Prog Med Phys.
2016 Sep;27(3):169-174. 10.14316/pmp.2016.27.3.169.
Treatment Plan Delivery Accuracy of the ViewRay System in Two-Headed Mode
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. madangin@gmail.com
- 2Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Center for Convergence Research on Robotics, Advanced Institutes of Convergence Technology, Suwon, Korea.
- 5Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2376548
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2016.27.3.169
Abstract
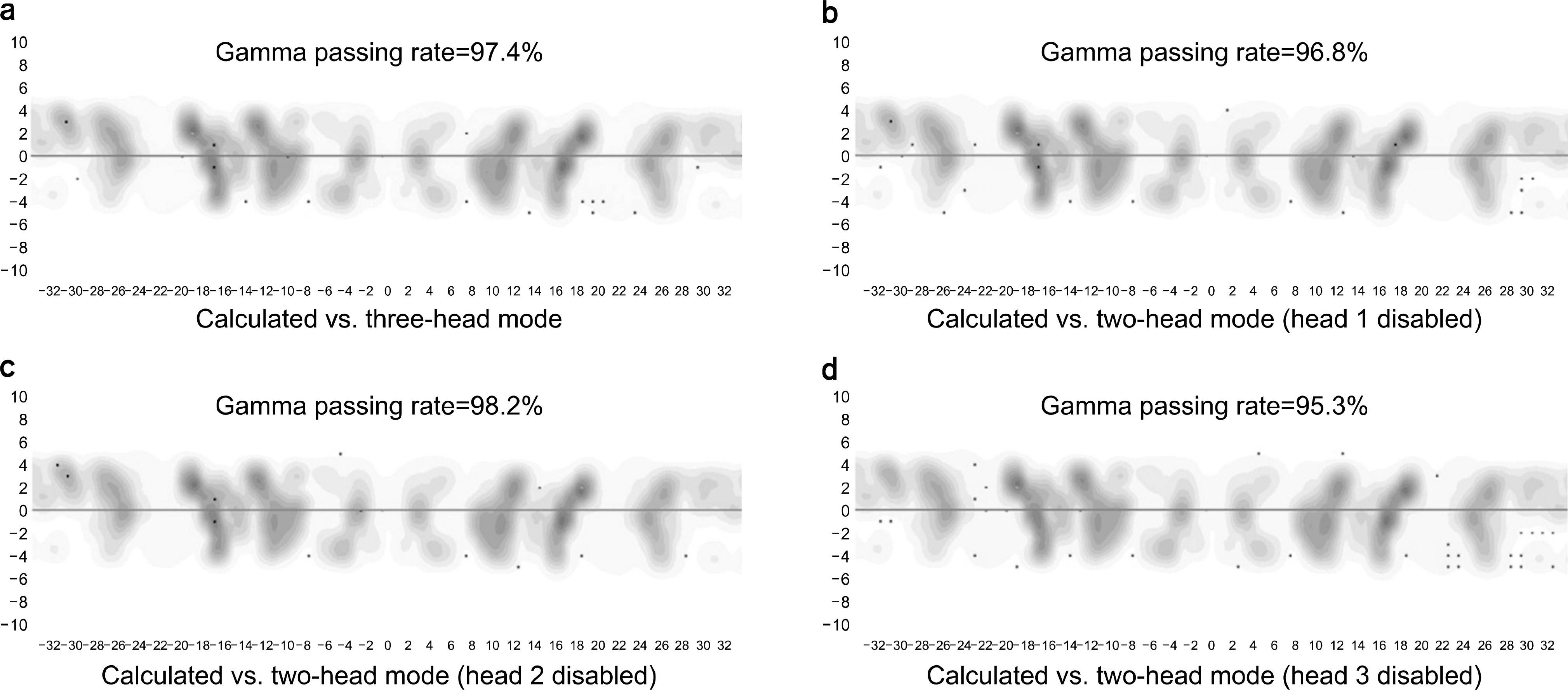
- The aim of this study is to investigate the delivery accuracy of intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) plans in the two-headed mode of the ViewRayâ„¢ system in comparison with that of the normal operation treatment plan of the machine. For this study, a total of eight IMRT plans and corresponding verification plans were generated (four head and neck, two liver, and two prostate IMRT plans). The delivered dose distributions were measured using ArcCHECKâ„¢ with the insertion of an ionization chamber. We measured the delivered dose distributions in three-headed mode (normal operation of the machine), two-headed mode with head 1 disabled, two-headed mode with head 2 disabled, and two-headed mode with head 3 disabled. Therefore, a total of four measurements were performed for each IMRT plan. The global gamma passing rates (3%/3 mm) in three-headed mode, head 1 disabled, head 2 disabled, and head 3 disabled were 99.9±0.1%, 99.8±0.3%, 99.6±0.7%, and 99.7±0.4%, respectively. The difference in the gamma passing rates of the three- and two-headed modes was insignificant. With 2%/2 mm, the rates were 96.6±3.6%, 97.2±3.5%, 95.7±6.2%, and 95.5±4.3%, respectively. Between three-headed mode and head 3 disabled, a statistically significant difference was observed with a p-value of 0.02; however, the difference was minimal (1.1%). The chamber readings showed differences of approximately 1% between three- and two-headed modes, which were minimal. Therefore, the treatment plan delivery in the two-headed mode of the ViewRayâ„¢ system seems accurate and robust.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1.Mera Iglesias M., Aramburu Nunez D., Del Olmo Claudio JL, et al. Multimodality functional imaging in radiation therapy planning: relationships between dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI, diffusion-weighted MRI, and 18F-FDG PET. Comput Math Methods Med 2015: 103843. 2015.
Article2.Ghose S., Mitra J., Rivest-Henault D, et al. MRI-alone radiation therapy planning for prostate cancer: Automatic fiducial marker detection. Med Phys. 43(5):2218. (2016).
Article3.Sun J., Dowling J., Pichler P, et al. MRI simulation: end-to- end testing for prostate radiation therapy using geometric pelvic MRI phantoms. Phys Med Biol. 60(8):3097–109. 2015.4.Ireland RH., Woodhouse N., Hoggard N, et al. An image acquisition and registration strategy for the fusion of hyperpolarized helium-3 MRI and x-ray CT images of the lung. Phys Med Biol. 53(21):6055–63. 2008.
Article5.Sarkar A., Santiago RJ., Smith R, et al. Comparison of manual vs. automated multimodality (CT-MRI) image registration for brain tumors. Med Dosim. 30(1):20–4. 2005.6.Mutic S., Dempsey JF. The ViewRay system: magnetic resonance-guided and controlled radiotherapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 24(3):196–9. 2014.
Article7.Park JM., Park S., Wu H, et al. Commissioning experience of tri-cobalt-60 MRI-guided radiation therapy system. Prog Med Phys. 26(4):193–200. 2015.
Article8.Wooten HO., Green O., Yang M, et al. Quality of Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy Treatment Plans Using a 60Co Magnetic Resonance Image Guidance Radiation Therapy System. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 92(4):771–8. 2015.9.Wooten HO., Rodriguez V., Green O, et al. Benchmark IMRT evaluation of a Co-60 MRI-guided radiation therapy system. Radiother Oncol. 114(3):402–5. 2015.
Article10.Park JM., Park SY., Kim HJ, et al. A comparative planning study for lung SABR between tri-Co-60 magnetic resonance image guided radiation therapy system and volumetric modulated arc therapy. Radiother Oncol. 120(2):279–85. 2016.
Article11.Low DA., Harms WB., Mutic S, et al. A technique for the quantitative evaluation of dose distributions. Med Phys. 25(5):656–61. 1998.
Article12.Fredh A., Scherman JB., Fog LS, et al. Patient QA systems for rotational radiation therapy: a comparative experimental study with intentional errors. Med Phys. 40(3):031716. 2013.
Article13.Heilemann G., Poppe B., Laub W. On the sensitivity of common gamma-index evaluation methods to MLC misalignments in Rapidarc quality assurance. Med Phys. 40(3):031702. 2013.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Commissioning Experience of Tri-Cobalt-60 MRI-guided Radiation Therapy System
- Four-headed biceps brachii, three-headed coracobrachialis muscles associated with arterial and nervous anomalies in the upper limb
- The First Comprehensive Plan of National Health Insurance
- Implementation and Evaluation of the Electron Arc Plan on a Commercial Treatment Planning System with a Pencil Beam Algorithm
- Limitation and Improvement Plan of Maternity Healthcare Delivery System in Korea