J Korean Soc Transplant.
2017 Mar;31(1):52-57. 10.4285/jkstn.2017.31.1.52.
Fatal Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis after Combined Induction with Rituximab and Antithymocyte Globulin for Kidney Transplantation in a Sensitized Recipient, and Early Rejection Therapy with Plasmapheresis and Low-dose Immunoglobulin
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. lshkidney@khu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2375681
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/jkstn.2017.31.1.52
Abstract
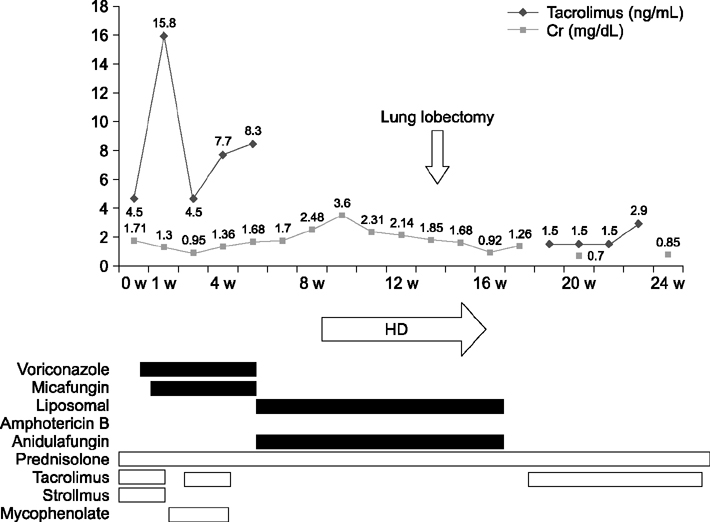
- A high degree of sensitization to human leukocyte antigen requires more intensive induction therapy; however, this increases vulnerability to opportunistic infections following kidney transplantation. Although recent studies have suggested that combined induction therapy with antithymocyte globulin and rituximab would be more effective in highly sensitized kidney recipients, we experienced a case of near-fatal invasive pulmonary aspergillosis 2 months after combined induction and early rejection therapy for graft dysfunction. Fortunately, the patient recovered with intensive antifungal treatment and lung lobectomy for a necrotic cavity. Antifungal prophylaxis should be considered in cases undergoing intensive induction therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Laftavi MR, Pankewycz O, Feng L, Said M, Patel S. Combined induction therapy with rabbit antithymocyte globulin and rituximab in highly sensitized renal recipients. Immunol Invest. 2015; 44:373–384.
Article2. Yin H, Wan H, Hu XP, Li XB, Wang W, Liu H, et al. Rituximab induction therapy in highly sensitized kidney transplant recipients. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011; 124:1928–1932.3. Cornet M, Fleury L, Maslo C, Bernard JF, Brucker G. Invasive Aspergillosis Surveillance Network of the Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris.Epidemiology of invasive aspergillosis in France: a six-year multicentric survey in the Greater Paris area. J Hosp Infect. 2002; 51:288–296.
Article4. Lopez-Medrano F, Fernandez-Ruiz M, Silva JT, Carver PL, van Delden C, Merino E, et al. Clinical presentation and determinants of mortality of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in kidney transplant recipients: a multinational cohort study. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16:3220–3234.
Article5. Ruhnke M, Bohme A, Buchheidt D, Donhuijsen K, Einsele H, Enzensberger R, et al. Diagnosis of invasive fungal infections in hematology and oncology: guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Working Party (AGIHO) of the German Society of Hematology and Oncology (DGHO). Ann Hematol. 2003; 82:Suppl 2. S141–S148.6. Soubani AO, Chandrasekar PH. The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis. Chest. 2002; 121:1988–1999.
Article7. Gerson SL, Talbot GH, Hurwitz S, Strom BL, Lusk EJ, Cassileth PA. Prolonged granulocytopenia: the major risk factor for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with acute leukemia. Ann Intern Med. 1984; 100:345–351.
Article8. Segal BH, Walsh TJ. Current approaches to diagnosis and treatment of invasive aspergillosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006; 173:707–717.
Article9. Lopez-Medrano F, Silva JT, Fernandez-Ruiz M, Carver PL, van Delden C, Merino E, et al. Risk factors associated with early invasive pulmonary Aspergillosis in kidney transplant recipients: results from a multinational matched case-control study. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16:2148–2157.
Article10. Kamar N, Milioto O, Puissant-Lubrano B, Esposito L, Pierre MC, Mohamed AO, et al. Incidence and predictive factors for infectious disease after rituximab therapy in kidney-transplant patients. Am J Transplant. 2010; 10:89–98.
Article11. Chung BH, Yun JT, Ha SE, Kim JI, Moon IS, Choi BS, et al. Combined use of rituximab and plasmapheresis pretransplant increases post-transplant infections in renal transplant recipients with basiliximab induction therapy. Transpl Infect Dis. 2013; 15:559–568.
Article12. Stiehm ER. Adverse effects of human immunoglobulin therapy. Transfus Med Rev. 2013; 27:171–178.
Article13. Kousha M, Tadi R, Soubani AO. Pulmonary aspergillosis: a clinical review. Eur Respir Rev. 2011; 20:156–174.
Article14. Kontoyiannis DP, Hachem R, Lewis RE, Rivero GA, Torres HA, Thornby J, et al. Efficacy and toxicity of caspofungin in combination with liposomal amphotericin B as primary or salvage treatment of invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematologic malignancies. Cancer. 2003; 98:292–299.
Article15. Moreau P, Zahar JR, Milpied N, Baron O, Mahe B, Wu D, et al. Localized invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with neutropenia. Effectiveness of surgical resection. Cancer. 1993; 72:3223–3226.
Article16. Park J, Hwang E, Park S, Kim H, Kim H. Simultaneous lung and liver Aspergillus in a kidney transplant recipient. J Korean Soc Transplant. 2012; 26:202–206.
Article17. Park SJ. A case of successful treatment of cutaneous Aspergillosis with voriconazole at the low cyclosporine trough level in a renal transplant. J Korean Soc Transplant. 2010; 24:35–39.
Article18. Na HH, Hong SW, Kim MC, Kang YK, Yoon YC, Koh HI. A case of invasive Aspergillosis in transplanted kidney and perirenal area. J Korean Soc Transplant. 2008; 22:135–137.19. Brizendine KD, Vishin S, Baddley JW. Antifungal prophylaxis in solid organ transplant recipients. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2011; 9:571–581.
Article20. Panackal AA, Dahlman A, Keil KT, Peterson CL, Mascola L, Mirza S, et al. Outbreak of invasive aspergillosis among renal transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2003; 75:1050–1053.
Article21. Linden E, Restrepo D, Dikman S, Murphy B, Huprikar S. Aspergillus infection limited to renal allograft: case report and review of literature. Transpl Infect Dis. 2006; 8:177–181.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Renal Transplantation in Highly Sensitized Recipients
- Treatment of Refractory Antibody-mediated Rejection with Bortezomib in a Kidney Transplant Recipient: A Case Report
- A Case of Successful Third Renal Transplantation Using Rituximab (anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibody) in a Highly Sensitized Patient
- Successful desensitization and transplantation of kidney transplant recipients with donor-specific antibodies
- Overcoming high pre-transplant isoagglutinin titers using high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin, salvage plasmapheresis, and booster rituximab without splenectomy in ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation: a case report