Clin Nutr Res.
2017 Jan;6(1):61-67. 10.7762/cnr.2017.6.1.61.
Diabetes Management via a Mobile Application: a Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dietetics, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Seoul 03181, Korea. emkim82@gmail.com
- 2Seoul Regional Headquarters, Health Maintenance & Promotion Center, National Health Insurance Service, Seoul 07241, Korea.
- 3Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 03181, Korea.
- KMID: 2377803
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7762/cnr.2017.6.1.61
Abstract
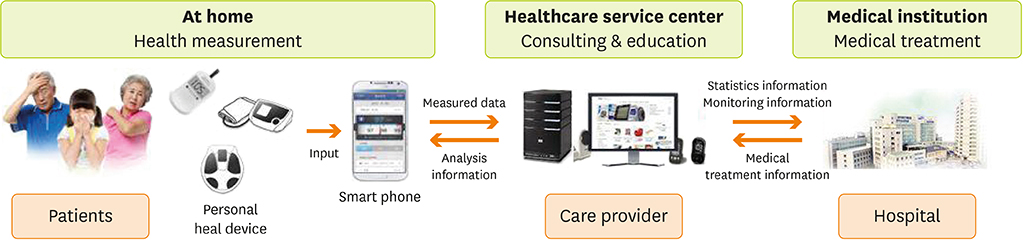
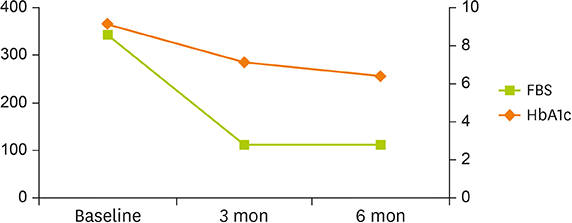
- Recently, mobile health care has been applied to manage diabetes requiring self-management. Health care by mobile applications (apps) has a great advantage when applied to patients with diabetes; the adherence to self-management activities for diabetes can be improved through mobile apps. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has cleared and approved the use of some mobile apps as medical devices for the management of diabetes since 2010. However, mobile apps may not be effective for all patients. We here report the effect of use of mobile-based diabetes care app (Healthy-note app) for 2 patients with diabetes, and discuss issues and strategies for effective mobile intervention. Further study is needed on improving patient's participation to increase the effect of management via a mobile app.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Free C, Phillips G, Felix L, Galli L, Patel V, Edwards P. The effectiveness of M-health technologies for improving health and health services: a systematic review protocol. BMC Res Notes. 2010; 3:250.2. Fiordelli M, Diviani N, Schulz PJ. Mapping mHealth research: a decade of evolution. J Med Internet Res. 2013; 15:e95.3. Quinn CC, Shardell MD, Terrin ML, Barr EA, Ballew SH, Gruber-Baldini AL. Cluster-randomized trial of a mobile phone personalized behavioral intervention for blood glucose control. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34:1934–1942.
Article4. Hood M, Wilson R, Corsica J, Bradley L, Chirinos D, Vivo A. What do we know about mobile applications for diabetes self-management? A review of reviews. J Behav Med. 2016; 39:981–994.
Article5. Yoo SH. Effects of smartphone application on diabetes management: randomized controlled trial [master's thesis]. Seoul: Ewha Womans University;2014.
Article6. Liang X, Wang Q, Yang X, Cao J, Chen J, Mo X, Huang J, Wang L, Gu D. Effect of mobile phone intervention for diabetes on glycaemic control: a meta-analysis. Diabet Med. 2011; 28:455–463.
Article7. Cho JH, Chang SA, Kwon HS, Choi YH, Ko SH, Moon SD, Yoo SJ, Song KH, Son HS, Kim HS, Lee WC, Cha BY, Son HY, Yoon KH. Long-term effect of the internet-based glucose monitoring system on HbA1c reduction and glucose stability: a 30-month follow-up study for diabetes management with a ubiquitous medical care system. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29:2625–2631.8. Waki K, Fujita H, Uchimura Y, Omae K, Aramaki E, Kato S, Lee H, Kobayashi H, Kadowaki T, Ohe K. DialBetics: a novel smartphone-based self-management support system for type 2 diabetes patients. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2014; 8:209–215.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Six-month Outcomes of Mobile Phone Application-based Self-management in a Patient with Type 2 Diabetes
- Using a Mobile-based Nutritional Intervention Application Improves Glycemic Control but Reduces the Intake of Some Nutrients in Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Case Series Study
- Diabetes Management according to Blood Glucose Measurement Trend
- HealthTWITTER Initiative: Design of a Social Networking Service Based Tailored Application for Diabetes Self-Management
- Research Trend on Diabetes Mobile Applications: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling