J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Dec;31(12):1907-1913. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.12.1907.
Factors Contributing to Discordance between the 2011 ACR/EULAR Criteria and Physician Clinical Judgment for the Identification of Remission in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rheumatology, Hanyang University Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Seoul, Korea. scbae@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Rheumatology, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Rheumatology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Rheumatology, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 5Department of Rheumatology, Dong-A University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 6Department of Rheumatology, Kyung Hee University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Rheumatology, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 8Department of Rheumatology, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju, Korea.
- 9Department of Rheumatology, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 10Department of Rheumatology, Yeungnam University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 11Department of Rheumatology, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 12Department of Rheumatology, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Guri, Korea.
- 13Department of Rheumatology, Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2355618
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.12.1907
Abstract
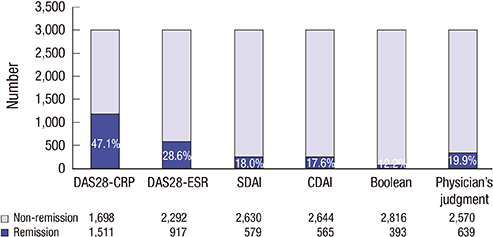
- Remission is a primary end point of in clinical practice and trials of treatments for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The 2011 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism (ACR/EULAR) remission criteria were developed to provide a consensus definition of remission. This study aimed to assess the concordance between the new remission criteria and the physician's clinical judgment of remission and also to identify factors that affect the discordance between these two approaches. A total of 3,209 patients with RA were included from the KORean Observational Study Network for Arthritis (KORONA) database. The frequency of remission was evaluated based on each approach. The agreement between the results was estimated by Cohen's kappa (κ). Patients with remission according to the 2011 ACR/EULAR criteria (i.e. the Boolean criteria) and/or physician judgment (n = 855) were divided into three groups: concordant remission, the Boolean criteria only, and physician judgment only. Multinomial logistic regression analysis was used to identify factors responsible for the assignment of patients with remission to one of the discordant groups rather than the concordant group. The remission rates using the Boolean criteria and physician judgment were 10.5% and 19.9%, respectively. The agreement between two approaches for remission was low (κ = 0.226) and the concordant remission rate was only 5.5% (n = 177). Pain affected classification in both discordant groups, whereas fatigue was associated with remission only by physician clinical judgment. The Boolean criteria were more stringent than clinical judgment. Patient subjective symptoms such as pain and fatigue were associated with discordance between the two approaches.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Treat-to-Target Strategy for Asian Patients with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: Result of a Multicenter Trial in Korea
Jason Jungsik Song, Yeong Wook Song, Sang Cheol Bae, Hoon-Suk Cha, Jung-Yoon Choe, Sung Jae Choi, Hyun Ah Kim, Jinseok Kim, Sung-Soo Kim, Choong-Ki Lee, Jisoo Lee, Sang-Heon Lee, Shin-Seok Lee, Soo-Kon Lee, Sung Won Lee, Sung-Hwan Park, Won Park, Seung Cheol Shim, Chang-Hee Suh, Bin Yoo, Dae-Hyun Yoo, Wan-Hee Yoo
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(52):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e346.
Reference
-
1. Kapetanovic MC, Lindqvist E, Nilsson JÅ, Geborek P, Saxne T, Eberhardt K. Development of functional impairment and disability in rheumatoid arthritis patients followed for 20 years: relation to disease activity, joint damage, and comorbidity. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2015; 67:340–348.2. van Nies JA, Krabben A, Schoones JW, Huizinga TW, Kloppenburg M, van der Helm-van Mil AH. What is the evidence for the presence of a therapeutic window of opportunity in rheumatoid arthritis? A systematic literature review. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014; 73:861–870.3. Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Bijlsma JW, Breedveld FC, Boumpas D, Burmester G, Combe B, Cutolo M, de Wit M, Dougados M, et al. Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010; 69:631–637.4. Singh JA, Saag KG, Bridges SL Jr, Akl EA, Bannuru RR, Sullivan MC, Vaysbrot E, McNaughton C, Osani M, Shmerling RH, et al. 2015 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68:1–26.5. Smolen JS, Landewé R, Breedveld FC, Buch M, Burmester G, Dougados M, Emery P, Gaujoux-Viala C, Gossec L, Nam J, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2013 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014; 73:492–509.6. Aletaha D, Landewe R, Karonitsch T, Bathon J, Boers M, Bombardier C, Bombardieri S, Choi H, Combe B, Dougados M, et al. Reporting disease activity in clinical trials of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: EULAR/ACR collaborative recommendations. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 59:1371–1377.7. Smolen JS, Aletaha D. The assessment of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2010; 28:S18–27.8. Mierau M, Schoels M, Gonda G, Fuchs J, Aletaha D, Smolen JS. Assessing remission in clinical practice. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007; 46:975–979.9. Sokka T, Hetland ML, Mäkinen H, Kautiainen H, Hørslev-Petersen K, Luukkainen RK, Combe B, Badsha H, Drosos AA, Devlin J, et al. Remission and rheumatoid arthritis: data on patients receiving usual care in twenty-four countries. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 58:2642–2651.10. Felson DT, Smolen JS, Wells G, Zhang B, van Tuyl LH, Funovits J, Aletaha D, Allaart CF, Bathon J, Bombardieri S, et al. American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism provisional definition of remission in rheumatoid arthritis for clinical trials. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011; 70:404–413.11. Lee YC, Cui J, Lu B, Frits ML, Iannaccone CK, Shadick NA, Weinblatt ME, Solomon DH. Pain persists in DAS28 rheumatoid arthritis remission but not in ACR/EULAR remission: a longitudinal observational study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011; 13:R83.12. Shaver TS, Anderson JD, Weidensaul DN, Shahouri SH, Busch RE, Mikuls TR, Michaud K, Wolfe F. The problem of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity and remission in clinical practice. J Rheumatol. 2008; 35:1015–1022.13. Sung YK, Cho SK, Choi CB, Park SY, Shim J, Ahn JK, Bang SY, Cha HS, Choe JY, Chung WT, et al. Korean observational study network for arthritis (KORONA): establishment of a prospective multicenter cohort for rheumatoid arthritis in South Korea. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012; 41:745–751.14. Klarenbeek NB, Koevoets R, van der Heijde DM, Gerards AH, Ten Wolde S, Kerstens PJ, Huizinga TW, Dijkmans BA, Allaart CF. Association with joint damage and physical functioning of nine composite indices and the 2011 ACR/EULAR remission criteria in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011; 70:1815–1821.15. Hoshi D, Nakajima A, Shidara K, Seto Y, Tanaka E, Taniguchi A, Momohara S, Yamanaka H. Disability is the major negative predictor for achievement of Boolean-based remission in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab. Mod Rheumatol. 2013; 23:1205–1210.16. Wolfe F, Boers M, Felson D, Michaud K, Wells GA. Remission in rheumatoid arthritis: physician and patient perspectives. J Rheumatol. 2009; 36:930–933.17. Krishnan E, Häkkinen A, Sokka T, Hannonen P. Impact of age and comorbidities on the criteria for remission and response in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005; 64:1350–1352.18. Khan NA, Spencer HJ, Abda E, Aggarwal A, Alten R, Ancuta C, Andersone D, Bergman M, Craig-Muller J, Detert J, et al. Determinants of discordance in patients’ and physicians’ rating of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012; 64:206–214.19. Cho SK, Sung YK, Choi CB, Bang SY, Cha HS, Choe JY, Chung WT, Hong SJ, Jun JB, Kim J, et al. What factors affect discordance between physicians and patients in the global assessment of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis? Mod Rheumatol. Forthcoming. 2016.20. van Tuyl LH, Hewlett S, Sadlonova M, Davis B, Flurey C, Hoogland W, Kirwan J, Sanderson T, van Schaardenburg D, Scholte-Voshaar M, et al. The patient perspective on remission in rheumatoid arthritis: ‘You’ve got limits, but you’re back to being you again’. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015; 74:1004–1010.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Preliminary Study for Applying Antiperinuclear Antibody Test to 2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis
- New Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis
- The Adequacy of Evaluation by Rheumatologists before Undergoing Arthroscopic Synovectomy in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
- The Role of Bone Scintigraphy in the Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis According to the 2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria
- Comparison of the 2022 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis with Previous Criteria