Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2017 Jan;9(1):92-95. 10.4168/aair.2017.9.1.92.
Palonosetron-Induced Anaphylaxis During General Anesthesia: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. tbkim@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2355899
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2017.9.1.92
Abstract
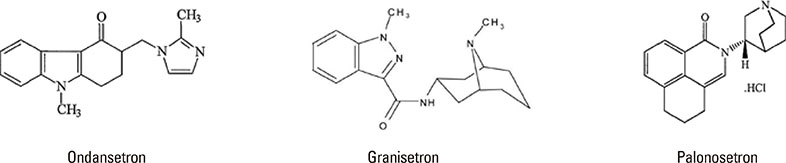
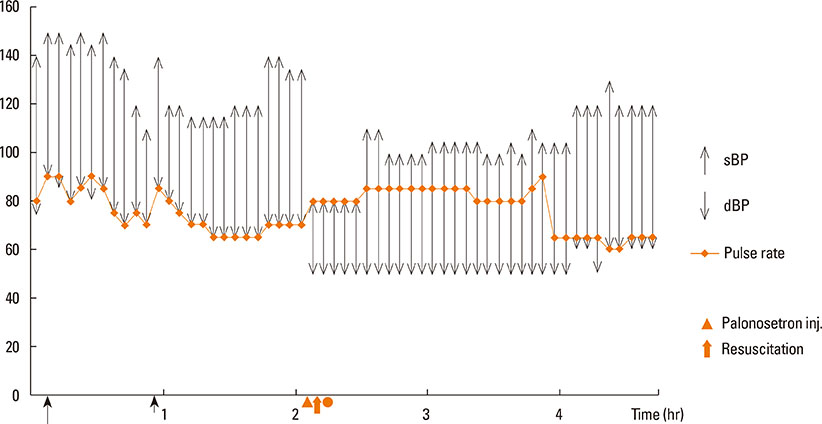
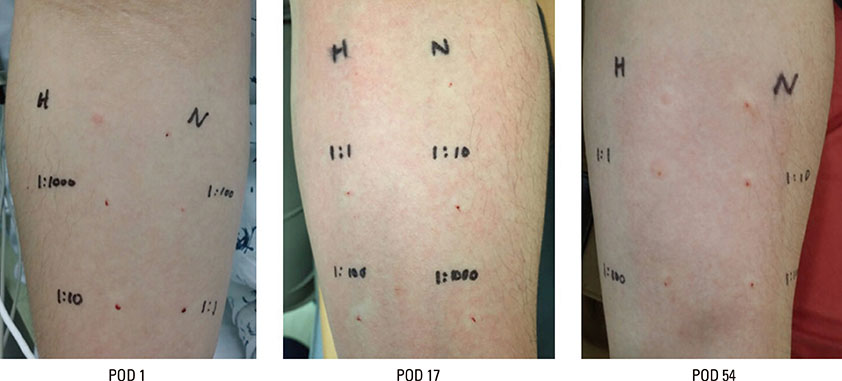
- Palonosetron is a 5-hydroxytryptamine-3 (5-HT-3) receptor antagonist used for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting. Compared with ondansetron and granisetron, it is a better drug because of prolonged action and minimal side effects. Some adverse effects of palonosetron have been reported. In this report, we describe a 37-year-old male who developed severe hypersensitivity reactions to palonosetron during surgery for kidney donation. His medical history was unremarkable, except for inguinal hernia with herniorrhaphy 8 years ago. The surgery was uneventful until 2 hours 20 minutes. After palonosetron injection, his blood pressure dropped to 80/50 mm Hg, and facial edema, rash, conjunctival swelling, and wheezing developed. The patient was resuscitated by administration of ephedrine, hydrocortisone, and peniramine. Following the surgery, the patient was monitored for 3 days, and there were no subsequent anaphylactic reactions or other complications. The skin test on postoperative day 54 was positive for hypersensitivity to palonosetron. Although palonosetron is known for its safety, other hypersensitivity events have been reported. Ondansetron is another widely used 5-HT-3 antagonist, which has been reported to cause anaphylaxis. Therefore, clinicians should be aware of the possibility of patients experiencing severe adverse reactions to palonosetron.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brockow K, Przybilla B, Aberer W, Bircher AJ, Brehler R, Dickel H, et al. Guideline for the diagnosis of drug hypersensitivity reactions: S2K-Guideline of the German Society for Allergology and Clinical Immunology (DGAKI) and the German Dermatological Society (DDG) in collaboration with the Association of German Allergologists (AeDA), the German Society for Pediatric Allergology and Environmental Medicine (GPA), the German Contact Dermatitis Research Group (DKG), the Swiss Society for Allergy and Immunology (SGAI), the Austrian Society for Allergology and Immunology (ÖGAI), the German Academy of Allergology and Environmental Medicine (DAAU), the German Center for Documentation of Severe Skin Reactions and the German Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Products (BfArM). Allergo J Int. 2015; 24:94–105.2. Laemmle-Ruff I, O’Hehir R, Ackland M, Tang ML. Anaphylaxis -identification, management and prevention. Aust Fam Physician. 2013; 42:38–42.3. Mirone C, Preziosi D, Mascheri A, Micarelli G, Farioli L, Balossi LG, et al. Identification of risk factors of severe hypersensitivity reactions in general anaesthesia. Clin Mol Allergy. 2015; 13:11.4. Kannan JA, Bernstein JA. Perioperative anaphylaxis: diagnosis, evaluation, and management. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2015; 35:321–334.5. Demir HA, Batu ED, Yalçın B, Civelek E, Saçkesen C, Büyükpamukçu M. Anaphylactic reaction owing to ondansetron administration in a child with neuroblastoma and safe use of granisetron: a case report. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2010; 32:e341–e342.6. Fernando SL, Broadfoot AJ. Ondansetron anaphylaxis: a case report and protocol for skin testing. Br J Anaesth. 2009; 102:285–286.7. Gupta YK, Shanmugam SP, Padhy BM, Goyal A. Palonosetron induced anaphylaxis in an adult female. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2010; 70:149–150.8. Leung J, Guyer A, Banerji A. IgE-mediated hypersensitivity to ondansetron and safe use of palonosetron. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2013; 1:526–527.9. Pietkiewicz JM. Possible anaphylaxis to palonoestron. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2012; 18:296–298.10. Tan J, Mehr S. Anaphylaxis to an ondansetron wafer. J Paediatr Child Health. 2012; 48:543–544.11. Gupta K, Singh I, Gupta PK, Chauhan H, Jain M, Rastogi B. Palonosetron, Ondansetron, and Granisetron for antiemetic prophylaxis of postoperative nausea and vomiting - a comparative evaluation. Anesth Essays Res. 2014; 8:197–201.12. Helsinn Healthcare SA (CH). Palonosetron prescribing information [Internet]. Woodcliff Lake (NJ): Eisai Inc.;2014. cited 2015 Oct 27. Available from: http://www.aloxi.com.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of postoperative serotonin syndrome following the administration of fentanyl, palonosetron, and meperidine: A case report
- Anaphylaxis induced by sugammadex and sugammadex-rocuronium complex -a case report-
- Consecutive anaphylaxis due to rocuronium and cisatracurium during general anesthesia: A case report
- Comparison of palonosetron with ondansetron in preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting after thyroidectomy during a 48-hour period
- Anaphylaxis caused by latex surgical gloves immediately after starting surgery: A case report