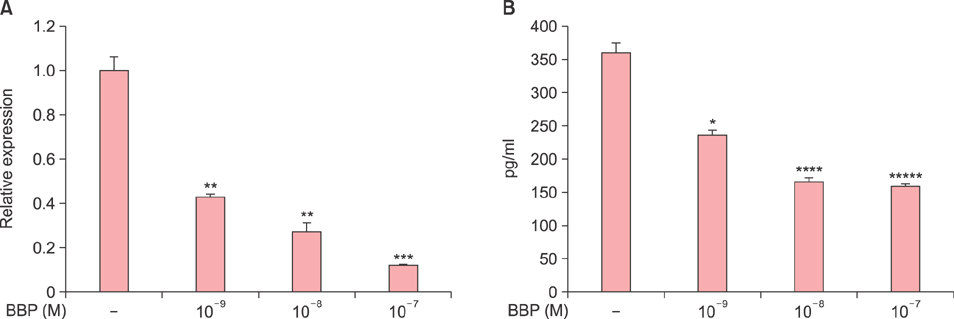
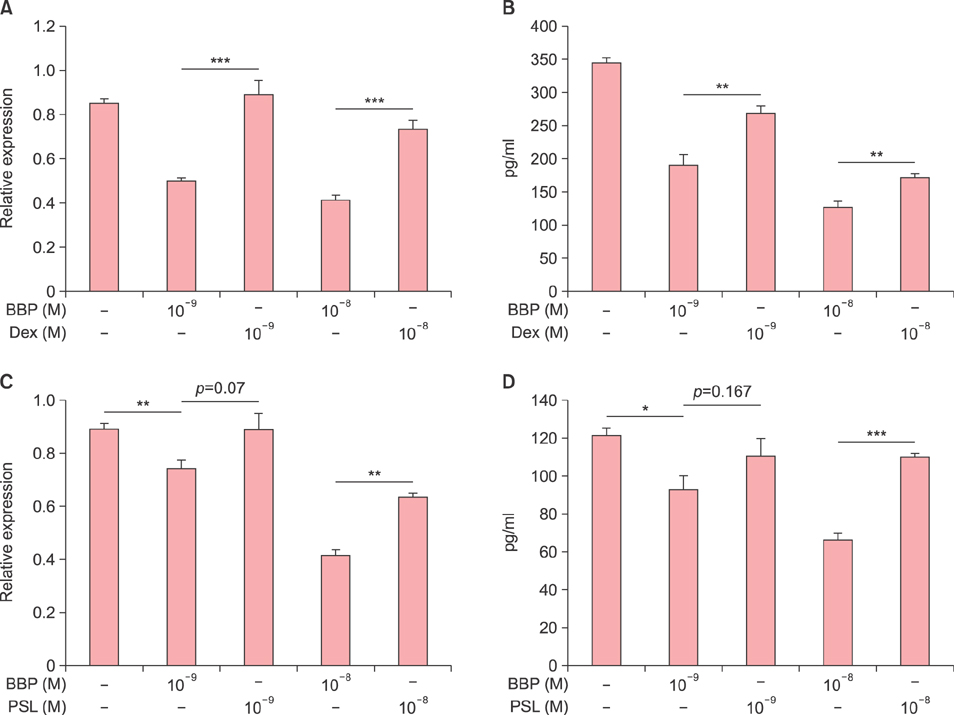
Ann Dermatol.
2016 Dec;28(6):772-775. 10.5021/ad.2016.28.6.772.
Betamethasone Butyrate Propionate Inhibits the Induction of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin in Cultured Normal Human Keratinocytes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Faculty of Medicine, Oita University, Yufu, Japan. hatano@oita-u.ac.jp
- KMID: 2368133
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2016.28.6.772
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Selective Inhibition of β-Catenin/Co-Activator Cyclic AMP Response Element-Binding Protein-Dependent Signaling Prevents the Emergence of Hapten-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-Like Dermatitis
Haruna Matsuda-Hirose, Tomoko Yamate, Mizuki Goto, Akira Katoh, Hiroyuki Kouji, Yuya Yamamoto, Takashi Sakai, Naoto Uemura, Takashi Kobayashi, Yutaka Hatano
Ann Dermatol. 2019;31(6):631-639. doi: 10.5021/ad.2019.31.6.631.
Reference
-
1. Soumelis V, Reche PA, Kanzler H, Yuan W, Edward G, Homey B, et al. Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell mediated allergic inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat Immunol. 2002; 3:673–680.
Article2. Leyva-Castillo JM, Hener P, Jiang H, Li M. TSLP produced by keratinocytes promotes allergen sensitization through skin and thereby triggers atopic march in mice. J Invest Dermatol. 2013; 133:154–163.
Article3. Le TA, Takai T, Kinoshita H, Suto H, Ikeda S, Okumura K, et al. Inhibition of double-stranded RNA-induced TSLP in human keratinocytes by glucocorticoids. Allergy. 2009; 64:1231–1232.
Article4. Hatano Y, Adachi Y, Elias PM, Crumrine D, Sakai T, Kurahashi R, et al. The Th2 cytokine, interleukin-4, abrogates the cohesion of normal stratum corneum in mice: implications for pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Exp Dermatol. 2013; 22:30–35.
Article5. Kinoshita H, Takai T, Le TA, Kamijo S, Wang XL, Ushio H, et al. Cytokine milieu modulates release of thymic stromal lymphopoietin from human keratinocytes stimulated with double-stranded RNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 123:179–186.
Article6. Sakai T, Hatano Y, Zhang W, Fujiwara S. Defective maintenance of pH of stratum corneum is correlated with preferential emergence and exacerbation of atopic-dermatitis-like dermatitis in flaky-tail mice. J Dermatol Sci. 2014; 74:222–228.
Article7. Ohmori K, Manabe H, Tamura T. Anti-inflammatory activities of betamethasone butyrate propionate (BBP), a topical anti-inflammatory steroid. (1). Effects of local and subcutaneous administration. Kiso to Rinsyo [The Clinical Report®]. 1990; 24:195–209.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Induction of Apoptosis by Fas Antibody, IFN - delta, IL - 1 alpha in Normal Human Keratinocytes and KB cells
- Effects of Interleukin 4 on the Production of Interleukin 6 in Human Keratinocytes
- The Role of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP) in Glomerulonephritis
- Phloxine O, a Cosmetic Colorant, Suppresses the Expression of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and Acute Dermatitis Symptoms in Mice
- Alternaria Induces Production of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin in Nasal Fibroblasts Through Toll-like Receptor 2