Endocrinol Metab.
2016 Dec;31(4):525-532. 10.3803/EnM.2016.31.4.525.
Current Status of Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Chung Hospital, Seoul, Korea. younbchoi@gmail.com
- 2Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2373071
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.4.525
Abstract
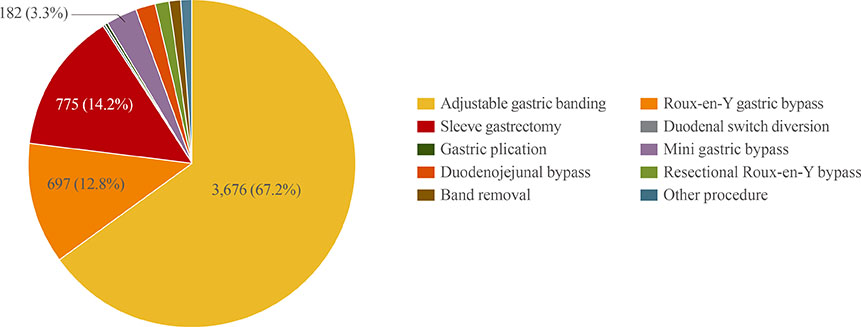
- Bariatric surgery is considered to be the most effective treatment modality in maintaining long-term weight reduction and improving obesity-related conditions in morbidly obese patients. In Korea, surgery for morbid obesity was laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy first performed in 2003. Since 2003, the annual number of bariatric surgeries has markedly increased, including adjustable gastric banding (AGB), Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, mini-gastric bypass, and others. In Korea, AGB is much more common than in others countries. A large proportion of doctors, the public, and government misunderstand the necessity and effectiveness of bariatric surgery, believing that bariatric surgery has an unacceptably high morbidity, and that it is not superior to non-surgical treatments to improve obesity and obesity-related diseases. The effectiveness, safety, and cost-effectiveness of bariatric surgery have been well demonstrated. The Korean Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery recommend bariatric surgery confining to morbidly obese patients (body mass index ≥40 or >35 in the presence of significant comorbidities).
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Angrisani L, Santonicola A, Iovino P, Formisano G, Buchwald H, Scopinaro N. Bariatric surgery worldwide 2013. Obes Surg. 2015; 25:1822–1832.2. Sjostrom CD, Peltonen M, Wedel H, Sjostrom L. Differentiated long-term effects of intentional weight loss on diabetes and hypertension. Hypertension. 2000; 36:20–25.3. Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, Jensen MD, Pories W, Fahrbach K, et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004; 292:1724–1737.4. Sjostrom CD, Peltonen M, Sjostrom L. Blood pressure and pulse pressure during long-term weight loss in the obese: the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) Intervention Study. Obes Res. 2001; 9:188–195.5. Spivak H, Hewitt MF, Onn A, Half EE. Weight loss and improvement of obesity-related illness in 500 U.S. patients following laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding procedure. Am J Surg. 2005; 189:27–32.6. Christou NV, Sampalis JS, Liberman M, Look D, Auger S, McLean AP, et al. Surgery decreases long-term mortality, morbidity, and health care use in morbidly obese patients. Ann Surg. 2004; 240:416–423.7. Buchwald H, Buchwald JN. Evolution of operative procedures for the management of morbid obesity 1950-2000. Obes Surg. 2002; 12:705–717.8. Jang SI, Nam JM, Choi J, Park EC. Disease management index of potential years of life lost as a tool for setting priorities in national disease control using OECD health data. Health Policy. 2014; 115:92–99.9. Lee SK. Current status of laparoscopic metabolic/bariatric surgery in Korea. J Minim Invasive Surg. 2015; 18:59–62.10. Lee JH. Current statue of bariatric and metabolic surgery in Korea. Panel discussion III: update on bariatric/metabolic surgery. In : Proceedings of the 2nd Seminar of the Korean Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery; 2015 Sep 12; Seoul, KR. Seoul: Korean Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery;2015. p. 63–65. .11. Ahn HS, Lee HJ, Kang SH, Kim GJ, Kim SS, Kim YJ, et al. 2013 Nationwide bariatric and metabolic surgery report in Korea. J Metab Bariatr Surg. 2014; 3:38–43.12. Aarts EO, Dogan K, Koehestanie P, Aufenacker TJ, Janssen IM, Berends FJ. Long-term results after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding: a mean fourteen year follow-up study. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2014; 10:633–640.13. Himpens J, Cadiere GB, Bazi M, Vouche M, Cadiere B, Dapri G. Long-term outcomes of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Arch Surg. 2011; 146:802–807.14. Choi YB, Lee IS. The current status of bariatric surgery in Korea. J Korean Diabetes. 2013; 14:55–57.15. Buchwald H, Ikramuddin S. Bariatric surgery primer [CD-ROM]. Chicago: American College of Surgeons;2002. Chapter 17, Outcomes.16. Mason EE. Vertical banded gastroplasty for obesity. Arch Surg. 1982; 117:701–706.17. MacLean LD, Rhode BM, Forse RA. Late results of vertical banded gastroplasty for morbid and super obesity. Surgery. 1990; 107:20–27.18. Alper D, Ramadan E, Vishne T, Belavsky R, Avraham Z, Seror D, et al. Silastic ring vertical gastroplasty- long-term results and complications. Obes Surg. 2000; 10:250–254.19. Belachew M, Legrand MJ, Defechereux TH, Burtheret MP, Jacquet N. Laparoscopic adjustable silicone gastric banding in the treatment of morbid obesity. A preliminary report. Surg Endosc. 1994; 8:1354–1356.20. Dixon AF, Dixon JB, O’Brien PE. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding induces prolonged satiety: a randomized blind crossover study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005; 90:813–819.21. Fisher BL. Comparison of recovery time after open and laparoscopic gastric bypass and laparoscopic adjustable banding. Obes Surg. 2004; 14:67–72.22. Dolan K, Hatzifotis M, Newbury L, Fielding G. A comparison of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding and biliopancreatic diversion in superobesity. Obes Surg. 2004; 14:165–169.23. Milone L, Strong V, Gagner M. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy is superior to endoscopic intragastric balloon as a first stage procedure for super-obese patients (BMI > or =50). Obes Surg. 2005; 15:612–617.24. Hamoui N, Anthone GJ, Kaufman HS, Crookes PF. Sleeve gastrectomy in the high-risk patient. Obes Surg. 2006; 16:1445–1449.25. Griffen WO Jr, Young VL, Stevenson CC. A prospective comparison of gastric and jejunoileal bypass procedures for morbid obesity. Ann Surg. 1977; 186:500–509.26. Scopinaro N, Adami GF, Marinari GM, Gianetta E, Traverso E, Friedman D, et al. Biliopancreatic diversion. World J Surg. 1998; 22:936–946.27. Hess DS, Hess DW. Biliopancreatic diversion with a duodenal switch. Obes Surg. 1998; 8:267–282.28. Fernandez AZ Jr, Demaria EJ, Tichansky DS, Kellum JM, Wolfe LG, Meador J, et al. Multivariate analysis of risk factors for death following gastric bypass for treatment of morbid obesity. Ann Surg. 2004; 239:698–702.29. McCarty TM, Arnold DT, Lamont JP, Fisher TL, Kuhn JA. Optimizing outcomes in bariatric surgery: outpatient laparoscopic gastric bypass. Ann Surg. 2005; 242:494–498.30. Shikora SA, Kim JJ, Tarnoff ME, Raskin E, Shore R. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: results and learning curve of a high-volume academic program. Arch Surg. 2005; 140:362–367.31. Sosa JL, Pombo H, Pallavicini H, Ruiz-Rodriguez M. Laparoscopic gastric bypass beyond age 60. Obes Surg. 2004; 14:1398–1401.32. Higa KD, Ho T, Boone KB. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: technique and 3-year follow-up. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2001; 11:377–382.33. Wang W, Wei PL, Lee YC, Huang MT, Chiu CC, Lee WJ. Short-term results of laparoscopic mini-gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2005; 15:648–654.34. Rutledge R. Similarity of Magenstrasse-and-Mill and mini-g-astric bypass. Obes Surg. 2003; 13:318.35. Bueter M, Miras AD, Chichger H, Fenske W, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR, et al. Alterations of sucrose preference after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Physiol Behav. 2011; 104:709–721.36. Karra E, Yousseif A, Batterham RL. Mechanisms facilitating weight loss and resolution of type 2 diabetes following bariatric surgery. Trends Endocrino Metab. 2010; 21:337–344.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- 2018 Korean Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Guidelines
- Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation Program and National Health Insurance System in Korea
- Training in Bariatric and Metabolic Endoscopic Therapies
- The Current Status and Necessity of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation System in Foreign Country
- Role of Endoscopy in the Treatment of Bariatric and Metabolic Disease