Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2016 Mar;4(2):133-139. 10.4168/aard.2016.4.2.133.
A single hospital survey of anaphylaxis awareness among health care providers and medical students
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Allergy & Clinical Immunology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 2Regional Pharmacovigilance Center, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Clinical Trial Center, Ajou University Hospital, Suwon, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. jsjs87@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 2361286
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2016.4.2.133
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Anaphylaxis is a rapidly progressive allergic reaction that requires precise recognition and immediate management. However, health care providers, awareness of anaphylaxis has not been acknowledged. The aim of this study is to investigate the extent of knowledge and principal management skills on anaphylaxis among medical personnel and students.
METHODS
We performed a questionnaire survey on knowledge, education, and managing skills for anaphylaxis to physicians, nurses, health personnel, and medical students in Ajou University Medical Center, from 26 June to 31 October, 2014. The survey contained 2 main sections: questions about demographic data and 2 types of questionnaire (type I for all participants and type II for only medical staffs) for self-assessment on anaphylaxis.
RESULTS
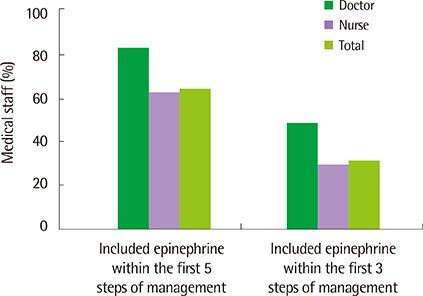
A total of 1,615 participants (128 doctors, 828 nurses, 436 students, and 223 health personnel) completed the survey. For questionnaire I, the percentages of correct answers in doctors, nurses, medical students, and health personnel were 77.5%, 56.4%, 47.8%, and 28.0% respectively, showing significant differences between groups (P<0.001). For questionnaire II, 93% of doctors and 75.6% of nurses indicated epinephrine as the drug of choice, and 79.7% of doctors and 71.3% of nurses selected the correct intramuscular route. More than 3 quarters of the doctors (80.5%) selected epinephrine within the first 5 steps of treatment, but only 48% included epinephrine within the first 3 steps.
CONCLUSION
Our study showed considerable lack of knowledge on anaphylaxis among health care providers, especially on the specific management steps of anaphylaxis. As significant gaps on overall knowledge of anaphylaxis were observed between different groups of medical personnel, regular education should be implemented for each department in the health care setting.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Anaphylaxis: diagnosis, management, and current barriers
Hyun Jung Jin
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2016;4(2):79-81. doi: 10.4168/aard.2016.4.2.79.The past, present, and future of research on anaphylaxis in Korean children
Sooyoung Lee
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(Suppl 1):S21-S30. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.S1.S21.Accuracy for registration of disease codes in pediatric anaphylaxis
Yeon Joo Cho, Sun Hyu Kim, Hyeji Lee, Byungho Choi, Mi Jin Kim, Jung Seok Hong
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017;5(3):159-164. doi: 10.4168/aard.2017.5.3.159.
Reference
-
1. Simons FE, Ardusso LR, Bilo MB, Cardona V, Ebisawa M, El-Gamal YM, et al. International consensus on (ICON) anaphylaxis. World Allergy Organ J. 2014; 7:9.
Article2. Panesar SS, Javad S, de Silva D, Nwaru BI, Hickstein L, Muraro A, et al. The epidemiology of anaphylaxis in Europe: a systematic review. Allergy. 2013; 68:1353–1361.
Article3. Tejedor Alonso MA, Moro Moro M, Mugica Garcia MV. Epidemiology of anaphylaxis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2015; 45:1027–1039.
Article4. Lim DH. Epidemiology of anaphylaxis in Korean children. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:351–354.
Article5. Lee SY, Kim KW, Lee HH, Lim DH, Chung HL, Kim SW, et al. Incidence and clinical characteristics of pediatric emergency department visits of children with severe food allergy. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 32:169–175.6. Jang GC, Chang YS, Choi SH, Song WJ, Lee SY, Park HS, et al. Overview of anaphylaxis in Korea: diagnosis and management. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:181–196.
Article7. Ye YM, Kim MK, Kang HR, Kim TB, Sohn SW, Koh YI, et al. Predictors of the severity and serious outcomes of anaphylaxis in korean adults: a multicenter retrospective case study. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015; 7:22–29.
Article8. Turner PJ, Gowland MH, Sharma V, Ierodiakonou D, Harper N, Garcez T, et al. Increase in anaphylaxis-related hospitalizations but no increase in fatalities: an analysis of United Kingdom national anaphylaxis data, 1992-2012. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015; 135:956–963.e1.
Article9. Koplin JJ, Martin PE, Allen KJ. An update on epidemiology of anaphylaxis in children and adults. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 11:492–496.
Article10. Ibrahim I, Chew BL, Zaw WW, Van Bever HP. Knowledge of anaphylaxis among Emergency Department staff. Asia Pac Allergy. 2014; 4:164–171.
Article11. Jung-Wu S. Anaphylaxis knowledge and practice preference of pediatric emergency medicine physicians: a national survey. Pediatrics. 2014; 134:Suppl 3. S148–S149.
Article12. Grossman SL, Baumann BM, Garcia Pena BM, Linares MY, Greenberg B, Hernandez-Trujillo VP. Anaphylaxis knowledge and practice preferences of pediatric emergency medicine physicians: a national survey. J Pediatr. 2013; 163:841–846.
Article13. Jacobsen RC, Toy S, Bonham AJ, Salomone JA 3rd, Ruthstrom J, Gratton M. Anaphylaxis knowledge among paramedics: results of a national survey. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2012; 16:527–534.
Article14. Baccıoglu A, Yılmazel Ucar E. Level of knowledge about anaphylaxis among health care providers. Tuberk Toraks. 2013; 61:140–146.
Article15. Droste J, Narayan N. Hospital doctors' knowledge of adrenaline (epinephrine) administration in anaphylaxis in adults is deficient. Resuscitation. 2010; 81:1057–1058.
Article16. Jeong JW, Park CS, Jung JW, Park HK, Kim SH, Kim TB, et al. Anaphylaxis: hospital doctors' knowledge of management guidelines. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131:AB221.
Article17. Anaphylaxis quiz [Internet]. Milwaukee (WI): American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology;c2016. cited 2014 Jun 1. Available from: http://www.aaaai.org/conditions-and-treatments/allergies/anaphylaxis/anaphylaxis-quiz.aspx.18. Rudders SA, Banerji A. An update on self-injectable epinephrine. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 13:432–437.
Article19. Plumb B, Bright P, Gompels MM, Unsworth DJ. Correct recognition and management of anaphylaxis: not much change over a decade. Postgrad Med J. 2015; 91:3–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Research on the Perceptions of Low Vision Rehabilitation
- Awareness of anaphylaxis among community and emergency responders in Korea
- ERRATUM: Author's English name correction. A single hospital survey of anaphylaxis awareness among health care providers and medical students
- Gender Differences in Awareness of Preconception Care and Pregnancy
- Factors Related to Emergency Department Healthcare Providers' Attitudes towards End-of-Life Care