J Gastric Cancer.
2015 Jun;15(2):127-131. 10.5230/jgc.2015.15.2.127.
Laparoscopic Partial Fundoplication in Case of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Patient with Absent Esophageal Motility
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. mipark@ns.kosinmed.or.kr
- KMID: 2372360
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2015.15.2.127
Abstract
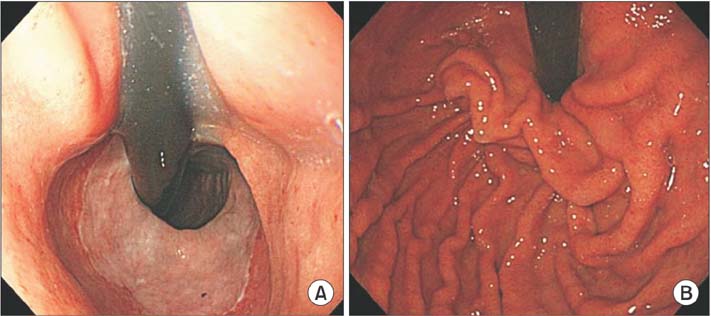
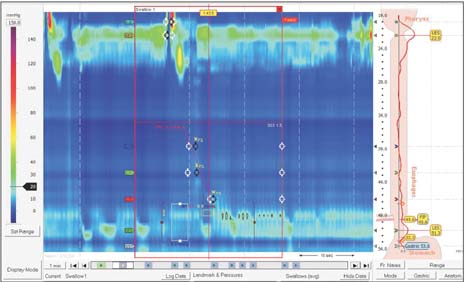
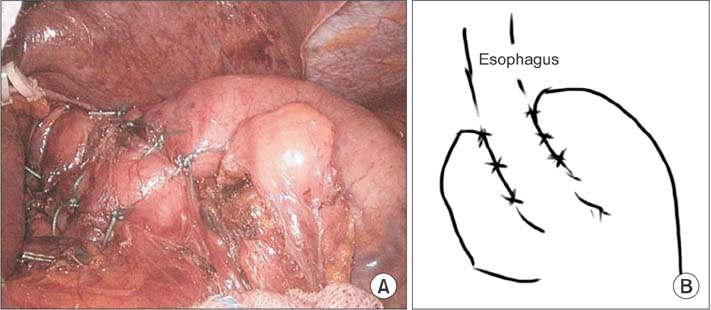
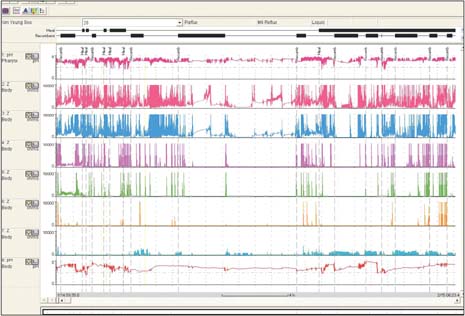
- The surgical indications for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in patients with esophageal motility disorders have been debated. We report a case of antireflux surgery performed in a patient with absent esophageal motility as categorized by the Chicago classification (2011). A 54-year-old man underwent laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication due to apparent GERD and desire to discontinue all medications. After surgery, his subjective symptoms improved. Furthermore, objective findings including manometry and 24-hour pH-metry also improved. In our experience, antireflux surgery can improve GERD symptoms patients, even with absent esophageal motility.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Nationwide survey of partial fundoplication in Korea: comparison with total fundoplication
Chang Min Lee, Joong-Min Park, Han Hong Lee, Kyong Hwa Jun, Sungsoo Kim, Kyung Won Seo, Sungsoo Park, Jong-Han Kim, Jin-Jo Kim, Sang-Uk Han,
Ann Surg Treat Res. 2018;94(6):298-305. doi: 10.4174/astr.2018.94.6.298.
Reference
-
1. Jung HK. Epidemiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease in Asia: a systematic review. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011; 17:14–27.2. Lee SB, Jeon KM, Kim BS, Kim KC, Jung HY, Choi YB. Early experiences of minimally invasive surgery to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Korean Surg Soc. 2013; 84:330–337.3. Lee SK, Kim EK. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication in Korean patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Yonsei Med J. 2009; 50:89–94.4. Kim KM, Cho YK, Bae SJ, Kim DS, Shim KN, Kim JH, et al. Prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease in Korea and associated health-care utilization: a national population-based study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 27:741–745.5. Galmiche JP, Hatlebakk J, Attwood S, Ell C, Fiocca R, Eklund S, et al. LOTUS Trial Collaborators. Laparoscopic antireflux surgery vs esomeprazole treatment for chronic GERD: the LOTUS randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2011; 305:1969–1977.6. Jung HK, Hong SJ, Jo YJ, Jeon SW, Cho YK, Lee KJ, et al. Korean Society of Neurogastroenterology and Motility. Updated guidelines 2012 for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2012; 60:195–218.7. Katz PO, Gerson LB, Vela MF. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108:308–328. quiz 3298. Munitiz V, Ortiz A, Martinez de Haro LF, Molina J, Parrilla P. Ineffective oesophageal motility does not affect the clinical outcome of open Nissen fundoplication. Br J Surg. 2004; 91:1010–1014.9. Herbella FA, Tedesco P, Nipomnick I, Fisichella PM, Patti MG. Effect of partial and total laparoscopic fundoplication on esophageal body motility. Surg Endosc. 2007; 21:285–288.10. Novitsky YW, Wong J, Kercher KW, Litwin DE, Swanstrom LL, Heniford BT. Severely disordered esophageal peristalsis is not a contraindication to laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Surg Endosc. 2007; 21:950–954.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication and Collis Gastroplasty
- A Case of Postfundoplication Dysphagia without Symptomatic Improvement after Endoscopic Dilatation
- Minimally Invasive Surgery for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- Laparoscopic Gastric Wedge Resection and Prophylactic Antireflux Surgery for a Submucosal Tumor of Gastroesophageal Junction
- Surgical treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease