Yonsei Med J.
2016 Mar;57(2):518-522. 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.2.518.
Surgical Treatment of Hemangioblastoma in the Pituitary Stalk: An Extremely Rare Case
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Bundang CHA Medical Center, CHA University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. sandori50@gmail.com
- KMID: 2374062
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2016.57.2.518
Abstract
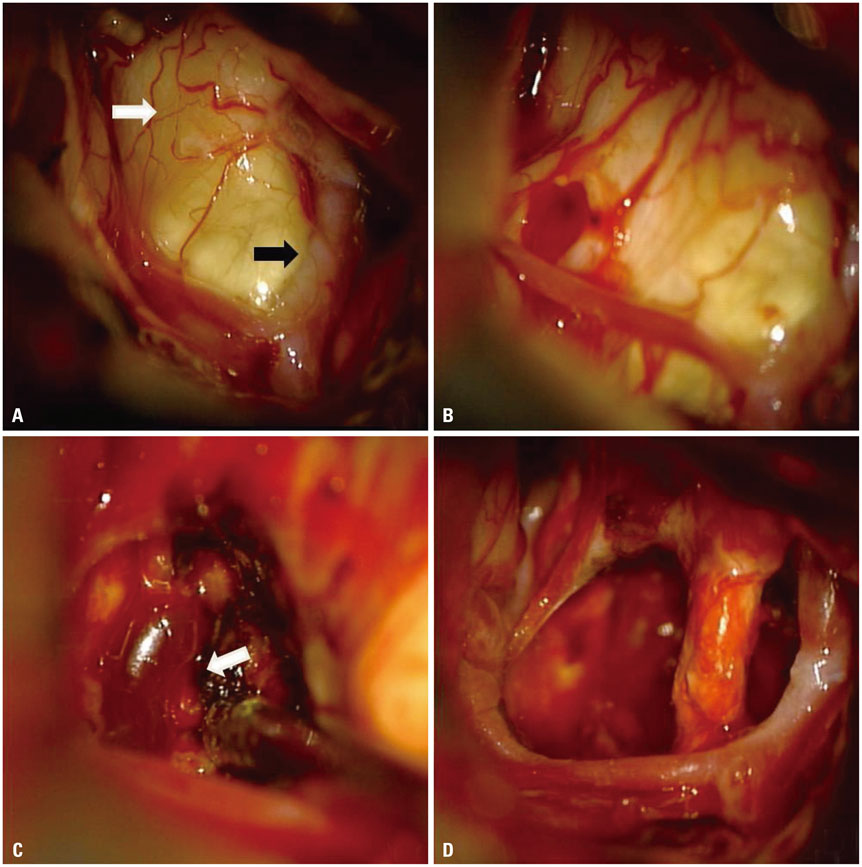
- Hemangioblastoma (HBL) in the pituitary stalk is extremely rare. Only 16 such cases have been reported in the past and 5 cases have been treated with surgical procedure. Here, we report surgical case of HBL in the pituitary stalk diagnosed in a 34-year-old woman. The patient underwent a gross-total resection via the modified lateral supra-orbital approach. No recurrence was observed in two years after surgery. To our knowledge, this is the 17th case of HBL in the pituitary stalk and the 6th surgical case. If the tumor is symptomatic and the volume is over 5 cubic centimeters as in our case, we recommend that the surgical resection of the HBL in the pituitary stalk is a more safe and reasonable than radiotherapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ho YS, Plets C, Goffin J, Dom R. Hemangioblastoma of the lateral ventricle. Surg Neurol. 1990; 33:407–412.
Article2. Neumann HP, Bender BU, Berger DP, Laubenberger J, Schultze-Seemann W, Wetterauer U, et al. Prevalence, morphology and biology of renal cell carcinoma in von Hippel-Lindau disease compared to sporadic renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 1998; 160:1248–1254.
Article3. Cao Y, Gao P, Wang S, Zhao J. Pituitary infundibulum hemangioblastoma detected by dynamic enhancement MRI. Can J Neurol Sci. 2010; 37:697–699.
Article4. Fomekong E, Hernalsteen D, Godfraind C, D'Haens J, Raftopoulos C. Pituitary stalk hemangioblastoma: the fourth case report and review of the literature. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2007; 109:292–298.
Article5. Fu H, Hao S, Wu Z, Zhang J, Zhang L. Sporadic pituitary stalk hemangioblastoma. Neurol India. 2011; 59:937–938.
Article6. Goto T, Nishi T, Kunitoku N, Yamamoto K, Kitamura I, Takeshima H, et al. Suprasellar hemangioblastoma in a patient with von Hippel-Lindau disease confirmed by germline mutation study: case report and review of the literature. Surg Neurol. 2001; 56:22–26.
Article7. Grisoli F, Gambarelli D, Raybaud C, Guibout M, Leclercq T. Suprasellar hemangioblastoma. Surg Neurol. 1984; 22:257–262.
Article8. Kouri JG, Chen MY, Watson JC, Oldfield EH. Resection of suprasellar tumors by using a modified transsphenoidal approach. Report of four cases. J Neurosurg. 2000; 92:1028–1035.
Article9. Lee KM, Kim EJ, Choi WS, Kim TS. Pituitary stalk hemangioblastoma in a von hippel-lindau patient : clinical course follow-up over a 20-year period. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2013; 53:297–299.
Article10. Lonser RR, Butman JA, Kiringoda R, Song D, Oldfield EH. Pituitary stalk hemangioblastomas in von Hippel-Lindau disease. J Neurosurg. 2009; 110:350–353.
Article11. Neumann HP, Eggert HR, Scheremet R, Schumacher M, Mohadjer M, Wakhloo AK, et al. Central nervous system lesions in von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992; 55:898–901.
Article12. Mills SA, Oh MC, Rutkowski MJ, Sughrue ME, Barani IJ, Parsa AT. Supratentorial hemangioblastoma: clinical features, prognosis, and predictive value of location for von Hippel-Lindau disease. Neuro Oncol. 2012; 14:1097–1104.
Article13. Lonser RR, Glenn GM, Walther M, Chew EY, Libutti SK, Linehan WM, et al. von Hippel-Lindau disease. Lancet. 2003; 361:2059–2067.
Article14. Peyre M, David P, Van Effenterre R, François P, Thys M, Emery E, et al. Natural history of supratentorial hemangioblastomas in von Hippel-Lindau disease. Neurosurgery. 2010; 67:577–587.
Article15. Kano H, Niranjan A, Mongia S, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD. The role of stereotactic radiosurgery for intracranial hemangioblastomas. Neurosurgery. 2008; 63:443–450.16. Moss JM, Choi CY, Adler JR Jr, Soltys SG, Gibbs IC, Chang SD. Stereotactic radiosurgical treatment of cranial and spinal hemangioblastomas. Neurosurgery. 2009; 65:79–85.
Article17. Hild W. [Morphological, kinetic and endocrinological behavior of the hypothalamic and neurohypophysial tissue in vitro]. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1954; 40:257–312.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sporadic Hemangioblastoma in the Pituitary Stalk: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Pituitary Stalk Hemangioblastoma in a von Hippel-Lindau Patient : Clinical Course Follow-Up Over a 20-Year Period
- Pituitary Stalk Transection Syndrome
- Characterization of the Anatomic Location of the Pituitary Stalk and Its Relationship to the Dorsum Sellae, Tuberculum Sellae and Chiasmatic Cistern
- Intraosseous Hemangioblastoma Mimicking Spinal Metastasis in the Patient with Renal Cell Carcinoma