J Korean Soc Radiol.
2017 Feb;76(2):158-164. 10.3348/jksr.2017.76.2.158.
Injectable Bulking Agents for Urinary Incontinence after Radical Prostatectomy, Mimicking Local Recurrence: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Kyung Hee University Hospital, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. uroradiolim@dreamwiz.com
- 2Department of Urology, Kyung Hee University Hospital, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2367865
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2017.76.2.158
Abstract
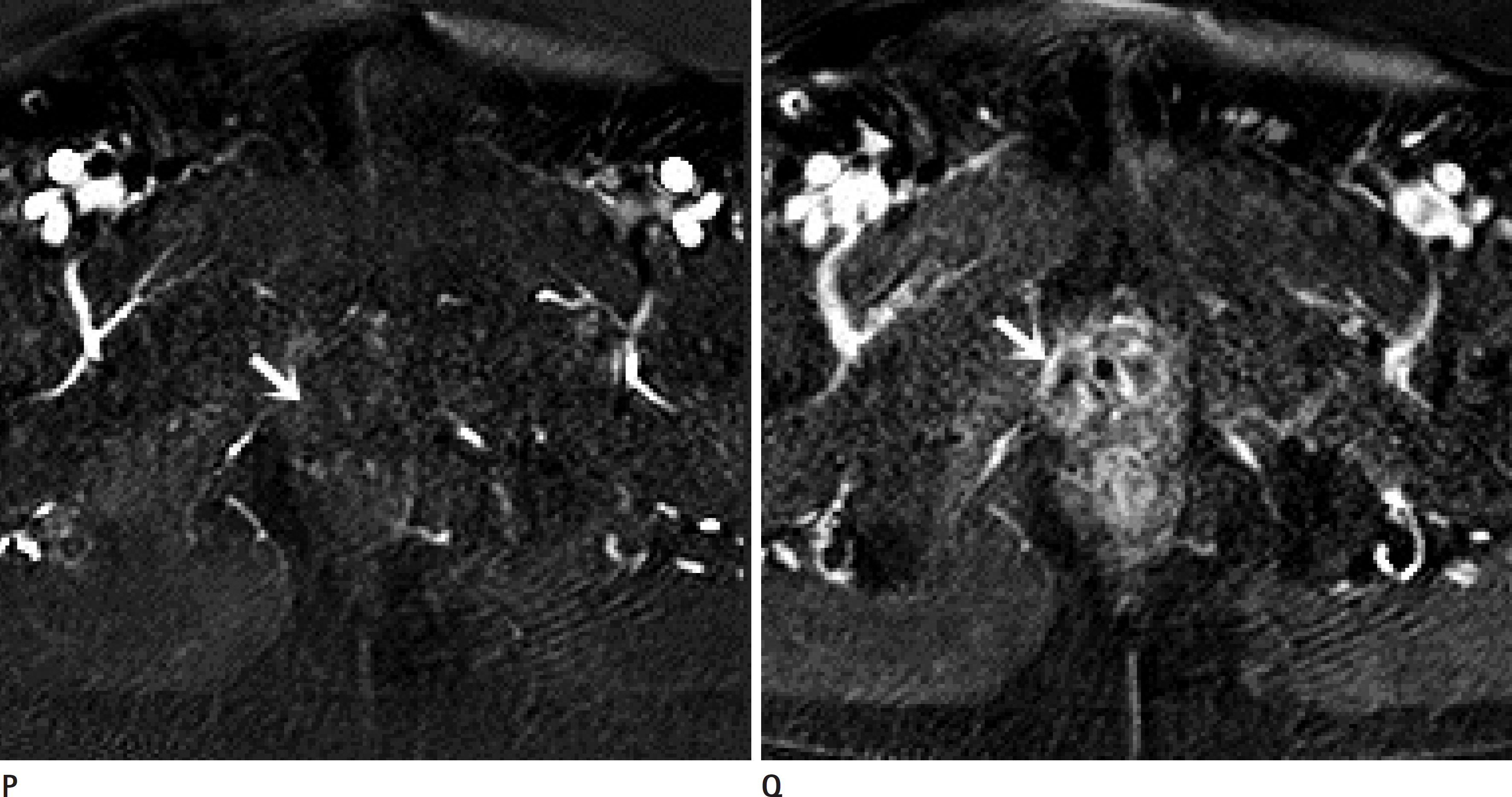
- Periurethral bulking agent injection (or transurethral submucosal injection) is a comparatively less invasive procedure for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence in patients who develop incontinence after radical prostatectomy, and who are more frequently being treated with transurethral submucosal injection. However, as the radiologic findings of bulking agents are not very well known, they can be mistaken for local recurrence in prostate cancer patients who have undergone prostatectomy. Unlike some of the literatures, in which the radiologic features of collagen injections have been reported, the radiologic findings of silicone injections are yet to be determined. Thus, it is our intention to report this case along with the literature review as the authors have experienced an actual case of a silicone injection mistaken as local recurrence.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. King T, Almallah YZ. Post-radical-prostatectomy urinary incontinence: the management of concomitant bladder neck contracture. Adv Urol. 2012; 2012:295798.
Article2. Maki DD, Banner MP, Ramchandani P, Stolpen A, Rovner ES, Wein AJ. Injected periurethral collagen for postprosta-tectomy urinary incontinence: MR and CT appearance. Abdom Imaging. 2000; 25:658–662.
Article3. Kumar D, Kaufman MR, Dmochowski RR. Case reports: periurethral bulking agents and presumed urethral diver-ticula. Int Urogynecol J. 2011; 22:1039–1043.
Article4. Bridges MD, Petrou SP, Lightner DJ. Urethral bulking agents: imaging review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 185:257–264.
Article5. Yablon CM, Banner MP, Ramchandani P, Rovner ES. Com-plications of prostate cancer treatment: spectrum of imaging findings. Radiographics. 2004; 24(Suppl 1):S181–S194.
Article6. Doherty R, Almallah Z. Urinary incontinence after treatment for prostate cancer. BMJ. 2011; 343:d6298.
Article7. Shekarriz B, Upadhyay J, Wood DP. Intraoperative, periop-erative, and longterm complications of radical prostatectomy. Urol Clin North Am. 2001; 28:639–653.
Article8. Tamanini JT, D'Ancona CA, Tadini V, Netto NR Jr. Macro-plastique implantation system for the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence. J Urol. 2003; 169:2229–2233.
Article9. Defreitas GA, Wilson TS, Zimmern PE, Forte TB. Three-di-mensional ultrasonography: an objective outcome tool to assess collagen distribution in women with stress urinary incontinence. Urology. 2003; 62:232–236.
Article10. Sella T, Schwartz LH, Swindle PW, Onyebuchi CN, Scardino PT, Scher HI, et al. Suspected local recurrence after radical prostatectomy: endorectal coil MR imaging. Radiology. 2004; 231:379–385.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Trends in the Management of Post-Prostatectomy Incontinence
- Initial 4 Cases Experience of Male Sling Procedure for the Treatment in Patients with Post-prostatectomy Incontinence
- Improving Urinary Continence after Radical Prostatectomy: Review of Surgical Modifications
- Case of Fournier’s Gangrene in a Patient with Long-Term Indwelling Catheterization due to Urinary Incontinence after Open Radical Prostatectomy
- Injection of aluminum potassium sulfate and tannic acid in the treatment of fecal incontinence: a single-center observational study