J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Jan;31(1):120-124. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.1.120.
Factors Affecting Length of Hospital Stay and Mortality in Infected Diabetic Foot Ulcers Undergoing Surgical Drainage without Major Amputation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Konyang Universtiy Hospital, Daejon, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Hallym University Cheuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. oasis100@empas.com
- 4Department of Mathematics, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea.
- 5Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea.
- 6Department of Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 7Department of Plastic Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2360001
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.1.120
Abstract
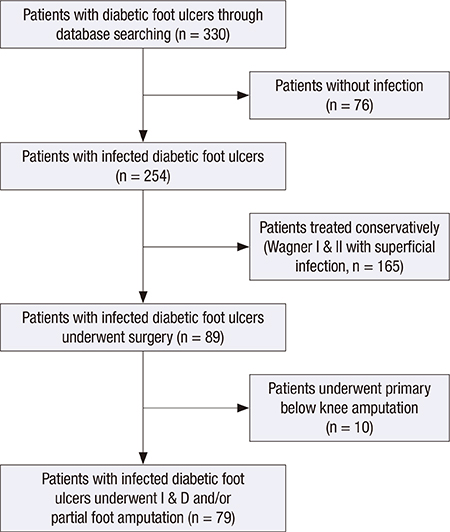
- This study aimed to investigate factors affecting length of hospital stay and mortality of a specific group of patients with infected diabetic foot ulcer who underwent surgical drainage without major amputation, which is frequently encountered by orthopedic surgeons. Data on length of hospital stay, mortality, demographics, and other medical information were collected for 79 consecutive patients (60 men, 19 women; mean age, 66.1 [SD, 12.3] yr) with infected diabetic foot ulcer who underwent surgical drainage while retaining the heel between October 2003 and May 2013. Multiple linear regression analysis was performed to determine factors affecting length of hospital stay, while multiple Cox regression analysis was conducted to assess factors contributing to mortality. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR, P=0.034), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level (P=0.021), body mass index (BMI, P=0.001), and major vascular disease (cerebrovascular accident or coronary artery disease, P=0.004) were significant factors affecting length of hospital stay, whereas age (P=0.005) and serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level (P=0.024) were significant factors contributing to mortality. In conclusion, as prognostic factors, the length of hospital stay was affected by the severity of inflammation, the recent control of blood glucose level, BMI, and major vascular disease, whereas patient mortality was affected by age and renal function in patients with infected diabetic foot ulcer undergoing surgical drainage and antibiotic treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Amputation
Blood Sedimentation
Blood Urea Nitrogen
Body Mass Index
Diabetic Foot/mortality/*pathology/*surgery
Drainage
Female
Hemoglobin A, Glycosylated/analysis
Humans
Length of Stay
Male
Middle Aged
Proportional Hazards Models
Retrospective Studies
Risk Factors
Severity of Illness Index
Survival Rate
Vascular Diseases/complications
Hemoglobin A, Glycosylated
Figure
Reference
-
1. Borghans I, Kool RB, Lagoe RJ, Westert GP. Fifty ways to reduce length of stay: an inventory of how hospital staff would reduce the length of stay in their hospital. Health Policy. 2012; 104:222–233.2. Frykberg RG, Piaggesi A, Donaghue VM, Schipani E, Habershaw GM, Navalesi R, Veves A. Difference in treatment of foot ulcerations in Boston, USA and Pisa, Italy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1997; 35:21–26.3. Ogbera AO, Chinenye S, Onyekwere A, Fasanmade O. Prognostic indices of diabetes mortality. Ethn Dis. 2007; 17:721–725.4. Nelson JP. Deep infection following total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977; 59:1042–1044.5. Pollard J, Hamilton GA, Rush SM, Ford LA. Mortality and morbidity after transmetatarsal amputation: retrospective review of 101 cases. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2006; 45:91–97.6. Sun JH, Tsai JS, Huang CH, Lin CH, Yang HM, Chan YS, Hsieh SH, Hsu BR, Huang YY. Risk factors for lower extremity amputation in diabetic foot disease categorized by Wagner classification. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012; 95:358–363.7. Wukich DK, Hobizal KB, Brooks MM. Severity of diabetic foot infection and rate of limb salvage. Foot Ankle Int. 2013; 34:351–358.8. Sharp CS, Bessman AN, Wagner FW Jr, Garland D. Microbiology of deep tissue in diabetic gangrene. Diabetes Care. 1978; 1:289–292.9. Perelman J, Shmueli A, Closon MC. Deriving a risk-adjustment formula for hospital financing: integrating the impact of socio-economic status on length of stay. Soc Sci Med. 2008; 66:88–98.10. Gornik I, Gornik O, Gasparović V. HbA1c is outcome predictor in diabetic patients with sepsis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007; 77:120–125.11. Ilavská S, Horváthová M, Szabová M, Nemessányi T, Jahnová E, Tulinská J, Líšková A, Wsolová L, Staruchová M, Volkovová K. Association between the human immune response and body mass index. Hum Immunol. 2012; 73:480–485.12. McDougall CJ, Gray HS, Simpson PM, Whitehouse SL, Crawford RW, Donnelly WJ. Complications related to therapeutic anticoagulation in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28:187–192.13. Ahn S, Park YJ, Min SI, Kim SY, Ha J, Kim SJ, Kim HS, Yoon BW, Min SK. High prevalence of peripheral arterial disease in Korean patients with coronary or cerebrovascular disease. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:625–629.14. Morbach S, Furchert H, Gröblinghoff U, Hoffmeier H, Kersten K, Klauke GT, Klemp U, Roden T, Icks A, Haastert B, et al. Long-term prognosis of diabetic foot patients and their limbs: amputation and death over the course of a decade. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:2021–2027.15. Lewis S, Raj D, Guzman NJ. Renal failure: implications of chronic kidney disease in the management of the diabetic foot. Semin Vasc Surg. 2012; 25:82–88.16. Lee JS, Lu M, Lee VS, Russell D, Bahr C, Lee ET. Lower-extremity amputation. Incidence, risk factors, and mortality in the Oklahoma Indian Diabetes Study. Diabetes. 1993; 42:876–882.17. Moulik PK, Mtonga R, Gill GV. Amputation and mortality in new-onset diabetic foot ulcers stratified by etiology. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:491–494.18. Boyko EJ, Ahroni JH, Smith DG, Davignon D. Increased mortality associated with diabetic foot ulcer. Diabet Med. 1996; 13:967–972.19. Tiwari S, Pratyush DD, Dwivedi A, Gupta SK, Rai M, Singh SK. Microbiological and clinical characteristics of diabetic foot infections in northern India. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2012; 6:329–332.