Korean J Ophthalmol.
2016 Dec;30(6):485-486. 10.3341/kjo.2016.30.6.485.
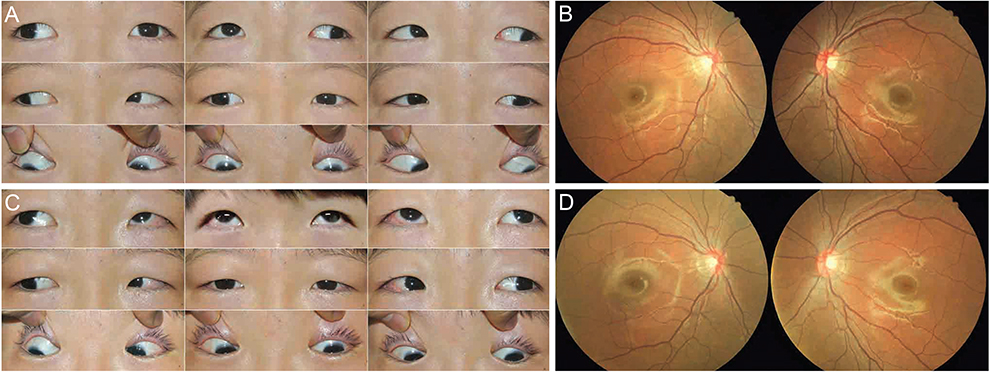
Antielevation Syndrome after Bilateral Anterior Transposition of the Inferior Oblique Muscles
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Konyang University Myunggok Medical Research Institute, Konyang University Hospital, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. smile-ri@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2374009
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2016.30.6.485
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Scott AB. Planning inferior oblique muscle surgery. In : Reinecke RD, editor. Strabismus. New York: Grune and Stratton;1978. p. 347–354.2. Kushner BJ. Torsion as a contributing cause of the anti-elevation syndrome. J AAPOS. 2001; 5:172–177.3. Kushner BJ. Restriction of elevation in abduction after inferior oblique anteriorization. J AAPOS. 1997; 1:55–62.4. Mims JL 3rd, Wood RC. Antielevation syndrome after bilateral anterior transposition of the inferior oblique muscles: incidence and prevention. J AAPOS. 1999; 3:333–336.5. Han J, Han SY, Lee JB, Han SH. Surgical management of long-standing antielevation syndrome after unilateral anterior transposition of the inferior oblique muscle. J AAPOS. 2014; 18:232–234.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Asymmetric Bilateral Inferior Oblique Transposition of a Bilateral Inferior Oblique Overaction Associated with Dissociated Vertical Deviation
- Comparison between Myectomy and Anterior Transposition on Inferior Oblique Overaction
- The Effect of Anterior Transposition with J-Deformity for Overaction of the Inferior Oblique Muscle
- The Effect of Anteriorization of The Inferior Oblique Muscle in +3 or +4 Inferior Oblique Overaction
- Antielevation Syndrome after Unilateral Anteriorization of the Inferior Oblique Muscle