Ann Dermatol.
2017 Feb;29(1):119-120. 10.5021/ad.2017.29.1.119.
A Case of Late-Onset Peeling Skin Syndrome Likely Triggered by Irritation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea. ahnsk@yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Chung Dam Hana Clinics of Dermatology, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2368045
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.1.119
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
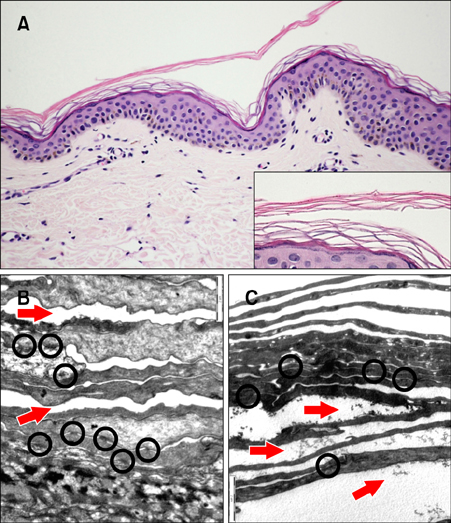
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kharfi M, Khaled A, Ammar D, Ezzine N, El Fekih N, Fazaa B, et al. Generalized peeling skin syndrome: case report and review of the literature. Dermatol Online J. 2010; 16:1.
Article2. Garg K, Singh D, Mishra D. Peeling skin syndrome: current status. Dermatol Online J. 2010; 16:10.
Article3. Köse O, Safali M, Koç E, Arca E, Açikgöz G, Özmen I, et al. Peeling skin diseases: 21 cases from Turkey and a review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012; 26:844–848.
Article4. Silverman AK, Ellis CN, Beals TF, Woo TY. Continual skin peeling syndrome. An electron microscopic study. Arch Dermatol. 1986; 122:71–75.
Article5. Causeret A, Grezard P, Haftek M, Roth B, Forestier J, Perrot H. Acquired peeling skin syndrome in an adult. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2000; 127:194–197.