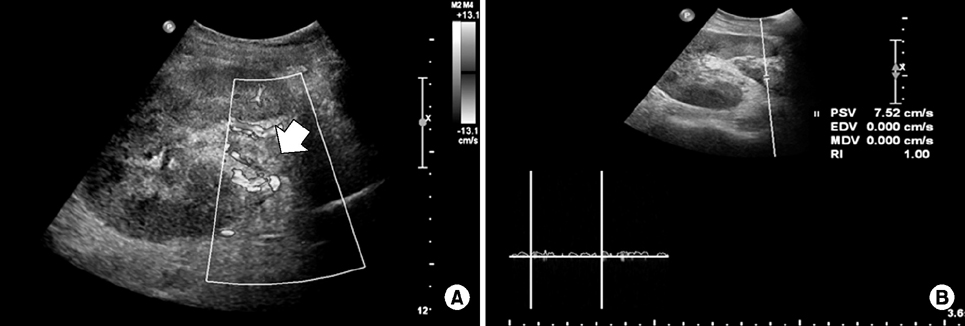
- Renal vein thrombosis is a rare but serious cause of graft loss in kidney transplant recipients that is usually associated with early surgical complications. Here, we report a rare case of sudden development of late onset renal vein thrombosis after kidney transplantation. A 32-year-old man underwent deceased kidney transplantation 2 years prior. Oliguria and pain suddenly developed at the allograft site along with an elevated serum creatinine level. Doppler ultrasound showed absence of venous flow in the transplanted kidney. Magnetic resonance imaging showed thrombosis from the allograft vein to the anastomosis with the left common iliac vein and a swollen allograft kidney. The patient underwent anticoagulation with unfractionated heparin and warfarin. Serum creatinine normalized and renal vein thrombosis disappeared after 3 months of treatment. Late-onset renal vein thrombosis is rare; however, early detection and treatment are very important to restore renal allograft function.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Irish A. Renal allograft thrombosis: can thrombophilia explain the inexplicable? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999; 14:2297–2303.
Article2. Ripert T, Menard J, Schoepen Y, Nguyen P, Rieu P, Staerman F. Preventing graft thrombosis after renal transplantation: a multicenter survey of clinical practice. Transplant Proc. 2009; 41:4193–4196.
Article3. Hogan JL, Rosenthal SJ, Yarlagadda SG, Jones JA, Schmitt TM, Kumer SC, et al. Late-onset renal vein thrombosis: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015; 6C:73–76.
Article4. Golden J, Stone RA, Goldberger L. Immune-related renal vein thrombosis in a renal allograft. Ann Intern Med. 1976; 85:612–613.
Article5. Abramowicz D, Pradier O, Marchant A, Florquin S, De Pauw L, Vereerstraeten P, et al. Induction of thromboses within renal grafts by high-dose prophylactic OKT3. Lancet. 1992; 339:777–778.
Article6. Irish AB, Green FR, Gray DW, Morris PJ. The factor V Leiden (R506Q) mutation and risk of thrombosis in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation. 1997; 64:604–607.
Article7. Ramirez PJ, Gohh RY, Kestin A, Monaco AP, Morrissey PE. Renal allograft loss due to proximal extension of ileofemoral deep venous thrombosis. Clin Transplant. 2002; 16:310–313.
Article8. Asghar M, Ahmed K, Shah SS, Siddique MK, Dasgupta P, Khan MS. Renal vein thrombosis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2007; 34:217–223.
Article9. Giustacchini P, Pisanti F, Citterio F, De Gaetano AM, Castagneto M, Nanni G. Renal vein thrombosis after renal transplantation: an important cause of graft loss. Transplant Proc. 2002; 34:2126–2127.
Article10. Li SJ, Tu YM, Zhou CS, Zhang LH, Liu ZH. Risk factors of venous thromboembolism in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis with nephrotic syndrome. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2016; 20:212–217.
Article11. Bakir N, Sluiter WJ, Ploeg RJ, van Son WJ, Tegzess AM. Primary renal graft thrombosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1996; 11:140–147.
Article12. Kamel MH, Mohan P, Conlon PJ, Little DM, O'Kelly P, Hickey DP. Rabbit antithymocyte globulin related decrease in platelet count reduced risk of pediatric renal transplant graft thrombosis. Pediatr Transplant. 2006; 10:816–821.
Article13. Ponticelli C, Moia M, Montagnino G. Renal allograft thrombosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009; 24:1388–1393.
Article14. Jones JA, Rosenthal SJ. Late onset of renal vein thrombosis after renal transplantation. Ultrasound Q. 2014; 30:228–229.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ipsilateral leg swelling after renal transplantation as an alarming sign of Iliac vein stenosis
- A case of Renal Vein Thorombosis Associated with Nephrotic Syndrome
- A Case of Replacement Lipomatosis of Allograft Kidney Presented with Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Spontaneous Renal Allograft Rupture Caused by Arteriovenous Fistula: 1 case
- A Case of Renal Vein Thrombosis in a Patient with Lung and Uterine Cervical Cancer