J Gastric Cancer.
2013 Jun;13(2):121-125.
Advanced Gastric Cancer Associated with Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Successfully Treated with 5-fluorouracil and Oxaliplatin
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gangneung Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea. anijune@gnah.co.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Gangneung Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea.
Abstract
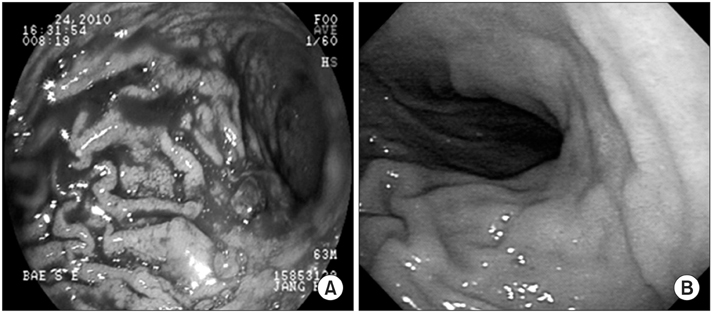
- Gastric cancer patients with acute disseminated intravascular coagulation experiences a rare but severe complication resulting in a dismal prognosis. We report a case of advanced gastric cancer complicated with disseminated intravascular coagulation with intractable tumor bleeding which was successfully treated with chemotherapy consisting of 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin. The patient was a 63-year-old man who complained of abdominal pain, melena, and dyspnea on 24 November 2010. We diagnosed stage IV gastric cancer complicated by disseminated intravascular coagulation. Gastric tumor bleeding was not controlled after procedures were repeated three times using gastrofiberscopy. With the patient's consent, we selected the 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin combination chemotherapy for treatment. After one cycle of 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin therapy, symptoms of bleeding improved and the disseminated intravascular coagulation process was successfully controlled. The primary tumor and multiple metastatic bone lesions were remarkably shrunken and metabolically remitted after eight cycles of chemotherapy. In spite of progression, systemic chemotherapy is effective in disease control; further, the patient gained the longest survival time among cases of gastric cancer with disseminated intravascular coagulation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hohenberger P, Gretschel S. Gastric cancer. Lancet. 2003. 362:305–315.2. Colman RW, Rubin RN. Disseminated intravascular coagulation due to malignancy. Semin Oncol. 1990. 17:172–186.3. Pasquini E, Gianni L, Aitini E, Nicolini M, Fattori PP, Cavazzini G, et al. Acute disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome in cancer patients. Oncology. 1995. 52:505–508.
Article4. Rhee J, Han SW, Oh DY, Im SA, Kim TY, Bang YJ. Clinicopathologic features and clinical outcomes of gastric cancer that initially presents with disseminated intravascular coagulation: a retrospective study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. 25:1537–1542.
Article5. Yeh KH, Cheng AL. Gastric cancer associated with acute disseminated intravascular coagulation: successful initial treatment with weekly 24-hour infusion of high-dose 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin. Br J Haematol. 1998. 100:769–772.
Article6. Tokar M, Bobilev D, Ariad S, Geffen DB. Disseminated intravascular coagulation at presentation of advanced gastric cancer. Isr Med Assoc J. 2006. 8:853–855.7. Hironaka SI, Boku N, Ohtsu A, Nagashima F, Sano Y, Muto M, et al. Sequential methotrexate and 5-fluorouracil therapy for gastric cancer patients with bone metastasis. Gastric Cancer. 2000. 3:19–23.
Article8. Kusumoto H, Haraguchi M, Nozuka Y, Oda Y, Tsuneyoshi M, Iguchi H. Characteristic features of disseminated carcinomatosis of the bone marrow due to gastric cancer: the pathogenesis of bone destruction. Oncol Rep. 2006. 16:735–740.
Article9. Etoh T, Baba H, Taketomi A, Nakashima H, Kohnoe S, Seo Y, et al. Diffuse bone metastasis with hematologic disorders from gastric cancer: clinicopathological features and prognosis. Oncol Rep. 1999. 6:601–605.
Article10. Yoshikawa T, Tsuburaya A, Kobayashi O, Sairenji M, Motohashi H, Noguchi Y. A combination immunochemotherapy of 5-fluorouracil, cisplatin, leucovorin, and OK-432 for advanced and recurrent gastric carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 2003. 50:2259–2263.11. Makino H, Naito K, Tsuruta A, Kan K, Toda S, Yoshimura N, et al. A case of complete remission of metastatic skin carcinoma (erythema type) from advanced gastric cancer by CDDP administration. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 1993. 20:2225–2228.12. De Vita F, Orditura M, Matano E, Bianco R, Carlomagno C, Infusino S, et al. A phase II study of biweekly oxaliplatin plus infusional 5-fluorouracil and folinic acid (FOLFOX-4) as first-line treatment of advanced gastric cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2005. 92:1644–1649.
Article13. Al-Batran SE, Hartmann JT, Probst S, Schmalenberg H, Hollerbach S, Hofheinz R, et al. Phase III trial in metastatic gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma with fluorouracil, leucovorin plus either oxaliplatin or cisplatin: a study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie. J Clin Oncol. 2008. 26:1435–1442.
Article14. Ferrand FR, Gontier E, Guymar S, Fagot T, Ceccaldi B, Malfuson JV, et al. Effectiveness and safe use of modified FOLFOX-6 for metastatic gastric cancer with signet ring cell components complicated by disseminated intravascular coagulation and diffuse bone marrow carcinomatosis. Onkologie. 2012. 35:118–120.
Article15. Huang TC, Yeh KH, Cheng AL, Hsu CH. Weekly 24-hour infusional 5-fluorouracil as initial treatment for advanced gastric cancer with acute disseminated intravascular coagulation. Anticancer Res. 2008. 28:1293–1297.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Gastric Cancer Presenting Acute Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Palliated with Combination Chemotherapy of Irinotecan and Cisplatin
- Spontaneous Subdural Hematoma Associated with Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation in Patient with Cancer
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation
- Heparin Therapy for Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation in Childhood
- A case of disseminated intravascular coagulation and acute renal insufficiency induced by falciparum malaria