J Bone Metab.
2017 May;24(2):97-103. 10.11005/jbm.2017.24.2.97.
Paget's Disease: Skeletal Manifestations and Effect of Bisphosphonates
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kyang@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2379991
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2017.24.2.97
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Paget's disease of bone leads to change in the shape and size of the bone and results in reduced bone strength, leading to the complications of deformity, arthritis, and fracture. Due to unknown reasons, Paget's disease is rare in Asian descendants. We report the cases of Paget's disease who visited our institute for 15 years and reviewed the literatures.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records and radiograms of 8 patients (6 female and 2 male) who were diagnosed as Paget's disease of bone. Diagnosis was confirmed by typical radiological feature in the involved skeletons and/or pathologic findings.
RESULTS
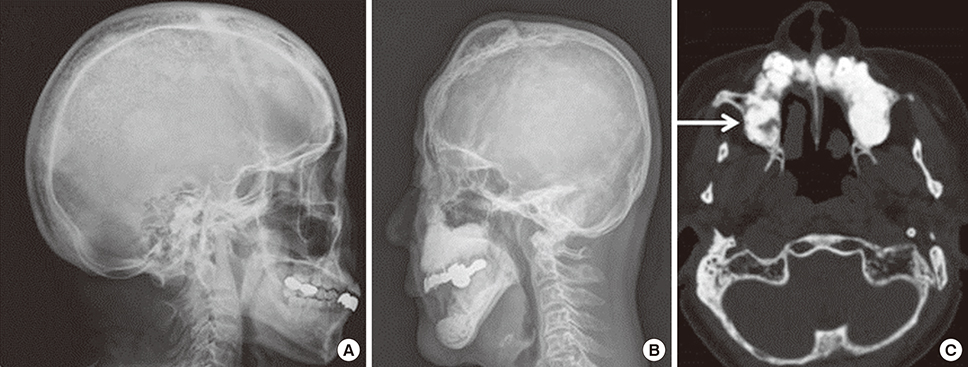
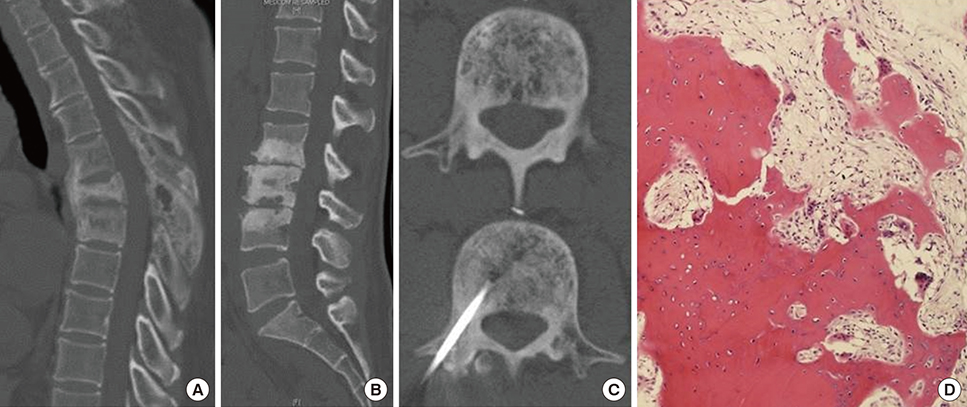
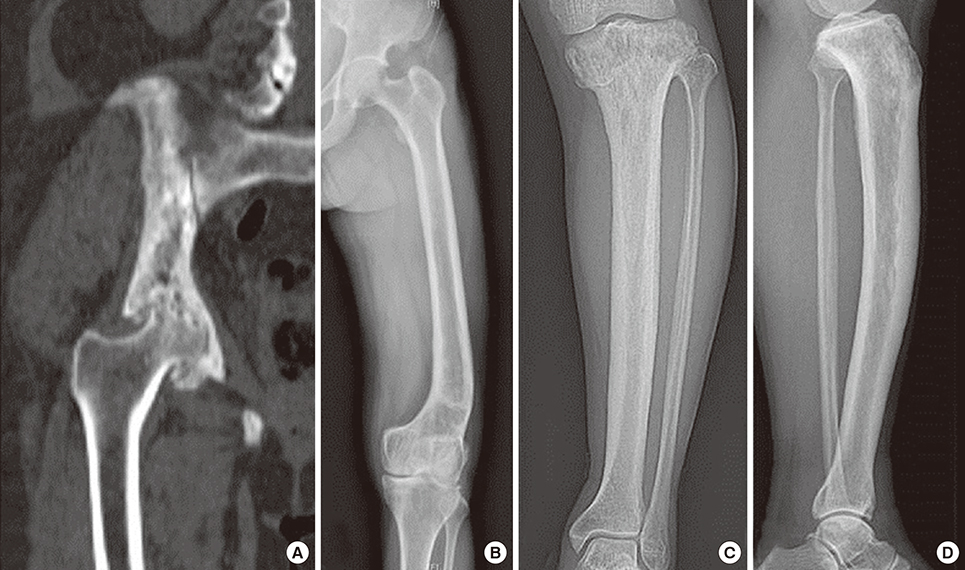
Pelvis, skull and spine were three most frequently involved bones. All involved bones in our cases showed changes in shape and trabecular pattern which resulted in bowing of lower extremity, secondary osteoarthritis, compression fracture of spine and enlargement of skull. Mean follow time was 4.71 years and all patient were treated bisphosphonate (BP). Use of BP controlled the level of serum alkaline phosphatase level effectively.
CONCLUSIONS
We have reviewed eight patients who were previously diagnosed as Paget's disease of bone in our institute. We could identify typical radiologic and clinical findings such as bowing deformity of long bone, secondary osteoarthritis, compression fracture and osteomyelitis of mandible that deteriorated the quality of their living.
MeSH Terms
-
Alkaline Phosphatase
Arthritis
Asian Continental Ancestry Group
Congenital Abnormalities
Diagnosis
Diphosphonates*
Female
Fractures, Compression
Humans
Lower Extremity
Mandible
Medical Records
Osteitis Deformans
Osteoarthritis
Osteomyelitis
Pelvis
Retrospective Studies
Skeleton
Skull
Spine
Alkaline Phosphatase
Diphosphonates
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Paget's Disease of Bone Affecting Peripheral Limb: Difficulties in Diagnosis: A Case Report
Jun-Ku Lee, Yun Kyung Kang, Pei Wei Wang, Soo Min Hong
J Bone Metab. 2020;27(1):71-75. doi: 10.11005/jbm.2020.27.1.71.Updates on Paget’s Disease of Bone
Yong Jun Choi, Young Bae Sohn, Yoon-Sok Chung
Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(5):732-743. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2022.1575.
Reference
-
1. Webb NR, Jesse MK. Hip pain. Bisphosphonate-related atypical subtrochanteric femoral fracture in patient with Paget disease. Skeletal Radiol. 2016; 45:825–826. 853–854.2. Rosen CJ, Compston JE, Lian JB, editors. Primer on the metabolic bone diseases and disorders of mineral metabolism. 7th ed. Washington, DC: American Society for Bone and Mineral Research;2008.3. Galson DL, Roodman GD. Pathobiology of paget's disease of bone. J Bone Metab. 2014; 21:85–98.
Article4. Chung YG, Kang YK, Rhee SK, et al. Skeletal manifestation of Paget's disease in Korean. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2002; 37:649–653.
Article5. Bhargava P, Maki JH. Images in clinical medicine. “Cotton wool” appearance of Paget's disease. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:e9.6. Khosla S, Burr D, Cauley J, et al. Bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw: report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res. 2007; 22:1479–1491.
Article7. Park YC, Song HK, Zheng XL, et al. Intramedullary nailing for atypical femoral fracture with excessive anterolateral bowing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017; 99:726–735.
Article8. Koh JS, Goh SK, Png MA, et al. Femoral cortical stress lesions in long-term bisphosphonate therapy: a herald of impending fracture? J Orthop Trauma. 2010; 24:75–81.
Article9. Tan A, Goodman K, Walker A, et al. Long-term randomized trial of intensive versus symptomatic management in Paget's disease of bone: The PRISM-EZ study. J Bone Miner Res. 2017; DOI: 10.1002/jbmr.3066.
Article10. Yang KH, Min BW, Ha YC. Atypical femoral fracture: 2015 position statement of the Korean society for bone and mineral research. J Bone Metab. 2015; 22:87–91.
Article11. Won Y, Lim JR, Kim YH, et al. Atypical femoral fracture combined with osteonecrosis of jaw during osteoporosis treatment with bisphosphonate. J Bone Metab. 2014; 21:155–159.
Article12. Oh Y, Wakabayashi Y, Kurosa Y, et al. Stress fracture of the bowed femoral shaft is another cause of atypical femoral fracture in elderly Japanese: a case series. J Orthop Sci. 2014; 19:579–586.
Article13. Shane E, Burr D, Abrahamsen B, et al. Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures: second report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res. 2014; 29:1–23.
Article14. Cho JW, Oh CW, Leung F, et al. Healing of atypical subtrochanteric femur fractures after cephalomedullary nailing: which factors predict union? J Orthop Trauma. 2017; 31:138–145.
Article15. Lim HS, Kim CK, Park YS, et al. Factors associated with increased healing time in complete femoral fractures after long-term bisphosphonate therapy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016; 98:1978–1987.
Article16. Reid IR, Sharma S, Kalluru R, et al. Treatment of Paget's disease of bone with denosumab: case report and literature review. Calcif Tissue Int. 2016; 99:322–325.
Article17. Sun LM, Lin MC, Muo CH, et al. Calcitonin nasal spray and increased cancer risk: a population-based nested case-control study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 99:4259–4264.
Article18. Wells G, Chernoff J, Gilligan JP, et al. Does salmon calcitonin cause cancer? A review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2016; 27:13–19.
Article