Korean J Gastroenterol.
2015 Jan;65(1):48-51. 10.4166/kjg.2015.65.1.48.
A Case of Autoimmune Hepatitis Combined with Graves' Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. DYK1025@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Institute of Gastroenterology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2373180
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2015.65.1.48
Abstract
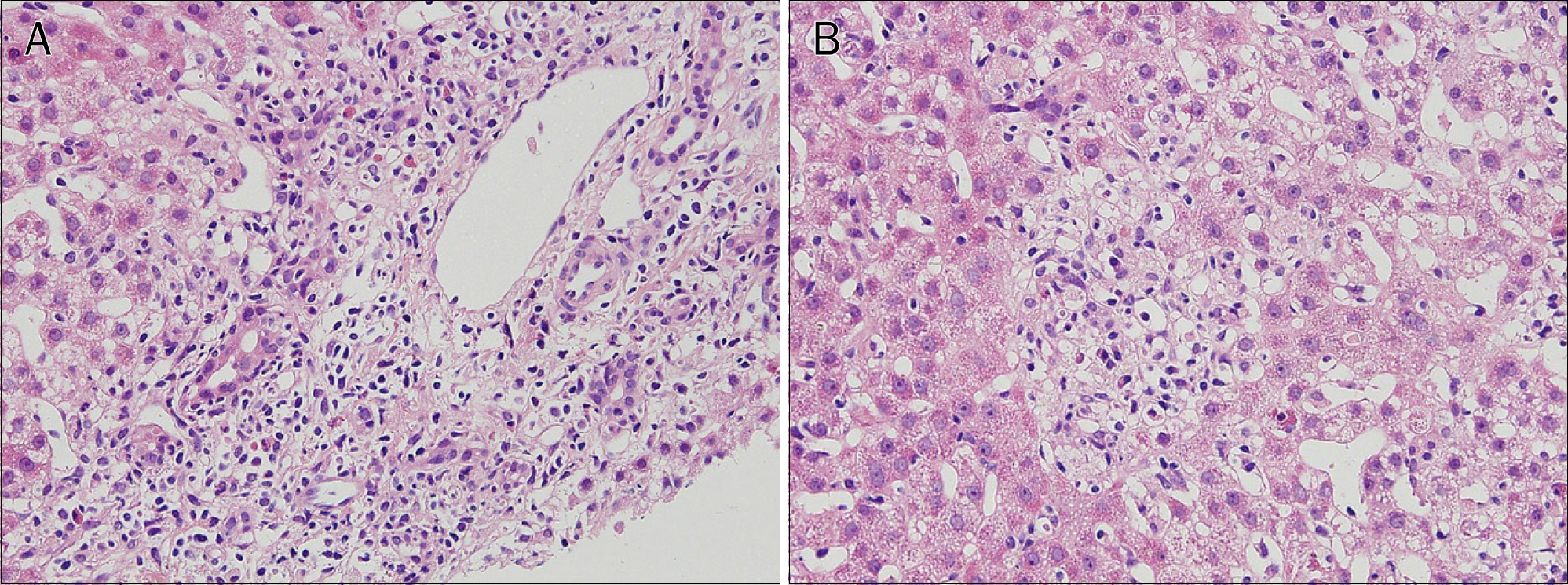
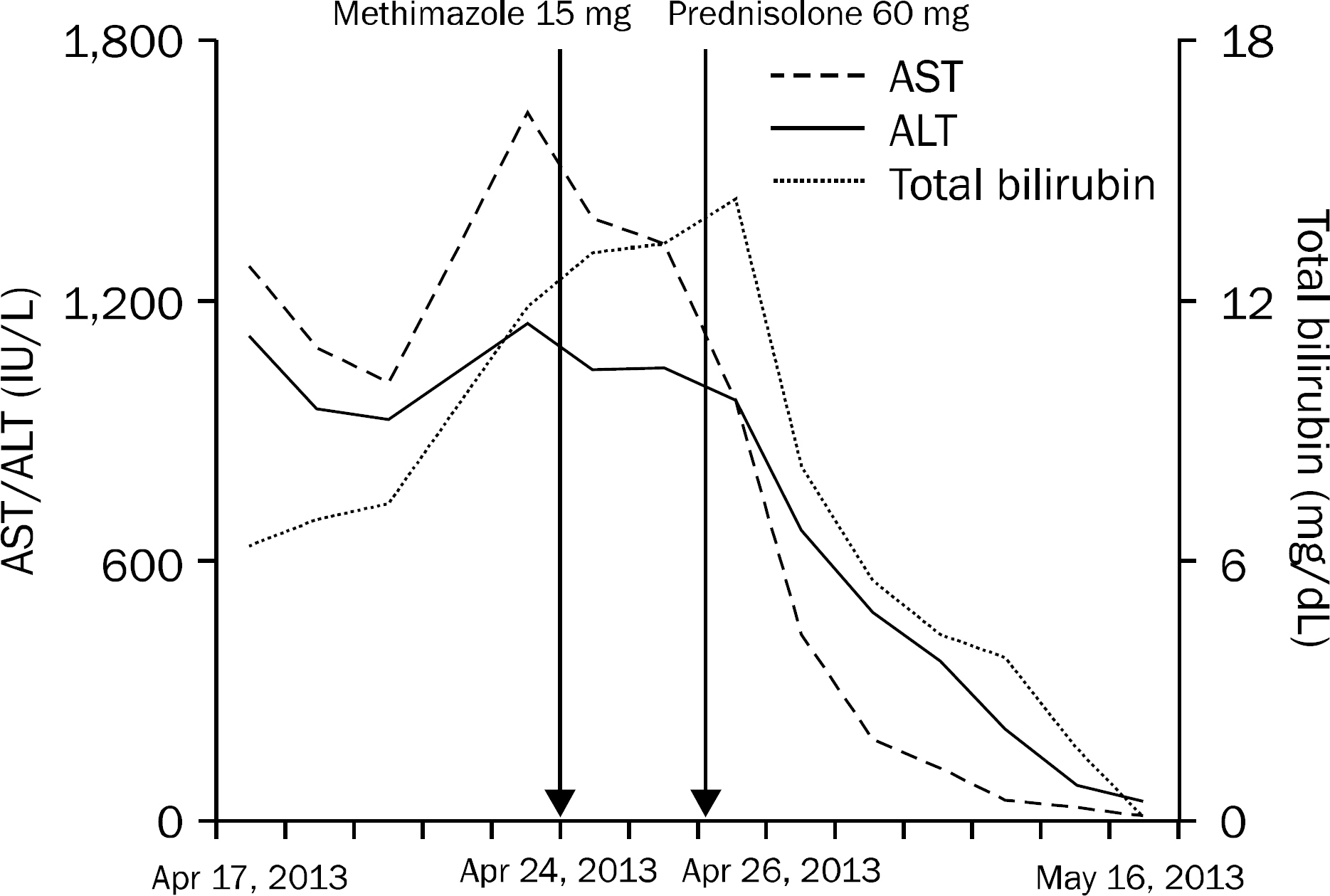
- A 25-year-old woman presented with jaundice, palpitation, and weight loss of 5 kg during a period of 2 weeks. Laboratory tests showed elevated levels of liver enzymes (AST 1,282 IU/L, ALT 1,119 IU/L) and total bilirubin (6.4 mg/dL); negative for hepatitis virus infection; elevated serum levels of triiodothyronine (T3, 3.60 ng/dL), free thyroxine (fT4, 3.82 ng/dL), and lowered serum level of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH, <0.025 microIU/mL); and positive for thyroid stimulating antibody and anti-mitochondrial antibody (AMA). The liver biopsy findings were consistent with autoimmune hepatitis (AIH). Accordingly, oral steroid therapy was started with 60 mg of prednisolone under the impression of AIH associated with Graves' disease. After a week of steroid therapy, the clinical manifestation showed significant improvement, with normalization of both liver and thyroid functions. Diagnosis of the liver condition of patients who present with hyperthyroidism and liver dysfunction is important, so that appropriate therapy can be promptly initiated.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Alanine Transaminase/analysis
Antibodies, Antinuclear/blood
Aspartate Aminotransferases/analysis
Bilirubin/blood
Female
Graves Disease/complications/*diagnosis/drug therapy
Hepatitis, Autoimmune/complications/*diagnosis/drug therapy
Humans
Immunoglobulins, Thyroid-Stimulating/blood
Liver/enzymology/metabolism/pathology
Prednisolone/therapeutic use
Steroids/therapeutic use
Thyrotropin/blood
Alanine Transaminase
Antibodies, Antinuclear
Aspartate Aminotransferases
Bilirubin
Immunoglobulins, Thyroid-Stimulating
Prednisolone
Steroids
Thyrotropin
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Krawitt EL. Autoimmune hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354:54–66.
Article2. Liberal R, Grant CR, Longhi MS, Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D. Diagnostic criteria of autoimmune hepatitis. Autoimmun Rev. 2014; 13:435–440.
Article3. Reich DJ, Fiel I, Guarrera JV, et al. Liver transplantation for autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology. 2000; 32:693–700.
Article4. Lim KN, Casanova RL, Boyer TD, Bruno CJ. Autoimmune hepatitis in African Americans: presenting features and response to therapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001; 96:3390–3394.
Article5. Czaja AJ, Freese DK. American Association for the Study of Liver Disease. Diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology. 2002; 36:479–497.
Article6. Krawitt EL, Bonis PAL. Treatment of autoimmune hepatitis. Rose BD, editor. UpToDate, version 13.1. Wellesley: UpToDate;2005.7. Alvarez F, Berg PA, Bianchi FB, et al. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Report: review of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1999; 31:929–938.
Article8. Johnson PJ, McFarlane IG. Meeting report: International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group. Hepatology. 1993; 18:998–1005.
Article9. Abe M, Hiasa Y, Masumoto T, et al. Clinical characteristics of autoimmune hepatitis with histological features of acute hepatitis. Hepatol Res. 2001; 21:213–219.
Article10. Cui B, Abe M, Hidata S, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis associated with Graves' disease. Intern Med. 2003; 42:331–335.
Article11. Gough A, Chapman S, Wagstaff K, Emery P, Elias E. Minocycline induced autoimmune hepatitis and systemic lupus eryth-ematosus-like syndrome. BMJ. 1996; 312:169–172.
Article12. Inoue K, Okajima T, Tanaka E, et al. A case of Graves' disease associated with autoimmune hepatitis and mixed connective tissue disease. Endocr J. 1999; 46:173–177.
Article13. Sato I, Tsunekawa T, Shinohara Y, et al. A case of autoimmune hepatitis with Graves' disease treated by propylthiouracil. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2011; 73:205–209.14. Duchini A, McHutchison JG, Pockros PJ. LKM-positive autoimmune hepatitis in the western United States: a case series. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000; 95:3238–3241.
Article15. Hennes EM, Zeniya M, Czaja AJ, et al. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group. Simplified criteria for the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology. 2008; 48:169–176.
Article16. Weetman AP. Graves' disease. N Engl J Med. 2000; 343:1236–1248.
Article17. Onji M, Nonaka T, Horiike N, Moriwaki H, Muto Y, Ohta Y. Present status of autoimmune hepatitis in Japan. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1993; 28(Suppl 4):134–138.
Article18. Mori T, Akamizu T, Kosugi S, et al. Recent progress in TSH receptor studies with a new concept of “autoimmune TSH receptor disease”. Endocr J. 1994; 41:1–11.
Article19. Biscoveanu M, Hasinski S. Abnormal results of liver function tests in patients with Graves' disease. Endocr Pract. 2000; 6:367–369.
Article20. Khemichian S, Fong TL. Hepatic dysfunction in hyperthyroidism. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2011; 7:337–339.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Interferon-Alpha Induced Severe Hypothyroidism Followed by Graves' Disease in a Patient Infected with Hepatitis C Virus
- A case of membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis in a patient with Graves' disease
- Autoimmune Thyroiditis during Antiviral Therapy with Peginterferon
- A Case of Graves' Disease Accompanied with Acute Hepatitis A Virus Infection
- Cyclosporine Treatment in a Patient with Concurrent Autoimmune Urticaria and Autoimmune Hepatitis