Imaging Sci Dent.
2016 Dec;46(4):291-296. 10.5624/isd.2016.46.4.291.
Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the sublingual gland: A case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju, Korea. 2460song@naver.com
- KMID: 2362749
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2016.46.4.291
Abstract
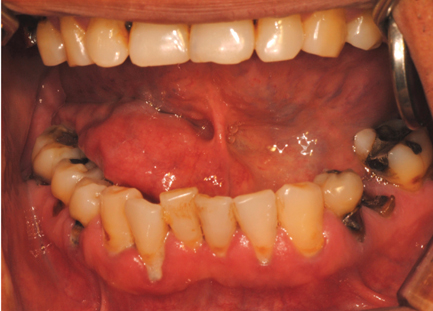
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) of the sublingual gland is an extremely rare neoplasm. The clinicopathological characteristics of ACC are slow-growing swelling with or without ulceration, perineural spread, local recurrence, and distant metastasis. This report describes a 58-year-old male who had a slowly growing swelling without ulceration on the right side of the mouth floor that had been present for 1 month. In a radiological examination, the mass showed multilocular cystic features and no bony or tongue muscle invasion. No enlarged cervical lymph nodes were detected. Excisional biopsy and histological analysis showed that the lesion was ACC. In addition to reporting a rare case of ACC, this report also discusses the differential diagnosis and treatment of ACC with a review of the relevant literature.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dong J, Tian L, Li S, Mo Y, Liu L, Zhong R. Differences in extension patterns between adenoid cystic carcinoma of the nasopharynx and nasopharyngeal carcinoma on MRI. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015; 8:15960–15968.2. Khan S, Agwani K, Bhargava P, Kumar SP. Adenoid cystic carcinoma presenting as an ulcer on the floor of the mouth: a rare case report. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 40:253–257.
Article3. Sepulveda I, Platin E, Delgado C, Rojas P. Sinonasal adenoid cystic carcinoma with intracranial invasion and perineural spread: a case report and review of the literature. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2015; 5:57.4. Feng H, Wang J, Guo P, Xu J, Feng J. C3 vertebral metastases from tongue adenoid cystic carcinoma: a rare case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e1135.5. Mesolella M, Luce A, Marino A, Caraglia M, Ricciardiello F, Iengo M. Treatment of c-kit positive adenoid cystic carcinoma of the tongue: a case report. Oncol Lett. 2014; 8:309–312.
Article6. Triantafillidou K, Dimitrakopoulos J, Iordanidis F, Koufogiannis D. Management of adenoid cystic carcinoma of minor salivary glands. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006; 64:1114–1120.
Article7. Falk GA, El-Hayek K, Morris-Stiff G, Tuthill RJ, Winans CG. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the base of the tongue: late metastasis to the pancreas. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2011; 2:1–3.
Article8. Sato K, Ueda Y, Sakurai A, Ishikawa Y, Kaji S, Nojima T, et al. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the maxillary sinus with gradual histologic transformation to high-grade adenocarcinoma: a comparative report with dedifferentiated carcinoma. Virchows Arch. 2006; 448:204–208.
Article9. Benson BW. Salivary gland radiology. In : White SC, Pharoah MJ, editors. Oral radiology: principles and interpretation. 5th ed. St. Louis, Mo: Mosby;2004. p. 658–676.10. Yousem DM, Kraut MA, Chalian AA. Major salivary gland imaging. Radiology. 2000; 216:19–29.
Article11. Kumar VS, Prathi VS, Manne RK, Beeraka S, Natarajan K. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of sublingual salivary gland obstructing the submandibular salivary gland duct. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2013; 3:Suppl 1. 10.
Article12. Ariji Y, Gotoh M, Naitoh M, Izumi M, Shimozato K, Kurita K, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of tumorous lesions in the floor of the mouth: case reports and review of the literature. Oral Radiol. 2006; 22:18–26.
Article13. Freling NJ, Molenaar WM, Vermey A, Mooyaart EL, Panders AK, Annyas AA, et al. Malignant parotid tumors: clinical use of MR imaging and histologic correlation. Radiology. 1992; 185:691–696.
Article14. Vogl TJ, Dresel SH, Spath M, Grevers G, Wilimzig C, Schedel HK, et al. Parotid gland: plain and gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology. 1990; 177:667–674.
Article15. Son PM, Brandwein MS. Adenoid cystic carcinoma. In : Som PM, Curtin HD, editors. Head and neck imaging. 4th ed. St. Louis, Mo: Mosby;2003. p. 2090–2096.16. Saito M, Nishiyama H, Maruyama S, Oda Y, Saku T, Hayashi T. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of sublingual gland involving the submandibular duct. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2008; 37:421–424.
Article17. Huang TT, Chou YF, Wen YH, Chen PR. Resected tumours of the sublingual gland: 15 years' experience. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016; 54:625–628.
Article18. Peravali RK, Bhat HH, Upadya VH, Agarwal A, Naag S. Salivary gland tumors: a diagnostic dilemma. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2015; 14:Suppl 1. 438–442.
Article19. Madani G, Beale T. Tumors of the salivary glands. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2006; 27:452–464.
Article20. Lee YY, Wong KT, King AD, Ahuja AT. Imaging of salivary gland tumours. Eur J Radiol. 2008; 66:419–436.
Article21. Ginsberg LE. Imaging of perineural tumor spread in head and neck cancer. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 1999; 20:175–186.
Article22. Laccourreye O, Bely N, Halimi P, Guimaraes R, Brasnu D. Cavernous sinus involvement from recurrent adenoid cystic carcinoma. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1994; 103:822–825.
Article23. Curtin HD. Detection of perineural spread: fat is a friend. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; 19:1385–1386.24. Swartz JD, Rothman MI, Marlowe FI, Berger AS. MR imaging of parotid mass lesions: attempts at histopathologic differentiation. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1989; 13:789–796.25. Assili S, Fathi Kazerooni A, Aghaghazvini L, Saligheh Rad HR, Pirayesh Islamian J. Dynamic contrast magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) and diffusion weighted MR imaging (DWI) for differentiation between benign and malignant salivary gland tumors. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2015; 5:157–168.26. Wang J, Takashima S, Takayama F, Kawakami S, Saito A, Matsushita T, et al. Head and neck lesions: characterization with diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology. 2001; 220:621–630.
Article27. King AD, Yeung DK, Ahuja AT, Tse GM, Yuen HY, Wong KT, et al. Salivary gland tumors at in vivo proton MR spectroscopy. Radiology. 2005; 237:563–569.
Article28. Hoseini AT, Razavi SM, Khabazian A. Lipoma in oral mucosa: two case reports. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2010; 7:41–43.29. Nilesh K, Malik NA, Patil P, Chapi MD. Large plunging ranula presenting as isolated neck swelling: steps in diagnosis and surgical steps in management. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015; 9:MD01–MD03.
Article30. More CB, Bhavsar K, Varma S, Tailor M. Oral mucocele: a clinical and histopathological study. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2014; 18:Suppl 1. S72–S77.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dedifferentiation in Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Neck
- Renal metastasis from adenoid cystic carcinoma of salivary gland: report of two cases
- A Case of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of Bartholin's Gland
- A Case of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Bartholin's Gland
- Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of Skin: A case report