Ann Lab Med.
2015 Mar;35(2):226-232. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.2.226.
Quantitative Measurement of Serum MicroRNA-21 Expression in Relation to Breast Cancer Metastasis in Chinese Females
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, The First Hospital of Zibo City, Zibo, China. wguinian@163.com
- 2Department of Pharmacy, Zibo Vocational Institute, Zibo, China.
- 3Department of Surgical Medicine, The First Hospital of Zibo City, Zibo, China.
- 4Key Laboratory of Biomedical Engineering, Shandong Wanjie Medical College, Zibo, China.
- KMID: 2363183
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.2.226
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in females. Aberrant expression of microRNA-21 (miR-21) has previously been reported in breast cancer tissue. The aim of this study was to investigate expression levels of serum miR-21 in breast cancer patients and evaluate its prognostic value in Chinese females.
METHODS
Real-time quantitative (RQ)-PCR was used to analyze miR-21 expression in archived serum, tumor tissue, and adjacent normal tissue from 549 participants (326 with breast cancer, 223 without breast cancer). We also analyzed associations between serum miR-21 expression and breast cancer subtypes and patient prognosis. Recurrence and survival were analyzed by using the multivariate Cox proportional hazards model.
RESULTS
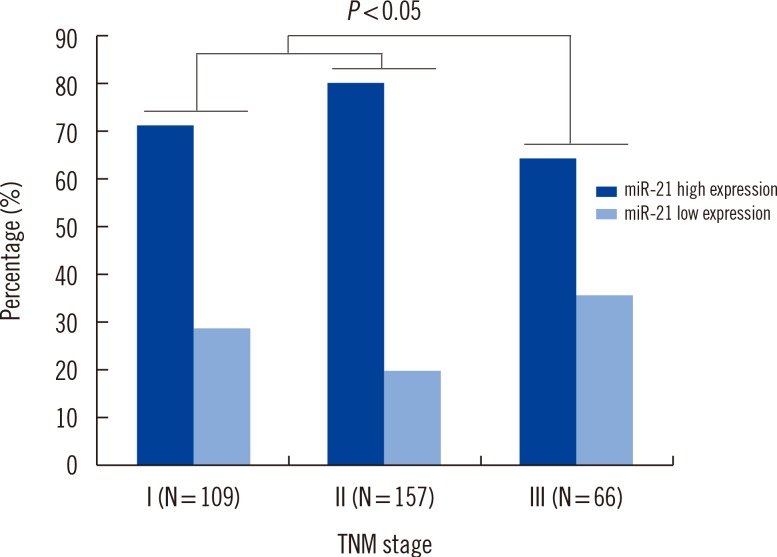
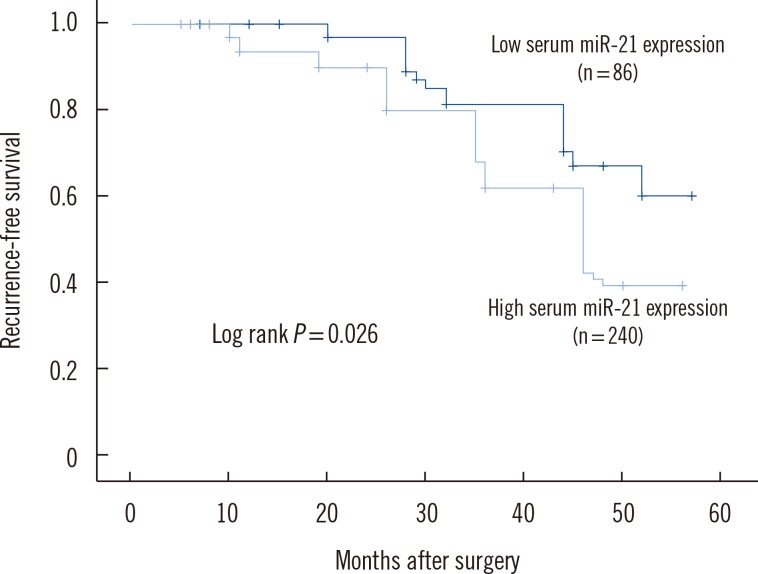
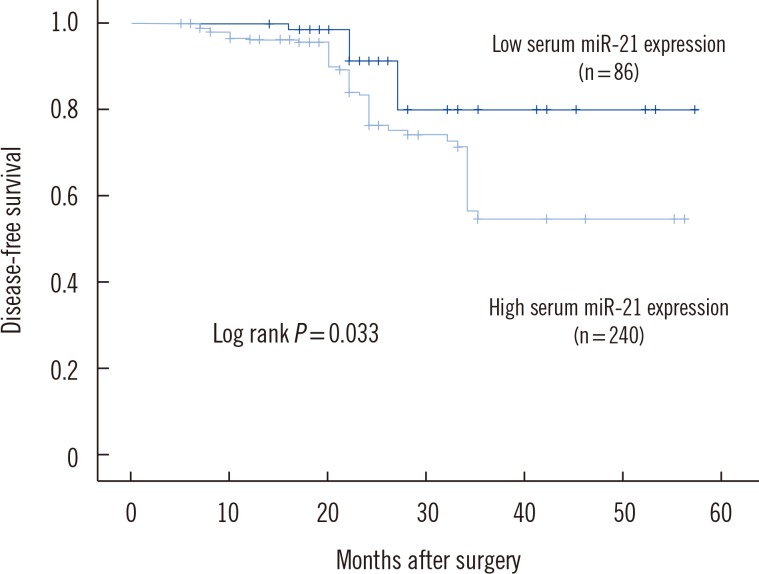
Expression of miR-21 was significantly higher in breast cancer tissues compared with normal adjacent breast tissues (P<0.001). The 2(-DeltaDeltaCt) values for serum miR-21 in breast cancer patients versus healthy controls were 9.12+/-3.43 and 2.96+/-0.73, respectively. Multivariate Cox proportional hazards model suggested that serum miR-21 expression was an independent poor prognostic factor for both recurrence (hazard ratio [HR]= 2.942; 95% confidence interval [CI]=1.420-8.325; P=0.008) and disease-free survival (HR=2.732; 95% CI=1.038-7.273, P=0.003) in breast cancer.
CONCLUSIONS
Increased serum miR-21 expression level was correlated with poor prognosis of breast cancer patients, indicating that serum miR-21 may be a novel prognostic marker for recurrence and survival of breast cancer patients before resection.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Biomarkers, Tumor/genetics
Breast/metabolism
Breast Neoplasms/metabolism/mortality/*pathology
Disease-Free Survival
Female
Humans
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Lymphatic Metastasis
MicroRNAs/*blood
Neoplasm Recurrence, Local
Prognosis
Proportional Hazards Models
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
Biomarkers, Tumor
MicroRNAs
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011; 61:69–90. PMID: 21296855.
Article2. Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell. 1993; 75:855–862. PMID: 8252622.
Article3. Michael MZ, O'Connor SM, van Holst Pellekaan NG, Young GP, James RJ. Reduced accumulation of specific microRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res. 2003; 1:882–891. PMID: 14573789.4. Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop T, Noch E, yendamuri S, et al. Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101:2999–3004. PMID: 14973191.
Article5. Wang F, Zheng ZG, Guo J, Ding X. Correlation and quantitation of microRNA aberrant expression in tissues and sera from patients with breast tumor. Gynecol Oncol. 2010; 119:586–593. PMID: 20801493.
Article6. Cortez MA, Bueso-Ramos C, Ferdin J, Lopez-Berestein G, Sood AK, Calin GA. MicroRNAs in body fluids--the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011; 8:467–477. PMID: 21647195.
Article7. Kishimoto T, Eguchi H, Nagano H, Kobayashi S, Akita H, Hama N, et al. Plasma miR-21 is a novel diagnostic biomarker for biliary tract cancer. Cancer Sci. 2013; 104:1626–1631. PMID: 24118467.
Article8. Zhao H, Shen J, Medico L, Wang D, Ambrosone CB, Liu S. A pilot study of circulating miRNAs as potential biomarkers of early stage breast cancer. PLos One. 2010; 5:e13735. PMID: 21060830.
Article9. Edge SB, Byrd DR, Carducci M, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, editors. AJCC cancer staging manual. 7th ed. New York: Springer-Verlag;2009.10. Asaga S, Kuo C, Nguyen T, Terpenning M, Giuliano AE, Hoon DS. Direct serum assay for microRNA-21 concentrations in early and advanced breast cancer. Clin Chem. 2011; 57:84–91. PMID: 21036945.
Article11. Mar-Aguilar F, Mendoza-Ramíreza JA, Malagón-Santiago I, Espino-Silva PK, Santuario-Facio SK, Ruiz-Flores P, et al. Serum circulating microRNA profiling for identification of potential breast cancer biomarkers. Dis Markers. 2013; 34:163–169. PMID: 23334650.
Article12. Chan M, Liaw CS, Ji SM, Tan HH, Wong CY, Thike AA, et al. Identification of circulating microRNA signatures for breast cancer detection. Clin Cancer Res. 2013; 19:4477–4487. PMID: 23797906.
Article13. Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronesse A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005; 65:7065–7070. PMID: 16103053.
Article14. Calin GA, Croce CM. Chromosomal rearrangements and microRNAs: a new cancer link with clinical implications. J Clin Invest. 2007; 117:2059–2066. PMID: 17671640.
Article15. Qian B, Katsaros D, Lu L, Preti M, Durango A, Arisio R, et al. High miR-21 expression in breast cancer associated with poor disease-free survival in early stage disease and high TGF-β1. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009; 117:131–140. PMID: 18932017.
Article16. Yan LX, Wu QN, Zhang Y, Li YY, Liao DZ, Hou JH, et al. Knockdown of miR-21 in human breast cancer cell lines inhibits proliferation, in vitro migration and in vivo tumor growth. Breast Cancer Res. 2011; 13:R2. PMID: 21219636.
Article17. Kumar S, Keerthana R, Pazhanimuthu A, Perumal P. Overexpression of circulating miRNA-21 and miRNA-146a in plasma samples of breast cancer patients. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 2013; 50:210–214. PMID: 23898484.18. Gao J, Zhang Q, Xu J, Guo L, Li X. Clinical significance of serum miR-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA. Chin J Cancer Res. 2013; 25:743–748. PMID: 24385703.19. Müller V, Gade S, Steinbach B, Loibl S, von Minckwitz G, Untch M, et al. Changes in serum levels of miR-21, miR-210, and miR-373 in HER2-positive breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy: a translational research project within the Geparquinto trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014; 147:61–68. PMID: 25086636.
Article20. Tamaki K, Ishida T, Tamaki N, Kamada Y, Uehara K, Miyashita M, et al. Analysis of clinically relevant values of Ki-67 labeling index in Japanese breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer. 2014; 21:325–333. PMID: 22782361.
Article21. Leivonen SK, Mäkelä R, Ostling P, Kohonen P, Haapa-Paananen S, Kleivi K, et al. Protein lysate microarry analysis to identify microRNAs regulating estrogen receptor signaling in braest cancer cell lines. Oncogene. 2009; 28:3926–3936. PMID: 19684618.22. Fackenthal JD, Olopade Ol. Breast cancer risk associated with BRCA1and BRCA2 in diverse populations. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007; 7:937–948. PMID: 18034184.23. Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F, Mo YY. miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene. 2007; 26:2799–2803. PMID: 17072344.
Article24. Li J, Shen L, Xiao XG, Fang L. MicroRNAs in breast cancer and breast cancer stem cells and their potential for breast cancer therapy. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013; 126:2556–2563. PMID: 23823834.25. Tsujiura M, Ichikawa D, Komatsu S, Shiozaki A, Takeshita H, Kosuga T, et al. Circulating microRNAs in plasma of patients with gastric cancers. Br J Cancer. 2010; 102:1174–1179. PMID: 20234369.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prognostic Implications of MicroRNA-21 Overexpression in Invasive Ductal Carcinomas of the Breast
- The Significance of MicroRNA Let-7b, miR-30c, and miR-200c Expression in Breast Cancers
- High MicroRNA-370 Expression Correlates with Tumor Progression and Poor Prognosis in Breast Cancer
- Stromal Expression of MicroRNA-21 in Advanced Colorectal Cancer Patients with Distant Metastases
- Prolactin Inhibits BCL6 Expression in Breast Cancer Cells through a MicroRNA-339-5p-Dependent Pathway