J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Apr;31(4):585-589. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.4.585.
Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Erectile Dysfunction in a Rat Model of Atherosclerosis-induced Chronic Pelvic Ischemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dgmoon@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2363698
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.4.585
Abstract
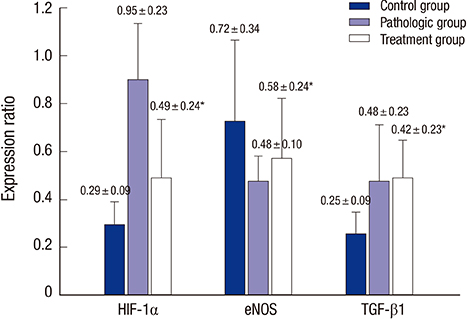
- The aim of this study was to investigate whether the omega-3 fatty acids help to improve erectile function in an atherosclerosis-induced erectile dysfunction rat model. A total of 20 male Sprague-Dawley rats at age 8 weeks were divided into three groups: Control group (n = 6, untreated sham operated rats), Pathologic group (n = 7, untreated rats with chronic pelvic ischemia [CPI]), and Treatment group (n = 7, CPI rats treated with omega-3 fatty acids). For the in vivo study, electrical stimulation of the cavernosal nerve was performed and erectile function was measured in all groups. Immunohistochemical antibody staining was performed for transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGF-β1), endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), and hypoxia inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α). In vivo measurement of erectile function in the Pathologic group showed significantly lower values than those in the Control group, whereas the Treatment group showed significantly improved values in comparison with those in the Pathologic group. The results of western blot analysis revealed that systemically administered omega-3 fatty acids ameliorated the cavernosal molecular environment. Our study suggests that omega-3 fatty acids improve intracavernosal pressure and have a beneficial role against pathophysiological consequences such as fibrosis or hypoxic damage on a CPI rat model, which represents a structural erectile dysfunction model.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Atherosclerosis/*complications
Blotting, Western
Carotid Arteries/physiology
Chronic Disease
Disease Models, Animal
Electric Stimulation
Fatty Acids, Omega-3/*pharmacology
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1, alpha Subunit/metabolism
Ischemia/etiology/*pathology
Male
Nitric Oxide Synthase Type III/metabolism
Penile Erection/*drug effects
Penis/metabolism/pathology
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Transforming Growth Factor beta1/metabolism
Fatty Acids, Omega-3
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1, alpha Subunit
Nitric Oxide Synthase Type III
Transforming Growth Factor beta1
Figure
Reference
-
1. Benet AE, Melman A. The epidemiology of erectile dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am. 1995; 22:699–709.2. Rosen RC, Wing R, Schneider S, Gendrano N 3rd. Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction: the role of medical comorbidities and lifestyle factors. Urol Clin North Am. 2005; 32:403–417.3. Russell S, McVary KT. Lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction: epidemiology and treatment in the aging man. Curr Urol Rep. 2005; 6:445–453.4. Aboseif SR, Breza J, Orvis BR, Lue TF, Tanagho EA. Erectile response to acute and chronic occlusion of the internal pudendal and penile arteries. J Urol. 1989; 141:398–402.5. Ritskes-Hoitinga J, Beynen AC. Atherosclerosis in the rat. Artery. 1988; 16:25–50.6. Ross R, Glomset JA. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976; 295:420–425.7. Aizawa N, Homma Y, Igawa Y. Effect of silodosin, a selective alpha1A-adrenoceptor antagonist on primary bladder afferent activity and bladder microcontractions in rats. Neurourol Urodyn. 2013; 32:569–571.8. Nomiya M, Yamaguchi O, Andersson KE, Sagawa K, Aikawa K, Shishido K, Yanagida T, Kushida N, Yazaki J, Takahashi N. The effect of atherosclerosis-induced chronic bladder ischemia on bladder function in the rat. Neurourol Urodyn. 2012; 31:195–200.9. Delgado-Lista J, Perez-Martinez P, Lopez-Miranda J, Perez-Jimenez F. Long chain omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: a systematic review. Br J Nutr. 2012; 107:Suppl 2. S201–13.10. Calder PC. The role of marine omega-3 (n-3) fatty acids in inflammatory processes, atherosclerosis and plaque stability. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2012; 56:1073–1080.11. Magee TR, Kovanecz I, Davila HH, Ferrini MG, Cantini L, Vernet D, Zuniga FI, Rajfer J, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF. Antisense and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) constructs targeting PIN (Protein Inhibitor of NOS) ameliorate aging-related erectile dysfunction in the rat. J Sex Med. 2007; 4:633–643.12. Rajasekaran M, Kasyan A, Jain A, Kim SW, Monga M. Altered growth factor expression in the aging penis: the Brown-Norway rat model. J Androl. 2002; 23:393–399.13. Williams JK, Andersson KE, Christ G. Animal models of erectile dysfunction (ED): potential utility of non-human primates as a model of atherosclerosis-induced vascular ED. Int J Impot Res. 2012; 24:91–100.14. Iacono F, Giannella R, Somma P, Manno G, Fusco F, Mirone V. Histological alterations in cavernous tissue after radical prostatectomy. J Urol. 2005; 173:1673–1676.15. Yaman O, Yilmaz E, Bozlu M, Anafarta K. Alterations of intracorporeal structures in patients with erectile dysfunction. Urol Int. 2003; 71:87–90.16. Ferrini MG, Davila HH, Valente EG, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Rajfer J. Aging-related induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase is vasculo-protective to the arterial media. Cardiovasc Res. 2004; 61:796–805.17. Moreland RB. Is there a role of hypoxemia in penile fibrosis: a viewpoint presented to the Society for the Study of Impotence. Int J Impot Res. 1998; 10:113–120.18. Sattar AA, Salpigides G, Vanderhaeghen JJ, Schulman CC, Wespes E. Cavernous oxygen tension and smooth muscle fibers: relation and function. J Urol. 1995; 154:1736–1739.19. Ajami M, Davoodi SH, Habibey R, Namazi N, Soleimani M, Pazoki-Toroudi H. Effect of DHA+EPA on oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by ischemia-reperfusion in rat kidneys. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2013; 27:593–602.20. Castillo RL, Arias C, Farías JG. Omega 3 chronic supplementation attenuates myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury through reinforcement of antioxidant defense system in rats. Cell Biochem Funct. 2014; 32:274–281.21. Brahmbhatt V, Oliveira M, Briand M, Perrisseau G, Bastic Schmid V, Destaillats F, Pace-Asciak C, Benyacoub J, Bosco N. Protective effects of dietary EPA and DHA on ischemia-reperfusion-induced intestinal stress. J Nutr Biochem. 2013; 24:104–111.22. Avramovic N, Dragutinovic V, Krstic D, Colovic M, Trbovic A, de Luka S, Milovanovic I, Popovic T. The effects of omega 3 fatty acid supplementation on brain tissue oxidative status in aged wistar rats. Hippokratia. 2012; 16:241–245.23. Miles EA, Wallace FA, Calder PC. Dietary fish oil reduces intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and scavenger receptor expression on murine macrophages. Atherosclerosis. 2000; 152:43–50.24. De Caterina R, Cybulsky MI, Clinton SK, Gimbrone MA Jr, Libby P. The omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoate reduces cytokine-induced expression of proatherogenic and proinflammatory proteins in human endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994; 14:1829–1836.25. Melman A, Gingell JC. The epidemiology and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. J Urol. 1999; 161:5–11.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Letter to the Editor: Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Erectile Dysfunction in a Rat Model of Atherosclerosis-induced Chronic Pelvic Ischemia
- Omega-3 Index as a Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease and Its Application to Korean Population
- Analysis of Plasma Long-Chain Fatty Acids in Hypertensive Patients
- Omega-3 and Menopause
- Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acid during Pregnancy