Ann Lab Med.
2015 Jan;35(1):178-180. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.1.178.
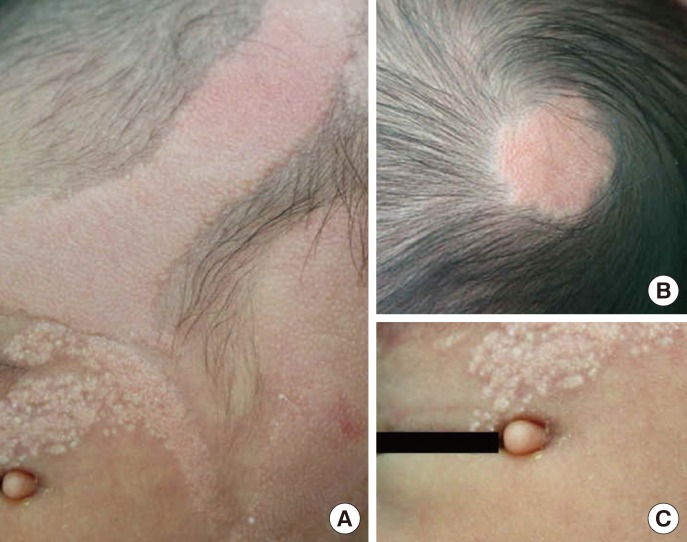
Identification of Somatic KRAS Mutation in a Korean Baby with Nevus Sebaceus Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. iamgawon@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. changski@skku.edu
- 3Department of Pathology, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2363174
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.1.178
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Groesser L, Herschberger E, Ruetten A, Ruivenkamp C, Lopriore E, Zutt M, et al. Postzygotic HRAS and KRAS mutations cause nevus sebaceus and Schimmelpenning syndrome. Nat Genet. 2012; 44:783–787. PMID: 22683711.2. Shaw RJ, Cantley LC. Ras, PI(3)K and mTOR signalling controls tumour cell growth. Nature. 2006; 441:424–430. PMID: 16724053.
Article3. Aslam A, Salam A, Griffiths CE, McGrath JA. Naevus sebaceus: a mosaic RASopathy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2014; 39:1–6. PMID: 24341474.
Article4. Levinsohn JL, Tian LC, Boyden LM, McNiff JM, Narayan D, Loring ES, et al. Whole-exome sequencing reveals somatic mutations in HRAS and KRAS, which cause nevus sebaceus. J Invest Dermatol. 2013; 133:827–830. PMID: 23096712.5. Happle R. Nevus sebaceus is a mosaic RASopathy. J Invest Dermatol. 2013; 133:597–600. PMID: 23399824.
Article6. Schubbert S, Zenker M, Rowe SL, Böll S, Klein C, Bollag G, et al. Germline KRAS mutations cause Noonan syndrome. Nat Genet. 2006; 38:331–336. PMID: 16474405.7. Aoki Y, Niihori T, Kawame H, Kurosawa K, Ohashi H, Tanaka Y, et al. Germline mutations in HRAS proto-oncogene cause Costello syndrome. Nat Genet. 2005; 37:1038–1040. PMID: 16170316.8. Brandling-Bennett HA, Morel KD. Epidermal nevi. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2010; 57:1177–1198. PMID: 20888465.
Article9. Sun BK, Saggini A, Sarin KY, Kim J, Benjamin L, LeBoit PE, et al. Mosaic activating RAS mutations in nevus sebaceus and nevus sebaceus syndrome. J Invest Dermatol. 2013; 133:824–827. PMID: 23096709.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Keratoacanthoma in Co-existence with Nevus Sebaceus
- Nevus Sebaceus Associated with Trichilemmoma, Trichilemmal Carcinoma and Trichoblastoma
- A Case of nevus Sebacens of Jadassohn Associated with Various Epidermal Appendage Tumors
- A study on cytokeratin and involucrin expression in the epidermis of nevus sebaceus
- A Case of Trichilemmoma Arising in Nevus Sebaceus