J Gastric Cancer.
2012 Sep;12(3):201-204.
Gastroduodenal Intussusception Resulting from Large Hyperplastic Polyp
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. kimwook@catholic.ac.kr
Abstract
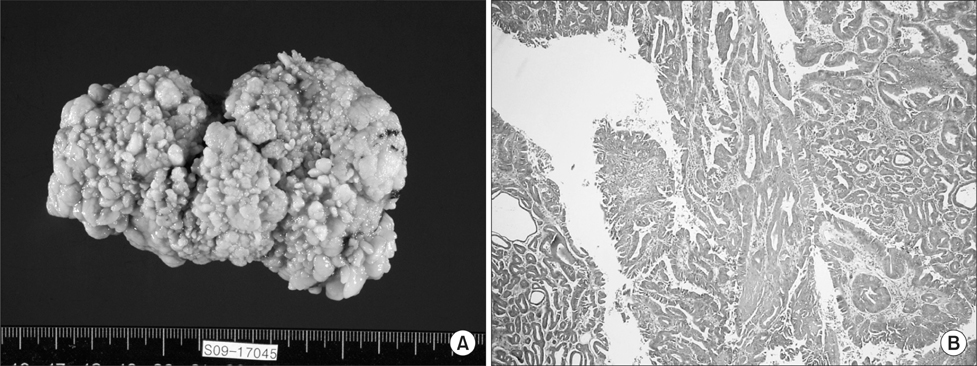
- Gastroduodenal intussusception is an infrequent cause of gastrointestinal obstructive disease. Benign neoplasms, gastrointestinal stromal tumors and pedunculated adenocarcinomas of less than 5 cm have been reported to cause gastroduodenal intussusception. We report a case of 76-year-old woman who was presented with a 3-day history of nausea and vomiting due to upper gastrointestinal obstruction. Computed tomography revealed gastroduodenal intussusception with the transpyloric herniation of alarge gastric hyperplastic polyp. The patient underwent laparoscopic wedge resection with the eversion method.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. White PG, Adams H, Sue-Ling HM, Webster DJ. Case report: gastroduodenal intussusception--an unusual cause of pancreatitis. Clin Radiol. 1991. 44:357–358.
Article2. Gyedu A, Reich SB, Hoyte-Williams PE. Gastrointestinal stromal tumour presenting acutely as gastroduodenal intussusception. Acta Chir Belg. 2011. 111:327–328.
Article3. Petersen JM, Felger TS, Goldstein JD. Gastroduodenal intussusception secondary to a giant brunner gland hamartoma. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2008. 4:471–473.4. Shum JS, Lo SS, Ka SY, Yeung CW, Ho JT. Gastroduodenal intussusception. Abdom Imaging. 2007. 32:698–700.
Article5. Adjepong SE, Parameswaran R, Perry A, Mathews R, Jones R, Butterworth JR, et al. Gastroduodenal intussusception due to gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) treated by laparoscopic billroth II distal gastrectomy. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2006. 16:245–247.
Article6. Sato N, Matoba N, Kameoka N, Fujii T, Sato K, Masuda H, et al. Gastroduodenal intussusception secondary to a gastric carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 1999. 46:626–628.7. Lin F, Setya V, Signor W. Gastroduodenal intussusception secondary to a gastric lipoma: a case report and review of the literature. Am Surg. 1992. 58:772–774.8. Asai S, Kijima H, Yamamoto S, Shiraishi S, Suzuki T, Maeda Y, et al. Gastroduodenal intussusception secondary to pedunculated gastric carcinoma. J Ultrasound Med. 2008. 27:673–676.
Article9. Juglard R, Rimbot A, Stéphant E, Paoletti H, Talarmin B, Arteaga C. Gastroduodenal intussusception complicating Menetrier's disease. J Radiol. 2006. 87:69–71.10. Kang HM, Oh TH, Seo JY, Joen TJ, Seo DD, Shin WC, et al. Clinical factors predicting for neoplastic transformation of gastric hyperplastic polyps. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011. 58:184–189.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Giant Hyperplastic Polyp of the Stomach Complicated by Intussusceptions and Intraepithelial Malignant Transformation
- Two Cases of Hyperplastic Polyposis in the Colon
- A Case of Ureteral Intussusception with Giant Ureteral Polyp
- Gastroduodenal Intussusception Caused by a Peutz-Jeghers Polyp in a Young Child: A Case Report
- Gastroduodenal Intussusception due to Gastric Submucosal Hemangiomatosis