J Gastric Cancer.
2017 Mar;17(1):52-62. 10.5230/jgc.2017.17.e6.
Epidemiologic Study of Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Expression in Advanced/Metastatic Gastric Cancer: an Assessment of Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Status in Tumor Tissue Samples of Gastric and Gastro-Esophageal Junction Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. gslsh@ns.kosinmed.or.kr
- 2Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 3Yeungnam University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 5Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 6Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 7Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- 8Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea.
- 9Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu, Korea.
- 10Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Busan, Korea.
- 11Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea.
- 12Dankook University Hospital, Cheonan, Korea.
- 13Daegu Catholic University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea.
- 14Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea. ydh@chonbuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 2372582
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2017.17.e6
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The Trastuzumab for gastric cancer (GC) trial identified human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) as a predictor of successful treatment with trastuzumab (HER2 receptor targeting agent) among patients with advanced/metastatic GC. To date, the prevalence of HER2 overexpression in the Korean population is unknown. The present study aimed to assess the incidence of HER2 positivity among GC and gastroesophageal (GE) junction cancer samples and the relationship between HER2 overexpression and clinicopathological characteristics in Korean patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
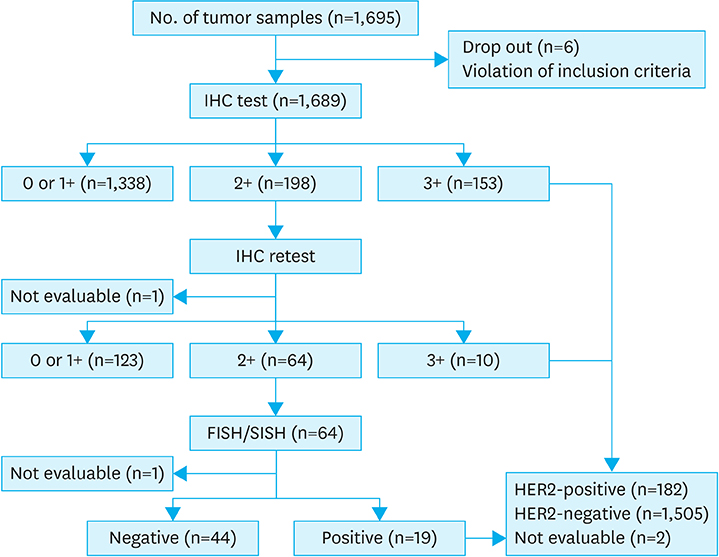
Tumor samples collected from 1,695 patients with histologically proven GC or GE junction enrolled at 14 different hospitals in Korea were examined. After gathering clinicopathological data of all patients, HER2 status was assessed by immunohistochemistry (IHC) at each hospital, and IHC 2+ cases were subjected to silver-enhanced in situ hybridization at 3 central laboratories.
RESULTS
A total of 182 specimens tested positive for HER2, whereas 1,505 tested negative. Therefore, the overall HER2-positive rate in this study was 10.8% (95% confidence interval: 9.3%-12.3%). The HER2-positive rate was higher among intestinal-type cases (17.6%) than among other types, and was higher among patients older than 70 years and 50 years of age, compared to other age groups.
CONCLUSIONS
Our evaluation of the HER2 positivity rate (10.8%) among Korean patients with GC and GE junction indicated the necessity of epidemiological data when conducting studies related to HER2 expression in GC and GE junction.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kamangar F, Dores GM, Anderson WF. Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:2137–2150.2. Kelley JR, Duggan JM. Gastric cancer epidemiology and risk factors. J Clin Epidemiol. 2003; 56:1–9.3. Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005; 55:74–108.4. Bang Y, Chung H, Xu J, Lordick F, Sawaki A, Al-Sakaff N, et al. Pathological features of advanced gastric cancer (GC): relationship to human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) positivity in the global screening programme of the ToGA trial. Paper presented at: 2009 ASCO Annual Meeting. 2009 May 29–June 2; Orlando, FL, USA. p. No. 4556.5. Van Cutsem E, Kang Y, Chung H, Shen L, Sawaki A, Lordick F, et al. Efficacy results from the ToGA trial: A phase III study of trastuzumab added to standard chemotherapy (CT) in first-line human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive advanced gastric cancer (GC). Paper presented at: 2009 ASCO Annual Meeting. 2009 May 29–June 2; Orlando, FL, USA. p. No. LBA4509.6. Kim MA, Jung EJ, Lee HS, Lee HE, Jeon YK, Yang HK, et al. Evaluation of HER-2 gene status in gastric carcinoma using immunohistochemistry, fluorescence in situ hybridization, and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Hum Pathol. 2007; 38:1386–1393.7. Takehana T, Kunitomo K, Kono K, Kitahara F, Iizuka H, Matsumoto Y, et al. Status of c-erbB-2 in gastric adenocarcinoma: a comparative study of immunohistochemistry, fluorescence in situ hybridization and enzyme-linked immuno-sorbent assay. Int J Cancer. 2002; 98:833–837.8. Wang YL, Sheu BS, Yang HB, Lin PW, Chang YC. Overexpression of c-erb-B2 proteins in tumor and non-tumor parts of gastric adenocarcinoma--emphasis on its relation to H. pylori infection and clinicohistological characteristics. Hepatogastroenterology. 2002; 49:1172–1176.9. Yano T, Doi T, Ohtsu A, Boku N, Hashizume K, Nakanishi M, et al. Comparison of HER2 gene amplification assessed by fluorescence in situ hybridization and HER2 protein expression assessed by immunohistochemistry in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 2006; 15:65–71.10. Son HS, Shin YM, Park KK, Seo KW, Yoon KY, Jang HK, et al. Correlation between HER2 overexpression and clinicopathological characteristics in gastric cancer patients who have undergone curative resection. J Gastric Cancer. 2014; 14:180–186.11. Huang D, Lu N, Fan Q, Sheng W, Bu H, Jin X, et al. HER2 status in gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer assessed by local and central laboratories: Chinese results of the HER-EAGLE study. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e80290.12. Kim A, Bae JM, Kim SW, Gu MJ, Bae YK. HER2 status in gastric adenocarcinomas assessed by immunohistochemistry, automated silver-enhanced in situ hybridization and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Korean J Pathol. 2010; 44:493–501.13. Park DI, Yun JW, Park JH, Oh SJ, Kim HJ, Cho YK, et al. HER-2/neu amplification is an independent prognostic factor in gastric cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 2006; 51:1371–1379.14. Dursun A, Poyraz A, Celik B, Akyol G. Expression of c-erbB-2 oncoprotein in gastric carcinoma: correlation with histopathologic characteristics and analysis of Ki-67. Pathol Oncol Res. 1999; 5:104–106.15. Gürel S, Dolar E, Yerci O, Samli B, Oztürk H, Nak SG, et al. The relationship between c-erbB-2 oncogene expression and clinicopathological factors in gastric cancer. J Int Med Res. 1999; 27:74–78.16. Lee KE, Lee HJ, Kim YH, Yu HJ, Yang HK, Kim WH, et al. Prognostic significance of p53, nm23, PCNA and c-erbB-2 in gastric cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2003; 33:173–179.17. Ougolkov A, Yamashita K, Bilim V, Takahashi Y, Mai M, Minamoto T. Abnormal expression of E-cadherin, beta-catenin, and c-erbB-2 in advanced gastric cancer: its association with liver metastasis. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2003; 18:160–166.18. Pinto-de-Sousa J, David L, Almeida R, Leitão D, Preto JR, Seixas M, et al. c-erb B-2 expression is associated with tumor location and venous invasion and influences survival of patients with gastric carcinoma. Int J Surg Pathol. 2002; 10:247–256.19. Brien TP, Depowski PL, Sheehan CE, Ross JS, McKenna BJ. Prognostic factors in gastric cancer. Mod Pathol. 1998; 11:870–877.20. Brien TP, Odze RD, Sheehan CE, McKenna BJ, Ross JS. HER-2/neu gene amplification by FISH predicts poor survival in Barrett's esophagus-associated adenocarcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2000; 31:35–39.21. Ishikawa T, Kobayashi M, Mai M, Suzuki T, Ooi A. Amplification of the c-erbB-2 (HER-2/neu) gene in gastric cancer cells. Detection by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1997; 151:761–768.22. Fan X, Sun Q, Chen J, Zhang Y, Wu H, Zhou Q, et al. [HER2 protein testing in gastric cancer: a retrospective analysis of 1 471 cases during two different periods in a single medical center]. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2014; 43:83–87.23. Yamashita-Kashima Y, Shu S, Yorozu K, Hashizume K, Moriya Y, Fujimoto-Ouchi K, et al. Importance of formalin fixing conditions for HER2 testing in gastric cancer: immunohistochemical staining and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Gastric Cancer. 2014; 17:638–647.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prognostic significance of epidermal growth factor receptor expression in human gastric carcinoma
- Effect of intracelluar cyclic AMP on EGF receptor binding in human gastric adenocarcinoma cells
- Amplification of epidermal growth factor receptor gene in primary cervical cancer
- Amplification of epidermal growth factor receptor gene in primary cervical cancer
- Correlation of epidermal growth factor receptor expression with prognostic factors in patients with ovarian neoplasms